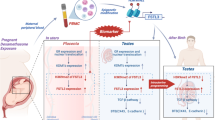
Abstract
Dexamethasone is widely used to treat pregnancy disorders related to premature delivery. However, lots of researches have confirmed that prenatal dexamethasone exposure (PDE) could increase the risk of offspring multiple diseases. This study was designed to elucidate the epigenetic mechanism of adrenal developmental programming and explore its early warning marker in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). We found the adrenal morphological and functional changes of PDE male offspring rats before and after birth, which were mainly performed as the decreased serum corticosterone concentration, steroidogenic acute regulatory (StAR) protein expression, and histone 3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) level of steroidogenic factor 1 (SF1) promoter region and its expression. Simultaneously, the expressions of glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and histone acetylation enzyme 5 (HDAC5) in the PDE male fetal rats were increased. In vitro, dexamethasone reduced the expression of SF1, StAR, and cortisol production and still increased the expression of GR and HDAC5, the binding between GR and SF1 promoter region, and protein interaction between GR and HDAC5. GR siRNA or HDAC5 siRNA was able to reverse the above roles of dexamethasone. Furthermore, in vivo, we confirmed that H3K27ac levels of SF1 promoter region and its expression in PBMC of the PDE group were decreased before and after birth, showing a positive correlation with the same indexes in adrenal. Meanwhile, in clinical trials, we confirmed that prenatal dexamethasone application decreased H3K27ac of SF1 promoter region and its expression in neonatal PBMC. In conclusion, PDE-caused adrenal insufficiency of male offspring rats was related to adrenal GR activated by dexamethasone in uterus. The activated GR, on the one hand, increased its direct binding to SF1 promoter region to inhibit its expression, on the other hand, upregulated and recruited HDAC5 to decrease H3K27ac level of SF1 promoter region, and strengthened the inhibition of SF1 and subsequent StAR expression.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Chawanpaiboon S, Vogel JP, Moller AB, Lumbiganon P, Petzold M, Hogan D, et al. Global, regional, and national estimates of levels of preterm birth in 2014: a systematic review and modelling analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2019;7(1):e37–46.
Roberts D, Brown J, Medley N, Dalziel SR 2017 Antenatal corticosteroids for accelerating fetal lung maturation for women at risk of preterm birth. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 3(3): Cd004454.
Onland W, De Jaegere AP, Offringa M, van Kaam A 2017 Systemic corticosteroid regimens for prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 1(1): Cd010941.
Vogel JP, Souza JP, Gülmezoglu AM, Mori R, Lumbiganon P, Qureshi Z, et al. Use of antenatal corticosteroids and tocolytic drugs in preterm births in 29 countries: an analysis of the WHO multicountry survey on maternal and newborn health. Lancet. 2014;384(9957):1869–77.
Asztalos EV, Murphy KE, Hannah ME, Willan AR, Matthews SG, Ohlsson A, et al. Multiple courses of antenatal corticosteroids for preterm birth study: 2-year outcomes. Pediatrics. 2010;126(5):e1045-1055.
Elfayomy AK, Almasry SM. Effects of a single course versus repeated courses of antenatal corticosteroids on fetal growth, placental morphometry and the differential regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2014;40(11):2135–45.
Xu D, Chen M, Pan XL, Xia LP, Wang H. Dexamethasone induces fetal developmental toxicity through affecting the placental glucocorticoid barrier and depressing fetal adrenal function. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2011;32(3):356–63.
Quinn TA, Ratnayake U, Castillo-Melendez M, Moritz KM, Dickinson H, Walker DW. Adrenal steroidogenesis following prenatal dexamethasone exposure in the spiny mouse. J Endocrinol. 2014;221(2):347–62.
Jefcoate CR, Lee J. Cholesterol signaling in single cells: lessons from STAR and sm-FISH. J Mol Endocrinol. 2018;60(4):R213-r235.
Gardiner JR, Shima Y, Morohashi K, Swain A. SF-1 expression during adrenal development and tumourigenesis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012;351(1):12–8.
Morohashi K, Honda S, Inomata Y, Handa H, Omura T. A common trans-acting factor, Ad4-binding protein, to the promoters of steroidogenic P-450s. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(25):17913–9.
Moisiadis VG, Matthews SG. Glucocorticoids and fetal programming part 2: mechanisms. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014a;10(7):403–11.
Heard E, Martienssen RA. Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance: myths and mechanisms. Cell. 2014;157(1):95–109.
Liu L, Wang JF, Fan J, Rao YS, Liu F, Yan YE, et al 2016 Nicotine suppressed fetal adrenal StAR expression via yy1 mediated-histone deacetylation modification mechanism. International journal of molecular sciences 17(9).
Yan YE, Liu L, Wang JF, Liu F, Li XH, Qin HQ, et al. Prenatal nicotinic exposure suppresses fetal adrenal steroidogenesis via steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) deacetylation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014;277(3):231–41.
Xu D, Wu Y, Liu F, Liu YS, Shen L, Lei YY, et al. A hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis-associated neuroendocrine metabolic programmed alteration in offspring rats of IUGR induced by prenatal caffeine ingestion. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012;264(3):395–403.
Harris A, Seckl J. Glucocorticoids, prenatal stress and the programming of disease. Horm Behav. 2011;59(3):279–89.
Giussani M, Triulzi T, Sozzi G, Tagliabue E 2019 Tumor extracellular matrix remodeling: new perspectives as a circulating tool in the diagnosis and prognosis of solid tumors. Cells 8(2).
Narimatsu H, Sato T. Wisteria floribunda agglutinin positive glycobiomarkers: a unique lectin as a serum biomarker probe in various diseases. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2018;15(2):183–90.
Ubolyam S, Iampornsin T, Sophonphan J, Avihingsanon A, Suwanpimolkul G, Kawkitinarong K, et al 2021 Performance of a simple flow cytometric assay in diagnosing active tuberculosis. Tuberculosis 126: 102017.
Fougère B, Landkocz Y, Lepers C, Martin PJ, Armand L, Grossin N, et al. Influence of aging in the modulation of epigenetic biomarkers of carcinogenesis after exposure to air pollution. Exp Gerontol. 2018;110:125–32.
Parashar S, Cheishvili D, Mahmood N, Arakelian A, Tanvir I, Khan HA, et al. DNA methylation signatures of breast cancer in peripheral T-cells. BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):574.
Chen GH, Yuan C, Duan FF, Liu YY, Zhang JZ, He Z, et al. IGF1/MAPK/ERK signaling pathway-mediated programming alterations of adrenal cortex cell proliferation by prenatal caffeine exposure in male offspring rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2018;341:64–76.
Kimura K, Hohjoh H, Fukuoka M, Sato W, Oki S, Tomi C, et al. Circulating exosomes suppress the induction of regulatory T cells via let-7i in multiple sclerosis. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):17.
Liu M, Chen B, Pei L, Zhang Q, Zou Y, Xiao H, et al. Decreased H3K9ac level of StAR mediated testicular dysplasia induced by prenatal dexamethasone exposure in male offspring rats. Toxicology. 2018;408:1–10.
Antenatal corticosteroids revisited 2001 repeat courses - National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference Statement, August 17–18, 2000 ObstetGynecol 98 1 144 150
Murphy KE, Hannah ME, Willan AR, Hewson SA, Ohlsson A, Kelly EN, et al. Multiple courses of antenatal corticosteroids for preterm birth (MACS): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2008;372(9656):2143–51.
Quinlivan JA, Evans SF, Dunlop SA, Beazley LD, Newnham JP. Use of corticosteroids by Australian obstetricians–a survey of clinical practice. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 1998;38(1):1–7.
Moisiadis VG, Matthews SG. Glucocorticoids and fetal programming part 1: outcomes. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014b;10(7):391–402.
Kemp MW, Newnham JP, Challis JG, Jobe AH, Stock SJ. The clinical use of corticosteroids in pregnancy. Hum Reprod Update. 2016;22(2):240–59.
Eguchi Y, Ariyuki F. Development of the fetal rat adrenal in prolonged pregnancy. Endocrinol Jpn. 1963;10:125–35.
He Z, Zhu C, Huang H, Liu L, Wang L, Chen L, et al. Prenatal caffeine exposure-induced adrenal developmental abnormality in male offspring rats and its possible intrauterine programming mechanisms. Toxicol Res. 2016;5(2):388–98.
Huang H, He Z, Zhu C, Liu L, Kou H, Shen L, et al. Prenatal ethanol exposure-induced adrenal developmental abnormality of male offspring rats and its possible intrauterine programming mechanisms. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015;288(1):84–94.
Hu MC, Hsu NC, Pai CI, Wang CK, Chung B. Functions of the upstream and proximal steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1)-binding sites in the CYP11A1 promoter in basal transcription and hormonal response. Mol Endocrinol. 2001;15(5):812–8.
Ben-Zimra M, Koler M, Orly J. Transcription of cholesterol side-chain cleavage cytochrome P450 in the placenta: activating protein-2 assumes the role of steroidogenic factor-1 by binding to an overlapping promoter element. Mol Endocrinol. 2002;16(8):1864–80.
Chen G, Xiao H, Zhang J, Zhang H, Li B, Jiang T, et al. Prenatal dexamethasone exposure-induced a gender-difference and sustainable multi-organ damage in offspring rats via serum metabolic profile analysis. Toxicol Lett. 2019;316:136–46.
Chen YW, Xu D, Xia X, Chen GH, Xiao H, Chen LB, et al 2021 Sex difference in adrenal developmental toxicity induced by dexamethasone and its intrauterine programming mechanism. Pharmacol Res. 174:105942. Online ahead of print.
Charles MA, Delpierre C, Bréant B. Developmental origin of health and adult diseases (DOHaD): evolution of a concept over three decades. Med Sci m/s. 2016;32(1):15–20.
Godfrey KM, Costello PM, Lillycrop KA. Development, epigenetics and metabolic programming. Nestle Nutr Inst Workshop Ser. 2016;85:71–80.
Xiao H, Wen Y, Pan Z, Shangguan Y, Qin J, Tan Y, et al. Increased H3K27ac level of ACE mediates the intergenerational effect of low peak bone mass induced by prenatal dexamethasone exposure in male offspring rats. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(6):638.
Kassel O, Herrlich P. Crosstalk between the glucocorticoid receptor and other transcription factors: molecular aspects. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007;275(1–2):13–29.
Grabiec AM, Potempa J. Epigenetic regulation in bacterial infections: targeting histone deacetylases. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2018;44(3):336–50.
Nebbioso A, Tambaro FP, Dell'Aversana C, Altucci L 2018 Cancer epigenetics: moving forward. Plos genet 2018 14 6 e1007362
Lomberk G, Blum Y. Distinct epigenetic landscapes underlie the pathobiology of pancreatic cancer subtypes. Nat Comm. 2018;9(1):1978.
Ma B, Wilker EH, Willis-Owen SA, Byun HM, Wong KC, Motta V, et al. Predicting DNA methylation level across human tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(6):3515–28.
Davies MN, Volta M, Pidsley R, Lunnon K, Dixit A, Lovestone S, et al. Functional annotation of the human brain methylome identifies tissue-specific epigenetic variation across brain and blood. Genome Biol. 2012;13(6):R43.
Hosseini A, Mirzaei A, Salimi V, Jamshidi K, Babaheidarian P, Fallah S, et al. The local and circulating SOX9 as a potential biomarker for the diagnosis of primary bone cancer. Journal of bone oncology 2020, 23: 100300.
Kundakovic M, Gudsnuk K, Herbstman JB, Tang D, Perera FP, Champagne FA. DNA methylation of BDNF as a biomarker of early-life adversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112(22):6807–13.
Xu XF, Xu SS, Fu LC, Hu QY, Lv Y, Du LZ. Epigenetic changes in peripheral leucocytes as biomarkers in intrauterine growth retardation rat. Biomedical Reports. 2016;5(5):548–52.
Bermick JR, Lambrecht NJ, denDekker AD, Kunkel SL, Lukacs NW, Hogaboam CM. Neonatal monocytes exhibit a unique histone modification landscape. Clin Epigenetics. 2016;8:99.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2020YFA0803900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82030111, 81673524, 82104312), the Major Technological Innovation Projects of Hubei Province (No. 2019ACA140, 2020BCA071), Hubei Province’s Outstanding Medical Academic Leader program, and Medical Science Advancement Program (Basic Medical Sciences) of Wuhan University, Grant No. TFJC2018001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guanghui Chen, Can Ai, and Jiangang Cao performed the research; Hui Wang designed the research study; Fangfang Duan, Jinzhi Zhang, and Yawen Chen analyzed the data; Guanghui Chen, Ying Ao, and Hui Wang wrote and revised the paper; all authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The experimental protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee for Animal (Certification No. 42000600002258; Permission No. 20170018) and Human (No: 2016016) Experiments of the Medical College of Wuhan University.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Guanghui Chen, Can Ai and Fangfang Duan contributed equally to this paper
Highlights
• Adrenal insufficiency induced by PDE associated with inhibited SF1/StAR expression.
• Dexamethasone inhibits H3K27ac level of SF1 promoter region by GR/HDAC5.
• H3K27ac level of SF1 promoter region in PBMC is a biomarker of adrenal insufficiency.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Ai, C., Duan, F. et al. Low H3K27 acetylation of SF1 in PBMC: a biomarker for prenatal dexamethasone exposure-caused adrenal insufficiency of steroid synthesis in male offspring. Cell Biol Toxicol 39, 2051–2067 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09691-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09691-0