Abstract
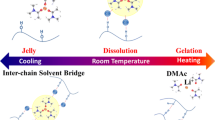
Cellulose/1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ([BMIM] Cl) solutions were prepared with different dissolving process including static state, mechanical stirring and kneading. Rheological measurements were employed to investigate the effect of dissolving process on the rheological behavior. It is found that the solutions prepared by static state showed the largest zero shear viscosity and relaxation time. From temperature sweep profiles, the temperature dependence of viscoelasticity on the three solutions followed the gel transition phenomenon with the characteristics of physical gels proposed by Winter et al. Further investigation showed that dissolving process had effects on the gel transition temperature. Solutions prepared by static state showed the highest gel transition temperature, whilst those prepared by kneading had the lowest. This indicates significant differences occurring in the structuralization of solutions prepared by different dissolving process. The SEM images of films regenerated from kneading solution exhibited a dense and homogeneous morphology while films prepared by static-state dissolving process were loose with coarse aggregation, which is consist with the deduce from the rheological results.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liebert TF, Heinze TJ (2001) Exploitation of reactivity and selectivity in cellulose functionalization using unconventional media for the design of products showing new superstructures. Biomacromolecules 2:1124–1132
Edgar KJ, Arnold KM, Blount WW, Lawniczak JE, Lowman DW (1995) Synthesis and properties of cellulose acetoacetates. Macromolecules 28:4122–4128
Nishino T, Matsuda I, Hirao K (2004) All-cellulose composite. Macromolecules 37:7683–7687
Williamson SL, Armentrout RS, Porter RS, McCormick CL (1998) Microstructural examination of semi-interpenetrating networks of poly (N, N-dimethylacrylamide) with cellulose or chitin synthesized in lithium chloride/N, N-dimethylacetamide. Macromolecules 31:8134–8141
Heinze T, Liebert T (2001) Unconventional methods in cellulose functionalization. Prog Polym Sci 26:1689–1762
Noishiki Y, Nishiyama Y, Wada M, Kuga S, Magoshi J (2002) Mechanical properties of silk fibroin-microcrystalline cellulose composite films. J Appl Polym Sci 86:3425–3429
Rajulu AV, Rao GB, Rao BRP, Reddy AMS, He J, Zhang J (2002) Properties of ligno-cellulose fiber Hildegardia. J Appl Polym Sci 84:2216–2221
Swatloski RP, Spear SK, Holbrey JD, Rogers RD (2002) Dissolution of cellulose with ionic liquids. J Am Chem Soc 124:4974–4975
Moulthrop JS, Swatloski RP, Moyna G, Rogers RD (2005) High-resolution 13C NMR studies of cellulose and cellulose oligomers in ionic liquid solutions. Chem Commun 0:1557–1559
Zhang H, Wu J, Zhang J, He JS (2005) 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride room temperature ionic liquid: a New and powerful Nonderivatizing solvent for cellulose. Macromolecules 38:8272–8277
Remsing RC, Swatloski RP, Rogers RD, Moyna G (2006) Mechanism of cellulose dissolution in the ionic liquid 1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride: a 13C and 35/37Cl NMR relaxation study on model systems. Chem Commun 0:1271–1273
Chen X, Zhang YM, Cheng LY, Wang HP (2009) Rheology of concentrated cellulose solutions in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. J Polym Environ 17:273–279
Chen X, Zhang YM, Wang HP, Wang SX, Liang SW, Colby RH (2011) Solution rheology of cellulose in 1-butyl-3-methyl imidazolium chloride. J Rheol 55:485–494
Kosan B, Michels C, Meister F (2008) Dissolution and forming of cellulose with ionic liquids. Cellulose 15:59–66
Cai T, Zhang HH, Guo QH, Shao HL, Hu XC (2010) Structure and properties of cellulose fibers from ionic liquids. J Appl Polym Sci 115:1047–1053
Zhang Y, Li HF, Li XD, Gibril ME, Han KQ, Yu MH (2013) Green chemical preparation of cellulose/high performance elastomer blend fibers by melt-spinning method. J Polym Res 20:171–179
Seddon KR (1997) Ionic liquids for clean technology. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 68:351–356
Jiang GS, Huang WF, Li L, Wang X, Pang FJ, Zhang YM, Wang HP (2012) Structure and properties of regenerated cellulose fibers from different technology processes. Carbohydr Polym 87:2012–2018
Shao ZQ, Men S, Zhu YC (2006) The changes of structure and dissolution in DMAc/LiCl of cellulose after pretreated with different methods. Appl Chem Ind 35:587–590, Chinese
Qin XZ, Lu A, Zhang LN (2012) Effect of stirring conditions on cellulose dissolution in NaOH/urea aqueous solution at low temperature. J Appl Polym Sci 126:E470–E477
Zhu XJ, Yin XM, Zhang YM, Wang HP (2014) Characteristics of polyacrylonitrile solutions and fibers varied with the dissolution process in ionic liquid. Polym Eng Sci. doi:10.1002/pen.23922
Csihony S, Fischmeister C, Bruneau C, Horváth IT, Dixneuf PH (2002) First ring-opening metathesis polymerization in an ionic liquid. Efficient recycling of a catalyst generated from a cationic ruthenium allenylidene complex. New J Chem 26:1667–1670
Marx-Figini M (1978) Significance of the intrinsic viscosity ratio of unsubstituted and nitrated cellulose in different solvents. Angew Makromol Chem 72:161–171
Gericke M, Schlufter K, Liebert T, Heinze T, Budtova T (2009) Rheolgical properties of cellulose/ionic liquid solutions: from dilute to concentrated states. Biomacromolecules 10:1188–1194
Carreau PJ (1972) Rheological equations from molecular network theories. Trans Soc Rheol 16:99–127
Collier JR, Watson JL, Collier BJ, Petrovan S (2008) Rheolgy of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride cellulose solutions. II. Solution character and preparation. J Appl Polym Sci 111:1019–1027
Rubinstein M, Colby RH (2003) Polymer physics, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Kobayashi K, Huang CI, Lodge TP (1999) Thermoreversible gelation of aqueous methylcellulose solutions. Macromolecules 32:7070–7077
Nijenhuis KT, Winter HH (1989) Mechanical properties at the gel point of a crystallizing poly (vinyl chloride) solution. Macromolecules 22:411–414
Aoki Y, Li L, Kakiuchi M (1998) Rheological images of poly (vinyl chloride) gels. 6. Effect of temperature. Macromolecules 31:8117–8123
Gao YT, Liu ZF, Gao XH, Yu JR, Hu ZM (2011) Dynamic rheological properties and microstructures of liquid-crystalline poly (p-phenyleneterephthalamide) solutions in the presence of single-walled carbon nanotubes. J Polym Res 18:263–271
Winter HH, Chambon F (1986) Analysis of linear viscoelasticity of a crosslinking polymer at the gel point. J Rheol 30:367–382
Udra SA, Mashchenko VI, Kazarin LA, Gerasimov VI (2008) Gelation in solutions of high-molecular-mass polyacrylonitrile under shear deformation. Polym Sci Ser A+ 50:1233–1237
Tan L, Pan D, Pan N (2009) Rheological study on thermal-induced gelation behavior of polyacrylonitrile solution. J Polym Res 64:341–350
Noro A, Matsushita Y, Lodge TP (2009) Gelation mechanism of thermoreversible supramacromolecular ion gels via hydrogen bonding. Macromolecules 42:5802–5810
Zhou YX, Fan XD, Zhang WB, Xue D, Kong J (2014) Stimuli-induced gel-sol transition of supramolecular hydrogels based on β-cyclodextrin polymer/ferrocene-containing triblock copolymer inclusion complexes. J Polym Res 21:359–368
Tan L, Chen H, Pan D, Pan N (2009) Investigation into the gelation and crystallization of polyacrylonitrile. Eur Polym J 45:1617–1624
Acknowledgments
The work is supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51273041).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 176 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, X., Yao, Y., Gong, M. et al. Rheological behaviors of cellulose/[BMIM]Cl solutions varied with the dissolving process. J Polym Res 21, 512 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-014-0512-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-014-0512-6