Abstract
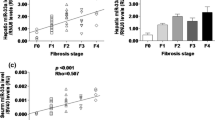
Exosomal miRNAs activates hepatic stellate cell (HSC) and promote fibrosis. miR-222 was found to be increased in hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infected hepatocytes, and ferroptosis was reported to ameliorate liver fibrosis (LF). Although miR-222 and ferroptosis have been implicated in LF, the association between miR-222 and ferroptosis and how they coordinate to regulate LF are still not explicit. This study investigates the roles of miR-222 and transferrin receptor (TFRC) in LF. Lipid reactive oxygen species (ROS) level was analyzed by flow cytometry. FerroOrange staining was used to measure intracellular iron level. Luciferase reporter assay was adopted to confirm the binding of miR-222 and TFRC. Real-time quantitative PCR and immunoblots were applied to analyze gene and protein expression. The results showed that supplementation of exosomes derived from HBV-infected LO2 cells remarkably enhanced LX-2 cell activation, evidenced by elevated hydroxyprolin (Hyp) secretion and α-SMA and COL1A2 expression. miR-222 was significantly increased in HBV-Exo. Overexpressing miR-222 upregulated cell viability, secretion of Hpy, and expression of α-SMA and COL1A2, which were all blocked by overexpression of TFRC. Further study showed that TFRC was a target of miR-222, and miR-222 promoted LX-2 cell activation through suppressing TFRC-induced ferroptosis in LX-2 cells. Exosomal miR-222 derived from HBV-infected hepatocytes promoted LF through inhibiting TFRC and TFRC-induced ferroptosis. This study emphasizes the significance of miR-222/TFRC axis in LF and suggests new insights in clinical decision making while treating LF.
Graphical abstract
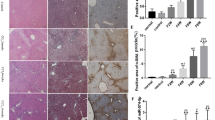
Exosomes derived from HBV-infected LO2 cells promote LX-2 cell activation and liver fibrosis in mouse
Exosomal miR-222 derived from HBV-infected LO2 cells promotes LX-2 cell activation
TFRC is a target of miR-222 and inhibits LX-2 cell activation induced by miR-222
miR-222 promotes LX-2 cell activation through inhibiting TFRC-induced ferroptosis








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm the availability of all data generated or analyzed in this manuscript.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdel-Al A, El-Ahwany E, Zoheiry M, Hassan M, Ouf A, Abu-Taleb H, Abdel Rahim A, El-Talkawy MD, Zada S. miRNA-221 and miRNA-222 are promising biomarkers for progression of liver fibrosis in HCV Egyptian patients. Virus Res. 2018;253:135–9.
Alim, I., Caulfield, J.T., Chen, Y., Swarup, V., Geschwind, D.H., Ivanova, E., Seravalli, J., Ai, Y., Sansing, L.H., Ste Marie, E.J., Hondal, R.J., Mukherjee, S., Cave, J.W., Sagdullaev, B.T., Karuppagounder, S.S., and Ratan, R.R. (2019). Selenium drives a transcriptional adaptive program to block ferroptosis and treat stroke. Cell 177, 1262–1279 e1225.
Arzberger S, Hosel M, Protzer U. Apoptosis of hepatitis B virus-infected hepatocytes prevents release of infectious virus. J Virol. 2010;84:11994–2001.
Azmi AS, Bao B, Sarkar FH. Exosomes in cancer development, metastasis, and drug resistance: a comprehensive review. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2013;32:623–42.
Basu A, Saito K, Meyer K, Ray RB, Friedman SL, Chang YH, Ray R. Stellate cell apoptosis by a soluble mediator from immortalized human hepatocytes. Apoptosis. 2006;11:1391–400.
Bataller R, Brenner DA. Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:209–18.
Chen L, Charrier A, Zhou Y, Chen R, Yu B, Agarwal K, Tsukamoto H, Lee LJ, Paulaitis ME, Brigstock DR. Epigenetic regulation of connective tissue growth factor by MicroRNA-214 delivery in exosomes from mouse or human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology. 2014;59:1118–29.
Dai X, Chen C, Xue J, Xiao T, Mostofa G, Wang D, Chen X, Xu H, Sun Q, Li J, Wei Y, Chen F, Quamruzzaman Q, Zhang A, Liu Q. Exosomal MALAT1 derived from hepatic cells is involved in the activation of hepatic stellate cells via miRNA-26b in fibrosis induced by arsenite. Toxicol Lett. 2019;316:73–84.
Devhare, P.B., Sasaki, R., Shrivastava, S., Di Bisceglie, A.M., Ray, R., and Ray, R.B. (2017). Exosome-mediated intercellular communication between hepatitis C virus-infected hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells. J Virol 91.
Ding S, Huang H, Xu Y, Zhu H, Zhong C. MiR-222 in cardiovascular diseases: physiology and pathology. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:4962426.
Dong R, Zheng Y, Chen G, Zhao R, Zhou Z, Zheng S. miR-222 overexpression may contribute to liver fibrosis in biliary atresia by targeting PPP2R2A. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015;60:84–90.
Enomoto Y, Takagi R, Naito Y, Kiniwa T, Tanaka Y, Hamada-Tsutsumi S, Kawano M, Matsushita S, Ochiya T, Miyajima A. Identification of the novel 3’ UTR sequences of human IL-21 mRNA as potential targets of miRNAs. Sci Rep. 2017;7:7780.
Fang X, Wang H, Han D, Xie E, Yang X, Wei J, Gu S, Gao F, Zhu N, Yin X, Cheng Q, Zhang P, Dai W, Chen J, Yang F, Yang HT, Linkermann A, Gu W, Min J, Wang F. Ferroptosis as a target for protection against cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116:2672–80.
Friedman SL. Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol Rev. 2008;88:125–72.
Galardi S, Mercatelli N, Farace MG, Ciafre SA. NF-kB and c-Jun induce the expression of the oncogenic miR-221 and miR-222 in prostate carcinoma and glioblastoma cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:3892–902.
Gao M, Monian P, Quadri N, Ramasamy R, Jiang X. Glutaminolysis and Transferrin Regulate Ferroptosis. Mol Cell. 2015;59:298–308.
Jiang X, Jiang L, Shan A, Su Y, Cheng Y, Song D, Ji H, Ning G, Wang W, Cao Y. Targeting hepatic miR-221/222 for therapeutic intervention of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. EBioMedicine. 2018;37:307–21.
Jiang XP, Elliott RL, Head JF. Manipulation of iron transporter genes results in the suppression of human and mouse mammary adenocarcinomas. Anticancer Res. 2010;30:759–65.
Kalluri, R., and Lebleu, V.S. (2020). The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 367.
Kong Z, Liu R, Cheng Y. Artesunate alleviates liver fibrosis by regulating ferroptosis signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:2043–53.
Kuo CY, Chiu V, Hsieh PC, Huang CY, Huang SJ, Tzeng IS, Tsai FM, Chen ML, Liu CT, Chen YR. Chrysophanol attenuates hepatitis B virus X protein-induced hepatic stellate cell fibrosis by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress and ferroptosis. J Pharmacol Sci. 2020;144:172–82.
Li X, Duan L, Yuan S, Zhuang X, Qiao T, He J. Ferroptosis inhibitor alleviates radiation-induced lung fibrosis (RILF) via down-regulation of TGF-beta1. J Inflamm (lond). 2019;16:11.
Li Y, Jin C, Shen M, Wang Z, Tan S, Chen A, Wang S, Shao J, Zhang F, Zhang Z, Zheng S. Iron regulatory protein 2 is required for artemether -mediated anti-hepatic fibrosis through ferroptosis pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;160:845–59.
Maciotta S, Meregalli M, Torrente Y. The involvement of microRNAs in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013;7:265.
Mashouri L, Yousefi H, Aref AR, Ahadi AM, Molaei F, Alahari SK. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis, and mechanisms in cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:75.
Mathivanan S, Ji H, Simpson RJ. Exosomes: extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J Proteomics. 2010;73:1907–20.
O'brien, J., Hayder, H., Zayed, Y., and Peng, C. (2018). Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 9, 402.
Peng Y, Croce CM. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2016;1:15004.
Sasaki, R., Kanda, T., Nakamura, M., Nakamoto, S., Haga, Y., Wu, S., Shirasawa, H., and Yokosuka, O. (2016). Possible involvement of hepatitis B virus infection of hepatocytes in the attenuation of apoptosis in hepatic stellate cells. PLoS One 11, e0146314.
Sato-Kuwabara Y, Melo SA, Soares FA, Calin GA. The fusion of two worlds: non-coding RNAs and extracellular vesicles–diagnostic and therapeutic implications (Review). Int J Oncol. 2015;46:17–27.
Schoenfeld JD, Sibenaller ZA, Mapuskar KA, Wagner BA, Cramer-Morales KL, Furqan M, Sandhu S, Carlisle TL, Smith MC, Abu Hejleh T, Berg DJ, Zhang J, Keech J, Parekh KR, Bhatia S, Monga V, Bodeker KL, Ahmann L, Vollstedt S, Brown H, Kauffman EPS, Schall ME, Hohl RJ, Clamon GH, Greenlee JD, Howard MA, Schultz MK, Smith BJ, Riley DP, Domann FE, Cullen JJ, Buettner GR, Buatti JM, Spitz DR, Allen BG. O2(-) and H2O2-mediated disruption of Fe metabolism causes the differential susceptibility of NSCLC and GBM cancer cells to pharmacological ascorbate. Cancer Cell. 2017;32:268.
Seo W, Eun HS, Kim SY, Yi HS, Lee YS, Park SH, Jang MJ, Jo E, Kim SC, Han YM, Park KG, Jeong WI. Exosome-mediated activation of toll-like receptor 3 in stellate cells stimulates interleukin-17 production by gammadelta T cells in liver fibrosis. Hepatology. 2016;64:616–31.
Shen Y, Li X, Dong D, Zhang B, Xue Y, Shang P. Transferrin receptor 1 in cancer: a new sight for cancer therapy. Am J Cancer Res. 2018;8:916–31.
Walter SR, Thein HH, Gidding HF, Amin J, Law MG, George J, Dore GJ. Risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma in a cohort infected with hepatitis B or C. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26:1757–64.
Wang L, Zhang Z, Li M, Wang F, Jia Y, Zhang F, Shao J, Chen A, Zheng S. P53-dependent induction of ferroptosis is required for artemether to alleviate carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation. IUBMB Life. 2019;71:45–56.
Xie H, Xie D, Zhang J, Jin W, Li Y, Yao J, Pan Z, Xie D. ROS/NF-kappaB signaling pathway-mediated transcriptional activation of TRIM37 promotes HBV-associated hepatic fibrosis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;22:114–23.
Yapali S, Talaat N, Lok AS. Management of hepatitis B: our practice and how it relates to the guidelines. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;12:16–26.
Yu F, Zheng J, Mao Y, Dong P, Lu Z, Li G, Guo C, Liu Z, Fan X. Long non-coding RNA growth arrest-specific transcript 5 (GAS5) inhibits liver fibrogenesis through a mechanism of competing endogenous RNA. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:28286–98.
Zhang HG, Grizzle WE. Exosomes: a novel pathway of local and distant intercellular communication that facilitates the growth and metastasis of neoplastic lesions. Am J Pathol. 2014;184:28–41.
Zhang Z, Guo M, Li Y, Shen M, Kong D, Shao J, Ding H, Tan S, Chen A, Zhang F, Zheng S. RNA-binding protein ZFP36/TTP protects against ferroptosis by regulating autophagy signaling pathway in hepatic stellate cells. Autophagy. 2020a;16:1482–505.
Zhang, Z., Guo, M., Shen, M., Kong, D., Zhang, F., Shao, J., Tan, S., Wang, S., Chen, A., Cao, P., and Zheng, S. (2020b). The BRD7-P53-SLC25A28 axis regulates ferroptosis in hepatic stellate cells. Redox Biol 36, 101619.
Zhou, J., Lan, Q., Li, W., Yang, L., You, J., Zhang, Y.M., and Ni, W. (2019). Tripartite motif protein 52 (TRIM52) promoted fibrosis in LX-2 cells through PPM1A-mediated Smad2/3 pathway. Cell Biol Int.
Zhou SS, Jin JP, Wang JQ, Zhang ZG, Freedman JH, Zheng Y, Cai L. miRNAS in cardiovascular diseases: potential biomarkers, therapeutic targets and challenges. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39:1073–84.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Science and Technology Major Project of China (2017ZX10202203-007-005), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81600479 and 81670548), and Wang Baoen liver fibrosis research fund (2020013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qidi Zhang and Lungen Lu conceived this study. Ying Qu, Qingqing Zhang, Fei Li, Binghang Li, Zhenghong Li, and Yuwei Dong performed the experiments, collected the data, and performed the data analysis. Xiaobo Cai and Ying Qu wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The study had approval from the Ethics Committee of Shanghai General Hospital and was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The animal study was approved by the IACUC and the Ethics Committee of Shanghai General Hospital.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Qu, Y., Zhang, Q. et al. Exosomes derived from hepatitis B virus-infected hepatocytes promote liver fibrosis via miR-222/TFRC axis. Cell Biol Toxicol 39, 467–481 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09684-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09684-z