Abstract
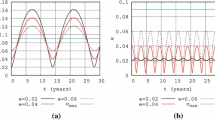
Halo orbits for solar sails at artificial Sun–Earth L1 points are investigated by a third order approximate solution. Two families of halo orbits are explored as defined by the sail attitude. Case I: the sail normal is directed along the Sun-sail line. Case II: the sail normal is directed along the Sun–Earth line. In both cases the minimum amplitude of a halo orbit increases as the lightness number of the solar sail increases. The effect of the z-direction amplitude on x- or y-direction amplitude is also investigated and the results show that the effect is relatively small. In case I, the orbit period increases as the sail lightness number increases, while in case II, as the lightness number increases, the orbit period increases first and then decreases after the lightness number exceeds ~0.01.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. V. Breakwell J. V. Brown (1979) ArticleTitle‘The ‘Halo’ family of 3-dimensional periodic orbits in the earth–moon restricted 3-body problem’ Celest. Mech. 20 389–404 Occurrence Handle1979CeMec..20..389B
R. W. Farquhar (1970) The Control and Use of Libration-Point Satellite Goddard Space Flight Center Greenbelt, MD
R. W. Farquhar (1971) The Utilization of Halo Orbits in Advanced Lunar Operations Goddard Space Flight Center Greenbelt, MD
R. W. Farquhar A. A. Kamel (1973) ArticleTitle‘Quasi-periodic orbits about the thanslunar libration point’ Celest. Mech. 7 458–473 Occurrence Handle1973CeMec...7..458F
R. W. Farquhar D. P. Muhonen D. L. Richardson (1977) ArticleTitle‘Mission design for a halo orbiter of the earth’ J. Spacecraft Rockets 14 IssueID3 170–177 Occurrence Handle1977JSpRo..14..170F
R. W. Farquhar D. P. Muhonen C. R. Newman H. S. Heuberber (1980) ArticleTitle‘Trajectories and orbital maneuvers for the first libration-point satellite’ J. Guidance Control 3 549–554
K. C. Howell (1984) ArticleTitle‘Three-dimensional, periodic, ‘halo’ orbit’ Celest. Mech. 32 53–71 Occurrence Handle1984CeMec..32...53H Occurrence Handle0544.70013 Occurrence Handle85c:70006
K. C. Howell J. V. Breakwell (1984) ArticleTitle‘Almost rectilinear halo orbit’ Celest. Mech. 32 29–52 Occurrence Handle1984CeMec..32...29H Occurrence Handle85c:70005
K. C. Howell H. J. Pernicka (1988) ArticleTitle‘Numerical determination of lissajous trajectories in the restricted three-body problem’ Celest. Mech. 41 107–124 Occurrence Handle1988CeMec..41..107H
A. I. S. McInnes (2000) Strategies for Solar Sail Mission Design in the Circular Restricted Three-Body Problem Purdue University West Lafayette
C.R. McInnes J. F. L. Simmons (1992a) ArticleTitle‘Solar Sail Halo orbit I: Heliocentric Case’ J. Spacecraft Rockets 29 IssueID4 466–471 Occurrence Handle1992JSpRo..29..466M
C. R. McInnes J. F. L. Simmons (1992b) ArticleTitle‘Solar Sail Halo orbit I: Geocentric Case’ J. Spacecraft Rockets 29 IssueID4 472–479 Occurrence Handle1992JSpRo..29..472M
C. R. McInnes (1993) ArticleTitle‘Solar sail trajectories at the lunar L2 lagrange point’ J. Spacecraft Rockets 30 IssueID6 782–784
C. R. McInnes A. J. C. Mcdonald J. F. L. Simmons E. W. MacDonald (1994) ArticleTitle‘Solar sail parking in restricted three-body system’ J. Guidance, Control, Dynamics 17 IssueID2 399–406 Occurrence Handle1994JGCD...17..399M
C. R. McInnes (1999) Solar Sailing: Technology, Dynamics and Mission Applications Springer-Verlag London
D. L. Richardson (1980) ArticleTitle‘Analytic construction of periodic orbits about the collinear points’ Celest. Mech. 22 241–253 Occurrence Handle1980CeMec..22..241R Occurrence Handle0465.34028
V. Szebehely (1967) Theory of Orbits: The Restricted Problem of Three Bodies Academic Press New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baoyin, H., Mcinnes, C.R. Solar Sail Halo Orbits at the Sun–Earth Artificial L 1 Point. Celestial Mech Dyn Astr 94, 155–171 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-005-4626-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-005-4626-3