Abstract
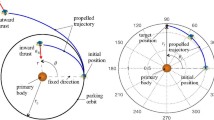
This paper studies the problem of a spacecraft subject to an outward radial thrust, with constant modulus, that may be switched on or off at suitable time intervals. The problem is to find the optimal strategy to guarantee the possibility of transferring the spacecraft from an initial to a final position in a given time interval using the least amount of thrust level. The problem is solved in an optimal framework, using an indirect approach. A number of different mission scenarios are studied in detail: escape missions, flyby missions and rendezvous missions. In the latter case the spacecraft uses a hybrid system comprising an high thrust propulsion system for the final impulsive maneuver. The optimal switching strategy allows one to substantially decrease the thrust level when compared to the continuous case (without thrust modulation).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baoyin H., Mcinnes C.R.: Solar sail halo orbits at the sun-earth artificial L 1 point. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 94(2), 155–171 (2006)
Bate R.R., Mueller D.D., White J.E.: Fundamentals of Astrodynamics, pp. 429. Dover Publications, New York (1971)
Battin R.H.: An Introduction to the Mathematics and Methods of Astrodynamics. AIAA Education Series, pp. 408–415. AIAA, New York (1987)
Bryson A.E., Ho Y.C.: Applied Optimal Control, Ch 2, pp. 71–89. Hemisphere, New York (1975)
Conway B.A., Chilan C.M., Wall B.J.: Evolutionary principles applied to mission planning problems. Celest. Mech. 97(2), 73–86 (2007)
Dachwald, B.: Fast solar system escape missions using non-futuristic solar sails. In: Pioneer Anomaly Workshop. ZARM, Bremen, 18–19 May (2004a)
Dachwald, B.: Solar sail performance requirements for missions to the outer solar system and beyond. In: 55th International Astronautical Congress. Paper IAC–04–S.P.11, Vancouver, 04–08 October (2004b)
Jacobson R.A., Powers W.F.: Optimal low-thrust takeoff from an orbit about an oblate planet. Celest. Mech. 15(2), 161–189 (1977)
Janhunen P.: Electric sail for spacecraft propulsion. J. Propuls. Power 20(4), 763–764 (2004)
Janhunen P.: The electrical sail—a new propulsion method which may enable fast missions to the outer solar system. J. Br. Interplanet. Soc. 61, 322–325 (2008)
Janhunen P.: On the feasibility of a negative polarity electric sail. Ann. Geophys. 27(4), 1439–1447 (2009)
Janhunen P., Sandroos A.: Simulation study of solar wind push on a charged wire: basis of solar wind electric sail propulsion. Ann. Geophys. 25(3), 755–767 (2007)
Kim M., Hall C.D.: Symmetries in the optimal control of solar sail spacecraft. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 92(4), 273–293 (2005)
Kirpichnikov S.N., Kirpichnikova E.S., Polyakhova E.N., Shmyrov A.S.: Planar heliocentric roto-translatory motion of a spacecraft with a solar sail of complex shape. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 63(3–4), 255–269 (1995)
Koblik V., Polyakhova E., Sokolov L.: Controlled solar sail transfers into near-sun regions combined with planetary gravity-assist flybys. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 86(1), 59–80 (2003)
Leipold M., Fichtner H., Heber B., Groepper P., Lascar S., Burger F., Eiden M., Niederstadt T., Sickinger C., Herbeck L., Dachwald B., Seboldt W.: Heliopause explorer—a sailcraft mission to the outer boundaries of the solar system. Acta Astronautica 59(8–11), 785–796 (2006)
McInnes C.R.: Orbits in a generalized two-body problem. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 26(5), 743–749 (2003)
McInnes C.R., Brown J.C.: The dynamics of solar sails with a non-point source of radiation pressure. Celest. Mech, Dyn. Astron. 49(3), 249–264 (1990)
Mengali G., Quarta A.A.: Earth escape by ideal sail and solar-photon thrustor spacecraft. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 27(6), 1105–1108 (2004)
Mengali G., Quarta A.A.: Near-optimal solar-sail orbit-raising from low earth orbit. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 42(5), 954–958 (2005a)
Mengali G., Quarta A.A.: Optimal control laws for axially symmetric solar sails. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 42(6), 1130–1133 (2005b)
Mengali G., Quarta A.A.: Optimal three-dimensional interplanetary rendezvous using nonideal solar sail. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 28(1), 173–177 (2005c)
Mengali G., Quarta A.A.: Time-optimal three-dimensional trajectories for solar photon thruster spacecraft. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 42(2), 379–381 (2005d)
Mengali G., Quarta A.A.: Minimagnetospheric plasma propulsion for outer planet missions. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 29(5), 1239–1242 (2006a)
Mengali G., Quarta A.A.: Optimal missions with minimagnetospheric plasma propulsion. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 29(1), 209–212 (2006b)
Mengali G., Quarta A.A.: Escape from elliptic orbit using constant radial thrust. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 32(3), 1018–1022 (2009a)
Mengali, G., Quarta, A.A.: Non-keplerian orbits for electric sails. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astr. (2009b, in press) doi:10.1007/s10569-009-9200-y
Mengali G., Quarta A.A., Janhunen P.: Considerations of electric sailcraft trajectory design. J. Br. Interplanet. Soc. 61, 326–329 (2008a)
Mengali G., Quarta A.A., Janhunen P.: Electric sail performance analysis. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 45(1), 122–129 (2008b)
Prussing J.E., Coverstone V.L.: Constant radial thrust acceleration redux. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 21(3), 516–518 (1998)
Quarta A.A., Mengali G.: Solar sail missions to mercury with venus gravity assist. Acta Astronautica 65(3–4), 495–506 (2009)
Racca G.D.: New challenges to trajectory design by the use of electric propulsion and other new means of wandering in the solar system. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 85, 1–24 (2003)
Stengel R.F.: Optimal Control and Estimation, pp. 222–254. Dover, Mineola (1994)
Trask, A.J., Mason, W.J., Coverstone, V.L.: Optimal interplanetary trajectories utilizing constant radial thrust and gravitational assists. In: AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference and Exhibit. AIAA Paper 2002-4731, Monterey (2002)
Trask A.J., Mason W.J., Coverstone V.L.: Optimal interplanetary trajectories using constant radial thrust and gravitational assists. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 27(3), 503–506 (2004)
Tsien H.S.: Take-off from satellite orbit. J. Am. Rocket Soc. 23(4), 233–236 (1953)
Winglee, R.M., Euripides, P., Ziemba, T., Slough, J., Giersch, L.: Simulation of mini-magnetospheric plasma propulsion (m2p2) interacting with an external plasma wind. In: 39th Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibition. AIAA Paper 2003-5225, Huntsville (2003)
Winglee R.M., Slough J., Ziemba T., Goodson A.: Mini-magnetospheric plasma propulsion: tapping the energy of the solar wind for spacecraft propulsion. J. Geophys. Res. 105(A9), 21067–21078 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quarta, A.A., Mengali, G. Optimal switching strategy for radially accelerated trajectories. Celest Mech Dyn Astr 105, 361–377 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-009-9233-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-009-9233-2