Abstract
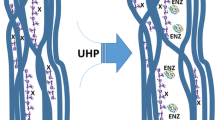
In this study, the effect of enzyme treatment on refined, never-dried bleached birch kraft pulp was investigated, using an endo-1,4-β-xylanase, that is substantially free from cellulase activity. The xylanase treatment of refined never-dried pulp revealed a rapid initial hydrolysis rate with a time-dependent saturation level in the amount of hydrolyzed pulp carbohydrates. Surprisingly short xylanase treatment times were found to have an impact on the fiber surface structure and on the physicochemical properties of kraft pulp fibers. Xylanase treatment led to mild microscopic differences in the ultrastructure of a never-dried fiber, whereas local topographical differences were distinguishable with atomic force microscopy. Results from the analysis of dissolved carbohydrates and the interfacial properties of the xylanase-treated never-dried fibers thus confirm a selective removal of xylan from the fiber surfaces. The zeta-potential charge and dewatering properties of the pulp slurry, fiber morphology, and strength properties of the paper were affected, which is a concomitant of xylanase treatment. However, the papermaking properties of the fibers were mainly preserved with simultaneous improvement in the dewatering rate of the pulp. Thus, optimized xylanase treatment of refined bleached kraft pulp provides a fiber for papermaking or fiber modification purposes with a selectively modified chemical composition of the fiber surface layer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aachary AA, Prapulla SG (2011) Xylooligosaccharides (XOS) as an emerging prebiotic: microbial synthesis, utilization, structural characterization, bioactive properties, and applications. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 10:2–16
Al-Dajani WW, Tschirner UW (2008) Pre-extraction of hemicelluloses and subsequent kraft pulping. Part I: alkaline extraction. Tappi J 7:3–8
Axegard P, Lindgren K, Dahlman O, Tomani P, Lundqvist F (2009) Method for separating polymeric pentose from a liquid/slurry. U.S. Patent 2009/0099354 (16 April 2009)
Axelsson S, Croon I, Enström B (1962) Dissolution of hemicelluloses during sulphate pulping. Svensk Papperstid 30:693–697
Bajpai P (2004) Biological bleaching of chemical pulps. Crit Rev Biotechnol 24:1–58
Bajpai P (2012) Fiber Modification. In: Bajpai P (ed) Biotechnology for pulp and paper processing. Springer, US, pp 159–183
Belle J, Kleemann S, Odermatt J (2014) Weighing of different impact factors on wet web strength by full-factorial design of experiments. Bioresources 9:1830–1844
Bhaduri SK, Ghosh IN, Deb Sarkar NL (1995) Ramie hemicellulose as beater additive in paper making from jute-stick kraft pulp. Ind Crop Prod 4:79–84
Blomstedt M, Asikainen J, Lähdeniemi A, Ylönen T, Paltakari J, Hakala TK (2010) Effect of xylanase treatment on dewatering properties of birch kraft pulp. Bioresources 5:1164–1177
Bronkhorst CA, Bennett KA (2002) Deformation and failure behaviour of paper: zero-span tensile strength. In: Mark RE, Habeger CC, Borch J, Lyne MD (eds) Handbook of physical testing of paper, vol 1, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York, pp 333–341
Buchert J, Carlsson G, Viikari L, Ström G (1996) Surface characterization of unbleached kraft pulps by enzymatic peeling and ESCA. Holzforschung 50:69–74
Carrillo F, Lis MJ, Colom X, López-Mesas M, Valldeperas J (2005) Effect of alkali pretreatment on cellulase hydrolysis of wheat straw: kinetic study. Process Biochem 40:3360–3364
Centola G, Borruso D (1967) The influence of hemicelluloses on the beatability of pulps. Tappi J 50:344–347
Chirat C, Lachenal D, Sanglard M (2012) Extraction of xylans from hardwood chips prior to kraft cooking. Process Biochem 47:381–385
Christiemin M, Henriksson G, Lindström ME, Brumer H, Teeri TT, Lindström T, Laine J (2003) The effects of xyloglucan on the properties of paper made from bleached kraft pulp. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 18:182–187
Christopher L (ed) (2012) Integrated forest biorefineries: challenges and opportunities. Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC Green Chemistry Series), London
Collins T, Gerday C, Feller G (2005) Xylanases, xylanase families and extremophilic xylanases. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:3–23
Cottrall LG (1950) The influence of hemicelluloses in wood pulp fibers on their papermaking properties. Tappi J 33:471–480
Dahlman O, Jacobs A, Sjöberg J (2003) Molecular properties of hemicelluloses located in the surface and inner layers of hardwood and softwood pulps. Cellulose 10:325–334
Daniel G, Duchesne I (1998) Revealing the surface ultrastructure of spruce fibres using field emission-SEM. In: The 7th International Conference on Biotechnology in the Pulp and Paper Industry, Vancouver, Canada, June 16–19
Deutschmann R, Dekker RFH (2012) From plant biomass to bio-based chemicals: latest developments in xylan research. Biotechnol Adv 30:1627–1640
Dickson AR, Wong KKY, Mansfield SD (2000) Response of xylanase-treated kraft pulp to Escher-Wyss and PFI-refining. Tappi J 83:64–74
Du M, Li XP, Li WG (2012) Modification of bleached softwood pulp with xylanase. Adv Mater Res 393:855–858
Duchesne I, Hult EL, Molin U, Daniel G, Iversen T, Lennholm H (2001) The influence of hemicellulose on fibril aggregation of kraft pulp fibres as revealed by FE-SEM and CP/MAS 13C-NMR. Cellulose 8:103–111
Fahlén J (2005) The cell wall ultrastructure of wood fibres—effects of the chemical pulp fibre line. Dissertation, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH)
Fuhrmann F, Krogerus B (2009) Xylan from bleached hardwood pulp—new opportunities. In: TAPPI PEERS Conference, Memphis, United States, Oct 11–14
Garg AP, Roberts JC, McCarthy AJ (1998) Bleach boosting effect of cellulase-free xylanase of Streptomyces thermoviolaceus and its comparison with two commercial enzyme preparations on birchwood kraft pulp. Enzyme Microb Technol 22:594–598
Gehmayr V, Schild G, Sixta H (2011) A precise study on the feasibility of enzyme treatments of a kraft pulp for viscose application. Cellulose 18:479–491
Hakala TK, Liitiä T, Suurnäkki A (2013) Enzyme-aided alkaline extraction of oligosaccharides and polymeric xylan from hardwood kraft pulp. Carbohydr Polym 93:102–108
Han W, Zhao C, Elder T, Chen K, Yang R, Kim D, Yunqiao P, Hsieh J, Ragauskas AJ (2012) Study on the modification of bleached eucalyptus kraft pulp using birch xylan. Carbohydr Polym 88:719–725
Hannuksela T, Holmbom B, Mortha G, Lachenal D (2004) Effect of sorbed galactoglucomannans and galactomannans on pulp and paper handsheet properties, especially strength properties. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 19:237–244
Helmerius J, von Walter JV, Rova U, Berglund KA, Hodge DB (2010) Impact of hemicellulose pre-extraction for bioconversion on birch kraft pulp properties. Bioresour Technol 101:5996–6005
Ibarra D, Köpcke V, Ek M (2009) Exploring enzymatic treatments for the production of dissolving grade pulp from different wood and non-wood paper grade pulps. Holzforschung 63:721–730
Ibarra D, Köpcke V, Larsson PT, Jääskeläinen AS, Ek M (2010) Combination of alkaline and enzymatic treatments as a process for upgrading sisal paper-grade pulp to dissolving-grade pulp. Bioresour Technol 101:7416–7423
Kibblewhite RP, Clark TA (1996) Enzymatic modification of radiata pine kraft fibre and handsheet properties. Appita J 49:390–396
Köhnke T, Gatenholm P (2007) The effect of controlled glucuronoxylan adsorption on drying-induced strength loss of bleached softwood pulp. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 22:508–515
Köhnke T, Lund K, Brelid H, Westman G (2010) Kraft pulp hornification: a closer look at the preventive effect gained by glucuronoxylan adsorption. Carbohydr Polym 81:226–233
Köpcke V, Ibarra D, Larsson PT, Ek M (2010) Optimization of treatment sequences for the production of dissolving pulp from birch kraft pulp. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 25:31–38
Lei X, Lin L, Li K (2008) Effect of xylanase pretreatment of wood chips on fiber separation in the CTMP refining process. Bioresources 3:801–815
Lei X, Zhao Y, Li K, Pelletier A (2012) Improved surface properties of CTMP fibers with enzymatic pretreatment of wood chips prior to refining. Cellulose 19:2205–2215
Liebert T, Hänsch C, Heinze T (2006) Click chemistry with polysaccharides. Macromol Rapid Commun 27:208–213
Lindström T, Ljunggren S, de Ruvo A, Söremark C (1978) Dissolution of carbohydrates and lignin during beating of kraft pulps. Svensk Papperstid 81:397–402
Luce JE (1964) Radial distribution of properties through the cell wall. Pulp Pap Mag Can 65:419–423
Lundberg V, Axelsson E, Mahmoudkhani M, Berntsson T (2012) Process integration of near-neutral hemicellulose extraction in a Scandinavian kraft pulp mill—consequences for the steam and Na/S balances. Appl Therm Eng 43:42–50
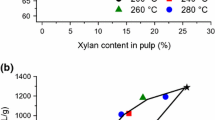
Lyytikäinen K, Saukkonen E, Väisänen M, Timonen J, Backfolk K (2014) Effect of reduced pulp xylan content on wet-end chemistry and paper properties—a pilot scale study. Tappi J 13:29–37
Mansfield SD, Wong KKY, Dickson AR (2000) Variation in the response of three different Pinus radiata pine kraft pulps to xylanase treatments. Wood Fiber Sci 32:105–115
Mao H, Genco JM, Yoon S-H, van Heiningen A, Pendse H (2008) Technical economic evaluation of a hardwood biorefinery using the “near-neutral” hemicellulose pre-extraction process. J Biobased Mater Bioenergy 2:177–185
Metsämuuronen S, Lyytikäinen K, Backfolk K, Sirén H (2013) Determination of xylo-oligosaccharides in enzymatically hydrolysed pulp by liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis. Cellulose 20:1121–1133
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Mironov VL (2004) Fundamentals of scanning probe microscopy. Nizhniy Novgorod, Russia
Moss PA, Pere J (2006) Microscopical study on the effects of partial removal of xylan on the swelling properties of birch kraft pulp fibres. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 21:8–12
Moure A, Gullon P, Dominquez H, Parajo JC (2006) Advances in the manufacture, purification and applications of xylooligosaccharides as food additives and nutraceuticals. Process Biochem 41:1913–19123
Noe P, Chevalier I, Mora F, Camtat I (1986) Action of xylanases on chemical pulp fibers. II. Enzymatic beating. J Wood Chem Technol 6:167–184
Öhman F, Danielsson S (2011) Separations of xylan from the kraft mill. In: The 3rd Nordic Wood Biorefinery Conference (NWBC), Stockholm, Sweden, March 22–24
Oksanen T, Pere J, Buchert J, Viikari L (1997a) The effect of Trichoderma reesei cellulases and hemicellulases on the paper technical properties of never-dried bleached kraft pulp. Cellulose 4:329–339
Oksanen T, Buchert J, Viikari L (1997b) The role of hemicelluloses in the hornification of bleached kraft pulps. Holzforschung 51:355–360
Oksanen A, Lehmonen J, Pere J (2009) Improving papermaking process by controlled modification of pulp carbohydrates. In: TAPPI Engineering, Pulping and Environmental Conference, Memphis, United States, Oct 11–14
Oliveira SC, Figueiredo AB, Evtuguin DV, Saraiva JA (2012) High pressure treatment as a tool for engineering of enzymatic reactions in cellulosic fibres. Bioresour Technol 107:530–534
Pönni R, Vuorinen T, Kontturi E (2012) Proposed nano-scale coalescense of cellulose in chemical pulp fibers during technical treatments. Bioresources 7:6077–6108
Ristolainen M, Alén R, Malkavaara P, Pere J (2002) Reflectance FTIR microspectroscopy for studying effect of xylan removal on unbleached and bleached birch kraft pulps. Holzforschung 56:513–521
Roncero MB, Torres AL, Colom JF, Vidal T (2005) The effect of xylanase on lignocellulosic components during the bleaching of wood pulps. Bioresour Technol 96:21–30
Rydholm S (1967) Relationship of pulp and paper properties. In: Rydholm S (ed) Pulping processes. Interscience Publishers, New York, pp 1152–1166
Salmén L, Burgert I (2009) Cell wall features with regard to mechanical performance—a review. Holzforschung 63:121–129
Saukkonen E, Lyytikäinen K, Backfolk K (2012) Alkaline xylan extraction of bleached kraft pulp—effect of extraction time on pulp chemical composition and physical properties. Tappi J 11:37–43
Schönberg C, Oksanen T, Suurnäkki A, Kettunen H, Buchert J (2001) The importance of xylan for the strength properties of spruce kraft pulp fibres. Holzforschung 55:639–644
Silva TCF, Colodette JL, Lucia LA, Oliveira RCD, Oliveira FN, Silva LHM (2011) Adsorption of chemically modified xylans on eucalyptus pulp and its effect on the pulp physical properties. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:1138–1145
Sjöberg J (2003) Characterization of chemical pulp fiber surfaces with an emphasis on the hemicelluloses. Dissertation, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH)
Sjöström E (1989) The origin of charge on cellulosic fibers. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 4:90–93
Sundberg A, Sundberg K, Lillandt C, Holmbom B (1996) Determination of hemicelluloses and pectins in wood and pulp fibres by acid methanolysis and gas chromatography. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 11:216–219
Teleman A, Larsson PT, Iversen T (2001) On the accessibility and structure of xylan in birch kraft pulp. Cellulose 8:209–215
Testova L, Chong S-L, Tenkanen M, Sixta H (2011) Autohydrolysis of birch wood. Holzforschung 65:535–542
Torres AL, Roncero M, Colom JF, Pastor FIJ, Blanco A, Vidal T (2000) Effect of a novel enzyme on fibre morphology during ECF bleaching of oxygen delignified Eucalyptus kraft pulps. Bioresour Technol 74:135–140
Treimanis A, Grinfelds U, Skute M (2009) Are the pulp fiber wall surface layers the most resistant ones towards bleaching. Bioresources 4:554–565
Viikari L, Kantelinen A, Sundquist J, Linko M (1994a) Xylanases in bleaching: from an idea to the industry. FEMS Microbiol Rev 13:335–350
Viikari L, Kantelinen A, Buchert J, Puls J (1994b) Enzymatic accessibility of xylans in lignocellulosic materials. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 41:124–129
Wallmo H, Theliander H, Jönsson AS, Wallberg O, Lindgren K (2009) The influence of hemicelluloses during the precipitation of lignin in kraft black liquor. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 24:165–171
Weise U (1998) Hornification—mechanisms and terminology. Pap Tim 80:110–115
Yang G, Lucia LA, Chen J, Cao X, Liu Y (2011) Effects of enzyme pretreatment on the beatability of fast-growing poplar APMP pulp. Bioresources 6:2568–2580
Zhou Q, Baumann MJ, Piispanen PS, Teeri TT, Brumer H (2006) Xyloglucan and xyloglucan endo-transglycosylases (XET): tools for ex vivo cellulose surface modification. Biocatal Biotransform 24:107–120
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out as part of the Future Biorefinery II (FuBio II) Research Program of Finnish Bioeconomy Cluster FIBIC Ltd (formerly ForestCluster Ltd), Finland. TEKES (the Finnish Funding Agency for Technology and Innovation) and the industrial partners of the FuBio II Program are acknowledged for their financial support. The authors wish to thank the pilot paper machine personnel at Stora Enso Research Centre Imatra, Finland for their assistance in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saukkonen, E., Lyytikäinen, K., Geydt, P. et al. Surface selective removal of xylan from refined never-dried birch kraft pulp. Cellulose 21, 3677–3690 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0354-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0354-8