Abstract
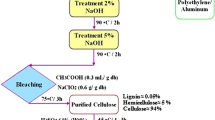
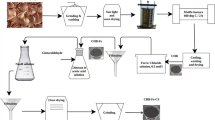
The aim of this study was developing novel membranes based on polyethersulfone (PES) as matrix and amine functionalized cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) as nanofiller for copper ion and direct red-16 removal from water. The surface modification of CNC was performed using (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane (APTES) and confirmed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Then, PES membranes were prepared by embedding various concentrations (0, 0.1, 0.5, and 1 wt%) of modified CNC (MCNC). The results showed that the maximum adsorption capacity of copper ions was 90% for membranes containing 1 wt% MCNC. Dye removal percentage was 89% for neat PES and increased to 99% for 1 wt% MCNC loading. The outcomes of this study demonstrated that incorporating this type of modified CNC in PES membranes improved the efficacy of impurities removal from water and can be suggested as a simple technique for water filtration.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abouzeid RE, Khiari R, El-Wakil N, Dufresne A (2018) Current state and new trends in the use of cellulose nanomaterials for wastewater treatment. Biomacromolecules. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.8b00839
de Castro Silva F, da Silva MMF, Lima LCB, Osajima JA, da Silva Filho EC (2018) Modifying cellulose with metaphosphoric acid and its efficiency in removing brilliant green dye. Int J Biol Macromol 114:470–478
El Haddad M, Slimani R, Mamouni R, ElAntri S, Lazar S (2013) Removal of two textile dyes from aqueous solutions onto calcined bones. J Associ Arab Univ Basic Appl Sci 14:51–59
Elimelech M, Phillip WA (2011) The future of seawater desalination: energy, technology, and the environment. Science 333:712–717
French AD, Santiago Cintrón MS (2013) Cellulose polymorphy, crystallite size, and the Segal crystallinity index. Cellulose 20:583–588
Gehrke I, Geiser A, Somborn-Schulz A (2015) Innovations in nanotechnology for water treatment. Nanotechnol Sci Appl 8:1–17
Jain P, Varshney S, Srivastava S (2016) Synthetically modified nano-cellulose for the removal of chromium: a green nanotech perspective. IET Nanobiotechnol 11:45–51
Khanjanzadeh H, Behrooz R, Bahramifar N, Gindl-Altmutter W, Bacher M, Edler M, Griesser T (2018) Surface chemical functionalization of cellulose nanocrystals by 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane. Int J Biol Macromol 106:1288–1296
Li B, Li M, Zhang J, Pan Y, Huang Z, Xiao H (2018) Adsorption of Hg(II) ions from aqueous solution by diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid-modified cellulose. Int J Biol Macromol 122:149–156
Madivoli E et al (2016) Adsorption of selected heavy metals on modified nanocellulose. Int Res J Pure Appl Chem 12:1–9
Mautner A, Maples H, Kobkeatthawin T, Kokol V, Karim Z, Li K, Bismarck A (2016) Phosphorylated nanocellulose papers for copper adsorption from aqueous solutions. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:1861–1872
Misra AK (2014) Climate change and challenges of water and food security. Int J Sustain Built Environ 3:153–165
Nam S, French AD, Condon BD, Concha M (2016) Segal crystallinity index revisited by the simulation of X-ray diffraction patterns of cotton cellulose Iβ and cellulose II. Carbohydr Polym 135:1–9
Pendergast MM, Hoek EM (2011) A review of water treatment membrane nanotechnologies. Energy Environ Sci 4:1946–1971
Rahimi M, Dadari S, Zeinaddini S, Mohamadian E (2017) Flux, antifouling and separation characteristics enhancement of nanocomposite polyethersulfone mixed-matrix membrane by embedding synthesized hydrophilic adipate ferroxane nanoparticles. Korean J Chem Eng 34:1444–1455
Rathoure AK (2015) Toxicity and waste management using bioremediation. IGI Global, Hershey
Saraswathi MSSA, Rana D, Nagendran A, Alwarappan S (2018) Custom-made PEI/exfoliated-MoS2 nanocomposite ultrafiltration membranes for separation of bovine serum albumin and humic acid. Mater Sci Eng C 83:108–114
Segal LGJMA, Creely JJ, Martin AE, Conrad CM (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29(10):786–794
Sun N, Wen X, Yan C (2018) Adsorption of mercury ions from wastewater aqueous solution by amide functionalized cellulose from sugarcane bagasse. Int J Biol Macromol 108:1199–1206
Tahir U, Yasmin A, Khan UH (2016) Phytoremediation: potential flora for synthetic dyestuff metabolism. J King Saud Univ-Sci 28:119–130
Yin J, Deng B (2015) Polymer-matrix nanocomposite membranes for water treatment. J Membr Sci 479:256–275
Zhang D, Karkooti A, Liu L, Sadrzadeh M, Thundat T, Liu Y, Narain R (2018) Fabrication of antifouling and antibacterial polyethersulfone (PES)/cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) nanocomposite. J Membr Sci 549:350–356
Zhou Y, Jin Q, Hu X, Zhang Q, Ma T (2012) Heavy metal ions and organic dyes removal from water by cellulose modified with maleic anhydride. J Mater Sci 47:5019–5029
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge to the Iranian National Science Foundation for the financial support of the Research Project (# 92043921) and also the University of Tehran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rafieian, F., Jonoobi, M. & Yu, Q. A novel nanocomposite membrane containing modified cellulose nanocrystals for copper ion removal and dye adsorption from water. Cellulose 26, 3359–3373 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02320-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02320-4