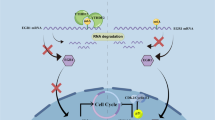
Abstract
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a pernicious plasma cell disorder and has a poor prognosis. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is an abundant epigenetic RNA modification and is important in cancer progression. Nevertheless, the function of m6A and its regulator METTL3 in MM are rarely reported. Here, we identified the m6A “writers”, METTL3, was enhanced in MM and found that Yin Yang 1 (YY1) and primary-miR-27a-3p were the potential target for METTL3. METTL3 promoted primary-miR-27a-3p maturation and YY1 mRNA stability in an m6A manner. YY1 also was found to facilitate miR-27a-3p transcription. METTL3 affected the growth, apoptosis, and stemness of MM cells through accelerating the stability of YY1 mRNA and the maturation of primary-miR-27a-3p in vitro and in vivo. Our results reveal the key function of the METTL3/YY1/miR-27a-3p axis in MM and may provide fresh insights into MM therapy.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alarcon CR, Lee H, Goodarzi H, Halberg N, Tavazoie SF. N6-methyladenosine marks primary microRNAs for processing. Nature. 2015;519:482–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14281.
Bach C, Leffler M, Flamann C, Kronke J, Mougiakakos D, Mackensen A, et al. Role of N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) RNA modification in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2018;132:5601. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2018-99-115820.
Bai H, Xu P, Chen B. Gene signatures and prognostic values of m6A-related genes in multiple myeloma. Curr Res Transl Med. 2021;69:103288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.retram.2021.103288.
Barlogie B, Attal M, Crowley J, van Rhee F, Szymonifka J, Moreau P, et al. Long-term follow-up of autotransplantation trials for multiple myeloma: update of protocols conducted by the intergroupe francophone du myelome, southwest oncology group, and university of arkansas for medical sciences. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1209–14. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.25.6081.
Bhat S, Kabekkodu SP, Adiga D, Fernandes R, Shukla V, Bhandari P, et al. ZNF471 modulates EMT and functions as methylation regulated tumor suppressor with diagnostic and prognostic significance in cervical cancer. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2021;37:731–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09582-4.
Bianchi G, Anderson KC. Understanding biology to tackle the disease: multiple myeloma from bench to bedside, and back. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:422–44. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21252.
Che F, Chen J, Wan C, Huang X. MicroRNA-27 inhibits autophagy and promotes proliferation of multiple myeloma cells by targeting the NEDD4/Notch1 axis. Front Oncol. 2020;10:571914. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.571914.
Che F, Wan C, Dai J, Chen J. Increased expression of miR-27 predicts poor prognosis and promotes tumorigenesis in human multiple myeloma. Biosci Rep. 2019;39.https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20182502.
Chen M, Wei L, Law CT, Tsang FH, Shen J, Cheng CL, et al. RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase-like 3 promotes liver cancer progression through YTHDF2-dependent posttranscriptional silencing of SOCS2. Hepatology. 2018;67:2254–70. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29683.
Chen J, Fang X, Zhong P, Song Z, Hu X. N6-methyladenosine modifications: interactions with novel RNA-binding proteins and roles in signal transduction. RNA Biol. 2019;16:991–1000. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2019.1620060.
Chen Q, Liu T, Bao Y, Zhao T, Wang J, Wang H, et al. CircRNA cRAPGEF5 inhibits the growth and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma via the miR-27a-3p/TXNIP pathway. Cancer Lett. 2020;469:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2019.10.017.
Chen X, Huang L, Yang T, Xu J, Zhang C, Deng Z, et al. METTL3 Promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma metastasis through enhancing GLS2 expression. Front Oncol. 2021a;11:667451. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.667451.
Chen Y, Pan C, Wang X, Xu D, Ma Y, Hu J, et al. Silencing of METTL3 effectively hinders invasion and metastasis of prostate cancer cells. Theranostics. 2021b;11:7640–57. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.61178.
Cheng M, Sheng L, Gao Q, Xiong Q, Zhang H, Wu M, et al. The m(6)A methyltransferase METTL3 promotes bladder cancer progression via AFF4/NF-kappaB/MYC signaling network. Oncogene. 2019;38:3667–80. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-0683-z.
Ding L, Zhang S, Xu M, Zhang R, Sui P, Yang Q. MicroRNA-27a contributes to the malignant behavior of gastric cancer cells by directly targeting PH domain and leucine-rich repeat protein phosphatase 2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017;36:45. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-017-0516-2.
Han J, Wang JZ, Yang X, Yu H, Zhou R, Lu HC, et al. METTL3 promote tumor proliferation of bladder cancer by accelerating pri-miR221/222 maturation in m6A-dependent manner. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:110. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1036-9.
Haussmann IU, Bodi Z, Sanchez-Moran E, Mongan NP, Archer N, Fray RG, et al. m(6)A potentiates Sxl alternative pre-mRNA splicing for robust Drosophila sex determination. Nature. 2016;540:301–4. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature20577.
Huang C, Liang J, Lin S, Wang D, Xie Q, Lin Z, et al. N(6)-Methyladenosine associated silencing of miR-193b promotes cervical cancer aggressiveness by targeting CCND1. Front Oncol. 2021;11:666597. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.666597.
Huerta-Yepez S, Liu H, Baritaki S, Del Lourdes C-M, Rivera-Pazos C, Maldonado-Valenzuela A, et al. Overexpression of Yin Yang 1 in bone marrow-derived human multiple myeloma and its clinical significance. Int J Oncol. 2014;45:1184–92. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2014.2511.
Jiang Y, Duan Y, Zhou H. MicroRNA-27a directly targets KRAS to inhibit cell proliferation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2015;9:471–7. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2014.2701.
Jiang F, Tang X, Tang C, Hua Z, Ke M, Wang C, et al. HNRNPA2B1 promotes multiple myeloma progression by increasing AKT3 expression via m6A-dependent stabilization of ILF3 mRNA. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-021-01066-6.
Ke S, Alemu EA, Mertens C, Gantman EC, Fak JJ, Mele A, et al. A majority of m6A residues are in the last exons, allowing the potential for 3’ UTR regulation. Genes Dev. 2015;29:2037–53. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.269415.115.
Lan Q, Liu PY, Bell JL, Wang JY, Huttelmaier S, Zhang XD, et al. The emerging roles of RNA m(6)A methylation and demethylation as critical regulators of tumorigenesis, drug sensitivity, and resistance. Cancer Res. 2021;81:3431–40. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-4107.
Li Y, Guo D, Lu G, Mohiuddin Chowdhury ATM, Zhang D, Ren M, et al. LncRNA SNAI3-AS1 promotes PEG10-mediated proliferation and metastasis via decoying of miR-27a-3p and miR-34a-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:685. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-02840-z.
Liang L, He Y, Wang H, Zhou H, Xiao L, Ye M, et al. The Wee1 kinase inhibitor MK1775 suppresses cell growth, attenuates stemness and synergises with bortezomib in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. 2020;191:62–76. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.16614.
Liu N, Pan T. N6-methyladenosine-encoded epitranscriptomics. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2016;23:98–102. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3162.
Liu Q, Ran R, Song M, Li X, Wu Z, Dai G, et al. LncRNA HCP5 acts as a miR-128-3p sponge to promote the progression of multiple myeloma through activating Wnt/beta-catenin/cyclin D1 signaling via PLAGL2. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2021a. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09628-7.
Liu Z, Han M, Meng N, Luo J, Fu R. lncRNA MSTRG.29039.1 Promotes proliferation by sponging hsa-miR-12119 via JAK2/STAT3 pathway in multiple myeloma. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021b;2021:9969449. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9969449.
Lokhorst HM, van der Holt B, Zweegman S, Vellenga E, Croockewit S, van Oers MH, et al. A randomized phase 3 study on the effect of thalidomide combined with adriamycin, dexamethasone, and high-dose melphalan, followed by thalidomide maintenance in patients with multiple myeloma. Blood. 2010;115:1113–20. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-05-222539.
Martinez-Ruiz GU, Morales-Sanchez A, Pacheco-Hernandez AF. Roles played by YY1 in embryonic, adult and cancer stem cells. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-021-10151-9.
Meliala ITS, Hosea R, Kasim V, Wu S. The biological implications of Yin Yang 1 in the hallmarks of cancer. Theranostics. 2020;10:4183–200. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.43481.
MirihanaArachchilage G, Dassanayake AC, Basu S. A potassium ion-dependent RNA structural switch regulates human pre-miRNA 92b maturation. Chem Biol. 2015;22:262–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.12.013.
Nombela P, Miguel-Lopez B, Blanco S. The role of m(6)A, m(5)C and Psi RNA modifications in cancer: novel therapeutic opportunities. Mol Cancer. 2021;20:18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01263-w.
Pan X, Hong X, Li S, Meng P, Xiao F. METTL3 promotes adriamycin resistance in MCF-7 breast cancer cells by accelerating pri-microRNA-221-3p maturation in a m6A-dependent manner. Exp Mol Med. 2021;53:91–102. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-020-00510-w.
Peng W, Li J, Chen R, Gu Q, Yang P, Qian W, et al. Upregulated METTL3 promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer via miR-1246/SPRED2/MAPK signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:393. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1408-4.
Pinto V, Bergantim R, Caires HR, Seca H, Guimaraes JE, Vasconcelos MH. Multiple myeloma: available therapies and causes of drug resistance. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020407.
Qian X, Yang J, Qiu Q, Li X, Jiang C, Li J, et al. LCAT3, a novel m6A-regulated long non-coding RNA, plays an oncogenic role in lung cancer via binding with FUBP1 to activate c-MYC. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:112. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-021-01123-0.
Shvartsur A, Givechian KB, Garban H, Bonavida B. Overexpression of RKIP and its cross-talk with several regulatory gene products in multiple myeloma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017;36:62. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-017-0535-z.
Sun Y, Li S, Yu W, Zhao Z, Gao J, Chen C, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine-dependent pri-miR-17-92 maturation suppresses PTEN/TMEM127 and promotes sensitivity to everolimus in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:836. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-03049-w.
Tripathi K, Ramani VC, Bandari SK, Amin R, Brown EE, Ritchie JP, et al. Heparanase promotes myeloma stemness and in vivo tumorigenesis. Matrix Biol. 2020;88:53–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2019.11.004.
Wang X, Lu Z, Gomez A, Hon GC, Yue Y, Han D, et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature. 2014;505:117–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12730.
Wang X, Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, Lu Z, Han D, Ma H, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine modulates messenger RNA translation efficiency. Cell. 2015;161:1388–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.014.
Wang H, Deng Q, Lv Z, Ling Y, Hou X, Chen Z, et al. N6-methyladenosine induced miR-143-3p promotes the brain metastasis of lung cancer via regulation of VASH1. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:181. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1108-x.
Wang H, Gong Y, Liang L, Xiao L, Yi H, Ye M, et al. Lycorine targets multiple myeloma stem cell-like cells by inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Br J Haematol. 2020a;189:1151–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.16477.
Wang Y, Wang H, Ruan J, Zheng W, Yang Z, Pan W. Long non-coding RNA OIP5-AS1 suppresses multiple myeloma progression by sponging miR-27a-3p to activate TSC1 expression. Cancer Cell Int. 2020b;20:155. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01234-7.
Wang Z, Wang W, Zhao W, Wang Z, Yang J, Wang W, et al. Folate inhibits miR-27a-3p expression during cervical carcinoma progression and oncogenic activity in human cervical cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020c;122:109654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109654.
Xiang P, Yeung YT, Wang J, Wu Q, Du R, Huang C, et al. miR-17-3p promotes the proliferation of multiple myeloma cells by downregulating P21 expression through LMLN inhibition. Int J Cancer. 2021;148:3071–85. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.33528.
Xu W, Yu S, Xiong J, Long J, Zheng Y, Sang X. CeRNA regulatory network-based analysis to study the roles of noncoding RNAs in the pathogenesis of intrahepatic cholangiocellular carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12:1047–86. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102634.
Yang R, Liu Z, Cao H, Shi Y. LINC01089, suppressed by YY1, inhibits lung cancer progression by targeting miR-301b-3p/HPDG axis. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09643-8.
Yao FY, Zhao C, Zhong FM, Qin TY, Wen F, Li MY, et al. m(6)A Modification of lncRNA NEAT1 regulates chronic myelocytic leukemia progression via miR-766-5p/CDKN1A axis. Front Oncol. 2021;11:679634. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.679634.
Yi YC, Chen XY, Zhang J, Zhu JS. Novel insights into the interplay between m(6)A modification and noncoding RNAs in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:121. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01233-2.
Yi H, Liang L, Wang H, Luo S, Hu L, Wang Y, et al. Albendazole inhibits NF-kappaB signaling pathway to overcome tumor stemness and bortezomib resistance in multiple myeloma. Cancer Lett. 2021;520:307–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2021.08.009.
Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, He C. Post-transcriptional gene regulation by mRNA modifications. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017;18:31–42. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2016.132.
Zhao W, Cui Y, Liu L, Ma X, Qi X, Wang Y, et al. METTL3 facilitates oral squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenesis by enhancing c-Myc stability via YTHDF1-mediated m(6)A modification. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;20:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2020.01.033.
Zhao Y, Bai D, Du J, Ren H, Zhang Z, Jiang C, et al. Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by CPUC002 through stabilization of p53 and suppression of STAT3 signaling pathway in multiple myeloma. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2021;37:97–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-020-09565-x.
Zhong L, He X, Song H, Sun Y, Chen G, Si X, et al. METTL3 induces AAA development and progression by modulating N6-Methyladenosine-dependent primary miR34a processing. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;21:394–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2020.06.005.
Zhou W, Xian Q, Wang Q, Wu C, Yan H, Li X, et al. m6A Methyltransferase 3 promotes the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells through the m6A modification of YAP1. J Oncol. 2021;2021:8875424. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8875424.
Funding
This work was supported by Sichuan Medical Scientific Research Youth Innovation Project (No. Q18017) and Scientific Research Foundation of Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital (No. 2020QN05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FFC, YW, and XMW have given substantial contributions to the conception and the design of the manuscript; SYM, YWT, and YM to acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of the data. All authors have participated to drafting the manuscript, FFC, XMY, and ZYL revised it critically. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital and University of Electronic Science and Technology of China Ethics Committee approved this study. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
All of the authors have approved the publication of the article.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Graphical headlights
1. METTL3 promotes the maturation of pri-miR-27a-3p in m6A dependent manner.
2. METTL3 enhances YY1 mRNA stability in an m6A manner.
3. YY1 is identified to be a transcriptional activator for miR-27a-3p.
4. The METTL3/YY1/miR-27a-3p axis affects the proliferation, stemness, and apoptosis MM cells in vivo and in vitro.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Che, F., Ye, X., Wang, Y. et al. METTL3 facilitates multiple myeloma tumorigenesis by enhancing YY1 stability and pri-microRNA-27 maturation in m6A-dependent manner. Cell Biol Toxicol 39, 2033–2050 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09690-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09690-1