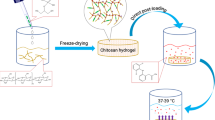
Abstract
Hydrogels were prepared from colloidal suspensions of polyelectrolyte complexes of xylan (Xyl) and chitosan (Ch) (mass ratio: 70 wt% Xyl/30 wt% Ch). They were formed at pH 5.0, at which both polyelectrolytes were highly charged according to their corresponding potentiometric titrations. They were treated with a polycarboxylic acid, sodium citrate, at different concentrations (0%, 3% and 7% w/v), and characterized by means of FTIR, scanning electron microscopy, wet-mechanical properties, swelling and solubility. FTIR spectra confirmed the presence of sodium citrate in the treated hydrogels. Wet-stress and wet-strain at break were increased by 150% and 57% respectively, when hydrogels were treated with 7% w/v of sodium citrate. The swelling capacity was clearly modified due to the presence of this compound and to the ionic strength of the liquid medium. The ability of these hydrogels for drug loading and controlled release was studied in vitro using diclofenac sodium (DS) as model drug. It was found that at pH 7.4, the hydrogel treated with sodium citrate absorbed significantly higher amounts of diclofenac sodium (up to 255 mg DS/g hydrogel) and its release was better controlled compared to that of the non-treated hydrogel. Particularly, the presence of sodium citrate in the liquid medium after the diclofenac sodium loading process and the influence of the ionic strength on the drug release rate indicated that an ion exchange process occurred, first between sodium citrate and diclofenac sodium and then between this drug and the ions present in the solution.
Graphic abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi F, Oveisi Z, Samani S, Amoozgar Z (2015) Chitosan based hydrogels: characteristics and pharmaceutical applications. Res Pharm Sci 10(1):1–16
Andrade-Vivero P, Fernandez-Gabriel E, Alvarez-Lorenzo C, Concheiro A (2007) Improving the loading and release of NSAIDs from pHEMA Hydrogels by copolymerization with functionalized monomers. J Pharm Sci 96(4):802–813. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.20761
Batycky RP, Hanes J, Langer R, Edwars DA (1997) A theoretical model of erosion and macromolecular drug release from biodegrading microspheres. J Pharm Sci 86(12):1464–1477. https://doi.org/10.1021/js9604117
Berger J, Reist M, Mayer JM, Felt O, Peppas NA, Gurny R (2004) Structure and interactions in covalently and ionically crosslinked chitosan hydrogels for biomedical applications. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 57(1):19–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0939-6411(03)00161-9
Bush JR, Liang H, Dickinson M, Botchwey EA (2016) Xylan hemicellulose improves chitosan hydrogel for bone tissue regeneration. Polym Adv Technol 27(8):1050–1055. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.3767
Caló E, Khutoryanskiy VV (2015) Biomedical applications of hydrogels: a review of patents and commercial products. Eur Polym J 65:252–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2014.11.024
Chen H, Hu X, Chen E, Wu S, McClements DJ, Liu S, Li B, Li Y (2016) Preparation, characterization, and properties of chitosan films with cinnamaldehyde nanoemulsions. Food Hydrocoll 61(662–6):71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.06.034
Cursaru B, Teodorescu M, Boscornea C, Stanescu PO, Stoleriu S (2013) Drug absorption and release properties of crosslinked hydrogels based on diepoxy-terminated poly(ethylene glycol)s and aliphatic polyamines—A study on the effect of the gel molecular structure. Mater Sci Eng C 33(3):1307–1314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2012.12.030
Dadsetan M, Taylor KE, Yong C, Bajzer Ž, Lichun L, Yaszemski MJ (2013) Controlled release of doxorubicin from pH-responsive microgels. Acta Biomater 9:5438–5446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2012.09.019
Don T-M, Huang M-L, Chiu A-C, Kuo K-H, Chiu W-Y, Chiu L-H (2008) Preparation of thermo-responsive acrylic hydrogels useful for the application in transdermal drug delivery systems. Mater Chem Phys 107(2–3):266–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2007.07.009
Draget KI, Värum KM, Moen E, Gynnild H, Smidsrød O (1992) Chitosan cross-linked with Mo (VI) polyoxyanions: a new gelling system. Biomaterials 13(9):635–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/0142-9612(92)90032-J
Drury JL, Mooney DJ (2003) Hydrogels for tissue engineering: scaffold design variables and applications, review. Biomaterials 24(24):4337–4351. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9612(03)00340-5
Esteban SL, Manzo RH, Alovero FL (2009) Azithromycin loaded on hydrogels of carbomer: chemical stability and delivery properties. Int J Pharm 366:53–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.08.043
Gabrielii I, Gatenholm P, Glasser WG, Jain RK, Kenne L (2000) Separation, characterization and hydrogel-formation of hemicellulose from aspen wood. Carbohydr Polym 43(4):367–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(00)00181-8
Gabrielli I, Gatenholm P (1998) Preparation and properties of hydrogels based on hemicellulose. J Appl Polym Sci 69:1661–1667. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4628(19980822)69:8%3c1661:AID-APP19%3e3.0.CO;2-X
Galván MV, Mocchiutti P, Cornaglia LM, Zanuttini MA (2012) Dual-polyelectrolyte adsorption of poly(allylamine hydrochloride) and xylan onto recycled unbleached fibers. BioResources 7(2):2075–2089
García MC (2018) Ionic-strength-responsive polymers for drug delivery applications. In: Makhlouf AS, Abu-Thabit NY (eds) Stimuli responsive polymeric nanocarriers for drug delivery applications, 1st edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 393–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-101995-5.00014-3
Gupta P, Vermani K, Garg S (2002) Hydrogels: from controlled release to pH-responsive drug delivery, review. Drug Discov Today 7(10):569–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6446(02)02255-9
Hamman JH (2010) Chitosan based polyelectrolyte complexes as potential carrier materials in drug delivery systems, review. Mar Drugs 8(4):1305–1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8041305
Huang X, Brazel CS (2001) On the importance and mechanisms of burst release in matrix-controlled drug delivery systems, review. J Control Release 73(2–3):121–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-3659(01)00248-6
Ikeda S, Kumagai H, Sakiyama T, Chu C-H, Nakamura K (1995) Method for analyzing pH-sensitive swelling of amphoteric hydrogels—application to a polyelectrolyte complex gel prepared from Xanthan and Chitosan. Biosci Biotech Biochem 59(8):1422–1427. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.59.1422
Jeong B, Bae YH, Kim SW (2000) Drug release from biodegradable injectable thermosensitive hydrogel of PEG–PLGA–PEG triblock copolymers. J Control Release 63(1–2):155–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-3659(99)00194-7
Karaaslan MA, Tshabalala MA, Buschle-Diller G (2010) Wood hemicellulose/chitosan-based semi-interpenetrating network hydrogels: mechanical, swelling, and controlled drug release properties. BioResources 5(2):1036–1054
Karaaslan MA, Tshabalala MA, Buschle-Diller G (2012) Semi-interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels based on aspen hemicellulose and chitosan: effect of crosslinking sequence on hydrogel properties. J Appl Polym Sci 124:1168–1177. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.35075
Khazaeinia T, Jamali F (2003) A comparison of gastrointestinal permeability induced by diclofenac-phospholipid complex with diclofenac acid and its sodium salt. J Pharm Pharm Sci 6(3):352–359
Kim S, Chu C (2000) Synthesis and characterization of dextran-methacrylate hydrogels and structural study by SEM. J Biomed Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4636(20000315)49:4%3c517:AID-JBM10%3e3.0.CO;2-8
Kim B, Peppas NA (2003) In vitro release behavior and stability of insulin in complexation hydrogels as oral drug delivery carriers. Int J Pharm 266:29–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5173(03)00378-8
Kim SW, Bae YH, Okano T (1992) Hydrogels: swelling, drug loading, and release, pharmaceutical research, review. Pharm Res 9(3):283–290
Krukowski S, Karasiewicz M, Kolodziejski W (2017) Convenient UV-spectrophotometric determination of citrates in aqueous solutions with applications in the pharmaceutical analysis of oral electrolyte formulations. J Food Drug Anal 25(3):717–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2017.01.009
Kumar S, Negi YS (2014) Cellulose and xylan based prodrug of diclofenac sodium: synthesis, physicochemical characterization and in vitro release. Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomater 63(6):283–292. https://doi.org/10.1080/00914037.2013.830256
Laine J, Buchert J, Viikari L, Stenius P (1996) Characterization of unbleached kraft pulps by enzymatic treatment, potentiometric titration and polyelectrolyte adsorption. Holzforschung 50(3):208–214. https://doi.org/10.1515/hfsg.1996.50.3.208
Lankalapalli S, Kolapalli VR (2009) Polyelectrolyte complexes: a review of their applicability in drug delivery technology. Indian J Pharm Sci 71(5):481–487. https://doi.org/10.4103/0250-474X.58165
Li X, Shi X, Wang M, Du Y (2011) Xylan chitosan conjugate—a potential food preservative. Food Chem 126(2):520–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.11.037
Linder Å, Bergman R, Bodin A, Gatenholm P (2003) Mechanism of assembly of xylan onto cellulose surface. Langmuir 19(12):5072–5077. https://doi.org/10.1021/la0341355
Mi FL, Chen CT, Tseng YC, Kuan CY, Shyu SS (1997) Iron (III)-carboxymethylchitin microsphere for the pH-sensitive release of 6-mercaptopurine. J Control Release 44(1):19–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-3659(96)01502-7
Mocchiutti P, Schnell CN, Rossi GD, Peresin MS, Zanuttini MA, Galván MV (2016) Cationic and anionic polyelectrolyte complexes of xylan and chitosan. Interaction with lignocellulosic surfaces. Carbohydr Polym 150:89–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.04.111
Palena MC, García MC, Manzo RH, Jimenez-Kairuz AF (2015) Self-organized drug- interpolyelectrolyte nanocomplexes loaded with anionic drugs. Characterization and in vitro release evaluation. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 30:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2015.09.014
Qiu Y, Park K (2012) Environment-sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64:49–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2012.09.024
Rinaudo M (2006) Chitin and chitosan: properties and applications. Progr Polym Sci 31(7):603–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2006.06.001
Sacco P, Borgogna M, Travan A, Marsich E, Paoletti S, Asaro F, Donati I (2014) Polysaccharide-based networks from homogeneous chitosan-tripolyphosphate hydrogels: synthesis and characterization. Biomacromol 15(9):3396–3405. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm500909n
Schnell CN, Galván MV, Peresin MS, Inalbon MC, Vartiainen J, Zanuttini MA, Mocchiutti P (2017) Films from xylan/chitosan complexes: preparation and characterization. Cellulose 24(10):4393–4403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1411-x
Shi R, Bi J, Zhang Z, Zhu A, Chen D, Zhou X, Zhang L, Tian W (2008) The effect of citric acid on the structural properties and cytotoxicity of the polyvinyl alcohol/starch films when molding at high temperature. Carbohydr Polym 74(4):763–770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2008.04.045
Shu XZ, Zhu KJ, Song W (2001) Novel pH-sensitive citrate cross-linked chitosan film for drug controlled release. Int J Pharm 212(1):19–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5173(00)00582-2
Sjöström E (1993) Wood chemistry. Fundamentals and applications. In: Sjöström E (ed) Wood polysaccharides, 2nd edn. Academic Press Inc., California, San Diego, pp 51–70
Skoog DA, Holler FJ, Neiman TA (2001) Principios de análisis instrumental. McGraw-Hill Interamericana de España SL, Madrid
Tan W-H, Takeuchi S (2007) Monodisperse alginate hydrogel microbeads for cell encapsulation. Adv Mater 19:2696–2701. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200700433
Tarvainen T, Svarfvar B, Åkerman S, Savolainen J, Karhu M, Paronen P, Järvinen K (1999) Drug release from a porous ion-exchange membrane in vitro. Biomaterials 20(22):2177–2183. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9612(99)00122-2
Wang Q, Zhang J, Wang A (2009) Preparation and characterization of a novel pH-sensitive chitosan-g-poly(acrylic acid)/attapulgite/sodium alginate composite hydrogel bead for controlled release of diclofenac sodium. Carbohydr Polym 78:731–737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.06.010
Wang H, Qian C, Roman M (2011) Effects of pH and salt concentration on the formation and properties of chitosan-cellulose nanocrystal polyelectrolyte-macroion complexes. Biomacromol 12(10):3708–3714. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm2009685
Wu T, Li Y, Lee DS (2017) Chitosan-based composite hydrogels for biomedical applications. Macromol Res 25(6):480–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-017-5066-0
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the financial support received from ANPCyT—PICT 2013 N°2212; CONICET-PIP 2013-2015 GI N°: 11220120100672CO; CAI + D 2012 N°500 201101 00057. Thanks are also given to Gabriel Exequiel Ramella for his help in the laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schnell, C.N., Galván, M.V., Zanuttini, M.A. et al. Hydrogels from xylan/chitosan complexes for the controlled release of diclofenac sodium. Cellulose 27, 1465–1481 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02850-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02850-x