Abstract
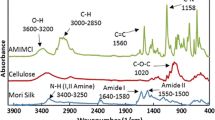
Collagen/cellulose blended solutions with collagen/cellulose mass ratio (Col/Cel) of 0, 1/40, 1/20, 1/10 and 1/5 were prepared using [Emim]Ac as solvent. The interactions between the two polymers before and after regeneration were investigated. In steady shear flow, all of the experimental viscosity values were greater than those of the estimated values calculated from the log-additivity rule for each sample, suggesting interactions between the two polymers in solutions. All solutions exhibited shear thinning behavior and the flow curves could be described by Cross model. Zero shear viscosity (η 0) versus Col/Cel was examined and a linear increase (from 8.73 to 16.39 Pa·s) can be observed for η 0 as Col/Cel ≤ 1/10, while there was only a slight increase (from 16.39 to 18.42 Pa·s) in η 0 as Col/Cel increased to 1/5. Dynamic rheology results suggested the existence of aggregates in solution with Col/Cel = 1/10. Furthermore, the activation energy of solution was 84.5 kJ mol−1 as Col/Cel = 1/10, higher than that of cellulose solution (44.2 kJ mol−1). Regenerated films were prepared and characterized to trace back the interactions between the two polymers in [Emim]Ac. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy indicated the hydrogen-bond interaction between collagen and cellulose in films. The denaturation temperature of collagen in films with Col/Cel ≤ 1/10 could be improved, but it was decreased with the increase of collagen content, and finally was reduced to be close to that of collagen as Col/Cel = 1/5. The features of dynamic mechanical analysis for films were indicative of the lack of homogeneity between collagen and cellulose as Col/Cel = 1/5. Atomic force microscopy images further confirmed the phase-separation when Col/Cel = 1/5.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Col/Cel:
-
Collagen/cellulose mass ratio
- Col–Cel(1/40), Col–Cel(1/20), Col–Cel(1/10) and Col–Cel(1/5):
-
Cellulose/collagen blends with ratios of 1/40, 1/20, 1/10 and 1/5, respectively
- [Emim]Ac:
-
1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate
- TTS:
-
Time–temperature superposition
References
Al-Ruqaie IM, Kasapis S, Abeysekera R (1997) Structural properties of pectin-gelatin gels. Part II: effect of sucrose/glucose syrup. Carbohyd Polym 34:309–321
Aono H, Tatsumi D, Matsumoto T (2006) Characterization of aggregate structure in mercerized cellulose/LiCl DMAc solution using light scattering and rheological measurements. Biomacromolecules 7:1311–1317
Cascone MG (1997) Dynamic–mechanical properties of bioartificial polymeric materials. Polym Int 43:55–69
Colby RH (2010) Structure and linear viscoelasticity of flexible polymer solutions: comparison of polyelectrolyte and neutral polymer solutions. Rheol Acta 49:425–442
Ding C, Zhang M, Li G (2014) Rheological properties of collagen/hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (COL/HPMC) blended solutions. J Appl Polym Sci 131. doi:10.1002/app.40042
El Seoud OA, Koschella A, Fidale LC, Dorn S, Heinze T (2007) Applications of ionic liquids in carbohydrate chemistry: a window of opportunities. Biomacromolecules 8:2629–2647
Feng L, Chen Z-L (2008) Research progress on dissolution and functional modification of cellulose in ionic liquids. J Mol Liq 142:1–5
Ferry JD (1980) Viscoelastic properties of polymers, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Fink H-P, Weigel P, Purz H, Ganster J (2001) Structure formation of regenerated cellulose materials from NMMO-solutions. Prog Polym Sci 26:1473–1524
Gómez-Guillén M, Giménez B, López-Caballero M, Montero M (2011) Functional and bioactive properties of collagen and gelatin from alternative sources: a review. Food Hydrocoll 25:1813–1827
Haward SJ, Sharma V, Butts CP, McKinley GH, Rahatekar SS (2012) Shear and extensional rheology of cellulose/ionic liquid solutions. Biomacromolecules 13:1688–1699
Hsieh TT, Tiu C, Simon GP, Wu RY (1999) Rheology and miscibility of thermotropic liquid crystalline polymer blends. J Non Newtonian Fluid Mech 86:15–35
Hu Y, Liu L, Dan W, Dan N, Gu Z (2013) Evaluation of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate based ionic liquid systems as a suitable solvent for collagen. J Appl Polym Sci 130:2245–2256
Itävaara M, Siika-Aho M, Viikari L (1999) Enzymatic degradation of cellulose-based materials. J Environ Polym Degrad 7:67–73
Kamide K (2005) Cellulose and cellulose derivatives. Elsevier, London
Kobayashi K, Huang CI, Lodge TP (1999) Thermoreversible gelation of aqueous methylcellulose solutions. Macromolecules 32(21):7070–7077
Kołodziejska I, Sikorski ZE, Niecikowska C (1999) Parameters affecting the isolation of collagen from squid (Illex argentinus) skins. Food Chem 66:153–157
Lai G, Du Z, Li G (2007) The rheological behavior of collagen dispersion/poly (vinyl alcohol) blends. Korea Aust Rheol J 19:81–88
Liao XP, Lu ZB, Zhang MN, Liu X, Shi B (2004) Adsorption of Cu(II) from aqueous solutions by tannins immobilized on collagen. Chem Technol Biotechnol 79:335–342
Liu W, Budtova T (2012) Ionic liquid: a powerful solvent for homogeneous starch–cellulose mixing and making films with tuned morphology. Polymer 53:5779–5787
Liu Z, Wang H, Li Z, Lu X, Zhang X, Zhang S, Zhou K (2011) Rheological properties of cotton pulp cellulose dissolved in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride solutions. Polym Eng Sci 51:2381–2386
Mantz R, Fox D, Green J, Fylstra P, De Long H, Trulove P (2007) Dissolution of biopolymers using ionic liquids. Z Naturforsch A Phys Sci 62:275–280
Mathew AP, Oksman K, Pierron D, Harmad M-F (2012) Crosslinked fibrous composites based on cellulose nanofibers and collagen with in situ pH induced fibrillation. Cellulose 19:139–150
Müller FA, Müller L, Hofmann I, Greil P, Wenzel MM, Staudenmaier R (2006) Cellulose-based scaffold materials for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials 27:3955–3963
Royall PG, Huang C-Y, Tang S-WJ, Duncan J, Van-de-Velde G, Brown MB (2005) The development of DMA for the detection of amorphous content in pharmaceutical powdered materials. Int J Pharm 301:181–191
Ruan D, Lue A, Zhang L (2008) Gelation behaviors of cellulose solution dissolved in aqueous NaOH/thiourea at low temperature. Polymer 49:1027–1036
Sammons R, Collier J, Rials T, Petrovan S (2008) Rheology of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride cellulose solutions. I. Shear rheology. J Appl Polym Sci 110:1175–1181
Shi X, Ma W, Sun C, Wu S (2001) The aggregation behavior of collagen in aqueous solution and its property of stabilizing liposomes in vitro. Biomaterials 22:1627–1634
Sionkowska A, Skopinska-Wisniewska J, Gawron M, Kozlowska J, Planecka A (2010) Chemical and thermal cross-linking of collagen and elastin hydrolysates. Int J Biol Macromol 47:570–577
Steele TW et al (2013) Collagen–cellulose composite thin films that mimic soft-tissue and allow stem-cell orientation. J Mater Sci Mater Med 24:1–15
Swatloski RP, Spear SK, Holbrey JD, Rogers RD (2002) Dissolution of cellulose with ionic liquids. J Am Chem Soc 124:4974–4975
Utracki L (1983) Melt flow of polymer blends. Polym Eng Sci 23:602–609
Wang J, Wei L, Ma Y, Li K, Li M, Yu Y, Wang L, Qiu H (2013) Collagen/cellulose hydrogel beads reconstituted from ionic liquid solution for Cu(II) adsorption. Carbohyd Polym 98:736–743
Yang G, Zhang L, Peng T, Zhong W (2000) Effects of Ca2+ bridge cross-linking on structure and pervaporation of cellulose/alginate blend membranes. J Membr Sci 175:53–60
Yao Y, Mukuze KS, Zhang Y, Wang H (2014) Rheological behavior of cellulose/silk fibroin blend solutions with ionic liquid as solvent. Cellulose 21:675–684
Zhang M, Chen Y, Li G, Du Z (2010) Rheological properties of fish skin collagen solution: effects of temperature and concentration. Korea Aust Rheol J 22:119–127
Zhang M, Wu K, Li G (2011) Interactions of collagen molecules in the presence of N-hydroxysuccinimide activated adipic acid (NHS-AA) as a crosslinking agent. Int J Biol Macromol 49:847–854
Zhang X, Liu X, Zheng W, Zhu J (2012) Regenerated cellulose/graphene nanocomposite films prepared in DMAC/LiCl solution. Carbohyd Polym 88:26–30
Zhang M, Li J, Ding C, Liu W, Li G (2013) The rheological and structural properties of fish collagen cross-linked by N-hydroxysuccinimide activated adipic acid. Food Hydrocoll 30:504–511
Zhang M, Ding C, Chen L, Huang L (2014) The preparation of cellulose/collagen composite films using 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate as a solvent. BioResources 9:757–771
Zhijiang C, Guang Y (2011) Bacterial cellulose/collagen composite: characterization and first evaluation of cytocompatibility. J Appl Polym Sci 120:2938–2944
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21306024), the Science and Technology Major Project of the Science and Technology Department of Fujian Province (2008HZ0001-1) and the Foundation of Distinguished Young Scholars of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (XJQ201212).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Ding, C., Huang, L. et al. Interactions of collagen and cellulose in their blends with 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate as solvent. Cellulose 21, 3311–3322 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0372-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0372-6