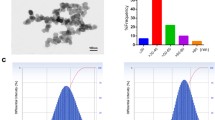
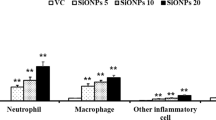
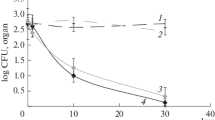
Abstract
Owing to the excellent antibacterial and antiviral activity, silver nanoparticles have a widespread use in the food and pharmaceutical industries. With the increase in the production and use of the related products, the potential hazard of silver nanoparticles has aroused public attention. The main purpose of this study is to explore the toxicity of silver nanoparticles and induction of lung inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Here, we validated that small amounts of silver ions dissolved from silver nanoparticles caused the depolarization of plasma membrane, resulting in an overload of intracellular sodium and calcium, and eventually led to the cell necrosis. The blockers of calcium or sodium channels inversed the toxicity of silver ions. Then, we instilled silver nanoparticles or silver nitrate (50 μg per mouse) into the lungs of mice, and this induced pulmonary injury and mitochondrial content release, led to the recruitment of neutrophils to the lung tissue via p38 MAPK pathway. Altogether, these data show that released silver ions from nanoparticles induced cell necrosis through Na+ and Ca2+ influx and triggered pulmonary inflammation through elevating mitochondrial-related contents released from these necrotic cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarts M, Iihara K, Wei WL, Xiong ZG, Arundine M, Cerwinski W, et al. A key role for TRPM7 channels in anoxic neuronal death. Cell. 2003;115:863–77.
Ajdary M, Moosavi MA, Rahmati M, Falahati M, Mahboubi M, Mandegary A, et al. Health concerns of various nanoparticles: a review of their in vitro and in vivo toxicity. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018;8:E634.
Alshehri AH, Jakubowska M, Mlozniak A, Horaczek M, Rudka D, Free C, et al. Enhanced electrical conductivity of silver nanoparticles for high frequency electronic applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012;4:7007–10.
Azocar MI, Alarcon R, Castillo A, Blamey JM, Walter M, Paez M. Capping of silver nanoparticles by anti-inflammatory ligands: antibacterial activity and superoxide anion generation. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2019;193:100–8.
Barbasz A, Ocwieja M, Roman M. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles towards tumoral human cell lines U-937 and HL-60. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2017;156:397–404.
Bianchini A, Playle RC, Wood CM, Walsh PJ. Mechanism of acute silver toxicity in marine invertebrates. Aquat Toxicol. 2005;72:67–82.
Blaustein MP, Lederer WJ. Sodium/calcium exchange: its physiological implications. Physiol Rev. 1999;79:763–854.
Braakhuis HM, Giannakou C, Peijnenburg WJ, Vermeulen J, van Loveren H, Park MV. Simple in vitro models can predict pulmonary toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology. 2016;10:770–9.
Braakhuis HM, Gosens I, Krystek P, Boere JA, Cassee FR, Fokkens PH, et al. Particle size dependent deposition and pulmonary inflammation after short-term inhalation of silver nanoparticles. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2014;11:49.
Braun GB, Friman T, Pang HB, Pallaoro A, Hurtado de Mendoza T, Willmore AM, et al. Etchable plasmonic nanoparticle probes to image and quantify cellular internalization. Nat Mater. 2014;13:904–11.
Bundschuh DS, Uhlig S, Wendel A. Isolation of rat primary lung cells: characterization of an improved method. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 1996;48:512–4.
Cai Z, Jitkaew S, Zhao J, Chiang HC, Choksi S, Liu J, et al. Plasma membrane translocation of trimerized MLKL protein is required for TNF-induced necroptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16:55–65.
Chung KF, Seiffert J, Chen S, Theodorou IG, Goode AE, Leo BF, et al. Inactivation, clearance, and functional effects of lung-instilled short and long silver nanowires in rats. ACS Nano. 2017;11:2652–64.
Cordani M, Somoza A. Targeting autophagy using metallic nanoparticles: a promising strategy for cancer treatment. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76:1215–42.
Davidovich P, Kearney CJ, Martin SJ. Inflammatory outcomes of apoptosis, necrosis and necroptosis. Biol Chem. 2014;395:1163–71.
Decker T, Lohmann-Matthes ML. A quick and simple method for the quantitation of lactate dehydrogenase release in measurements of cellular cytotoxicity and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) activity. J Immunol Methods. 1988;115:61–9.
Du J, Tang J, Xu S, Ge J, Dong Y, Li H, et al. A review on silver nanoparticles-induced ecotoxicity and the underlying toxicity mechanisms. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2018;98:231–9.
Durán N, Durán M, De Jesus MB, Seabra AB, Fávaro WJ, Nakazato G. Silver nanoparticles: a new view on mechanistic aspects on antimicrobial activity. Nanomedicine. 2016;12:789–99.
Feldman N, Rotter-Maskowitz A, Okun E. DAMPs as mediators of sterile inflammation in aging-related pathologies. Ageing Res Rev. 2015;24:29–39.
Franci G, Falanga A, Galdiero S, Palomba L, Rai M, Morelli G, et al. Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Molecules. 2015;20:8856–74.
Giladi M, Tal I, Khananshvili D. Structural features of ion transport and allosteric regulation in sodium-calcium exchanger (NCX) proteins. Front Physiol. 2016;7:30.
Gliga AR, Skoglund S, Wallinder IO, Fadeel B, Karlsson HL. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human lung cells: the role of cellular uptake, agglomeration and Ag release. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2014;11:11.
Gomes T, Araujo O, Pereira R, Almeida AC, Cravo A, Bebianno MJ. Genotoxicity of copper oxide and silver nanoparticles in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar Environ Res. 2013;84:51–9.
Gong T, Liu L, Jiang W, Zhou R. DAMP-sensing receptors in sterile inflammation and inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;20:95–112.
Haberl N, Hirn S, Wenk A, Diendorf J, Epple M, Johnston BD, et al. Cytotoxic and proinflammatory effects of PVP-coated silver nanoparticles after intratracheal instillation in rats. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2013;4:933–40.
Hussain S, Meneghini E, Moosmayer M, Lacotte D, Anner B. Potent and reversible interaction of silver with pure Na, K-ATPase and Na, K-ATPase-liposomes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes. 1994;1190:402–8.
Jiang J, Li M, Yue L. Potentiation of TRPM7 inward currents by protons. J Gen Physiol. 2005;126:137–50.
Kaczmarek A, Vandenabeele P, Krysko DV. Necroptosis: the release of damage-associated molecular patterns and its physiological relevance. Immunity. 2013;38:209–23.
Kaewamatawong T, Banlunara W, Maneewattanapinyo P, Thammachareon C, Ekgasit S. Acute and subacute pulmonary toxicity caused by a single intratracheal instillation of colloidal silver nanoparticles in mice: pathobiological changes and metallothionein responses. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2014;33:59–68.
Kawata K, Osawa M, Okabe S. In vitro toxicity of silver nanoparticles at noncytotoxic doses to HepG2 human hepatoma cells. Environ Sci Technol. 2009;43:6046–51.
Kim S, Choi JE, Choi J, Chung KH, Park K, Yi J, et al. Oxidative stress-dependent toxicity of silver nanoparticles in human hepatoma cells. Toxicol in Vitro. 2009;23:1076–84.
Kittler S, Greulich C, Diendorf J, Koller M, Epple M. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles increases during storage because of slow dissolution under release of silver ions. Chem Mater. 2010;22:4548–54.
Kwok KW, Dong W, Marinakos SM, Liu J, Chilkoti A, Wiesner MR, et al. Silver nanoparticle toxicity is related to coating materials and disruption of sodium concentration regulation. Nanotoxicology. 2016;10:1306–17.
Liu X, Songu-Mize E. Effect of Na+ on Na+,K+-ATPase alpha-subunit expression and Na+−pump activity in aortic smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998;351:113–9.
Livraghi A, Grubb BR, Hudson EJ, Wilkinson KJ, Sheehan JK, Mall MA, et al. Airway and lung pathology due to mucosal surface dehydration in {beta}-epithelial Na+ channel-overexpressing mice: role of TNF-{alpha} and IL-4R{alpha} signaling, influence of neonatal development, and limited efficacy of glucocorticoid treatment. J Immunol. 2009;182:4357–67.
Mao BH, Tsai JC, Chen CW, Yan SJ, Wang YJ. Mechanisms of silver nanoparticle-induced toxicity and important role of autophagy. Nanotoxicology. 2016;10:1021–40.
McGillicuddy E, Murray I, Kavanagh S, Morrison L, Fogarty A, Cormican M, et al. Silver nanoparticles in the environment: sources, detection and ecotoxicology. Sci Total Environ. 2017;575:231–46.
Mello de Queiroz F, Ponte CG, Bonomo A, Vianna-Jorge R, Suarez-Kurtz G. Study of membrane potential in T lymphocytes subpopulations using flow cytometry. BMC Immunol. 2008;9:63.
Morris CE. Cytotoxic swelling of sick excitable cells - impaired ion homeostasis and membrane tension homeostasis in muscle and neuron. Curr Top Membr. 2018;81:457–96.
Pandolfi F, Altamura S, Frosali S, Conti P. Key role of DAMP in inflammation, cancer, and tissue repair. Clin Ther. 2016;38:1017–28.
Park MV, Neigh AM, Vermeulen JP, de la Fonteyne LJ, Verharen HW, Briede JJ, et al. The effect of particle size on the cytotoxicity, inflammation, developmental toxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2011;32:9810–7.
Pasparakis M, Vandenabeele P. Necroptosis and its role in inflammation. Nature. 2015;517:311–20.
Patel S. Danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs): the derivatives and triggers of inflammation. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018;18:63.
Saunders R, Scheiner-Bobis G. Ouabain stimulates endothelin release and expression in human endothelial cells without inhibiting the sodium pump. Eur J Biochem. 2004;271:1054–62.
Seiffert J, Buckley A, Leo B, Martin NG, Zhu J, Dai R, et al. Pulmonary effects of inhalation of spark-generated silver nanoparticles in Brown-Norway and Sprague-Dawley rats. Respir Res. 2016;17:85.
Seiffert J, Hussain F, Wiegman C, Li F, Bey L, Baker W, et al. Pulmonary toxicity of instilled silver nanoparticles: influence of size, coating and rat strain. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0119726.
Shim YM, Paige M, Hanna H, Kim SH, Burdick MD, Strieter RM. Role of LTB(4) in the pathogenesis of elastase-induced murine pulmonary emphysema. Am J Phys Lung Cell Mol Phys. 2010;299:L749–59.
Smith JN, Thomas DG, Jolley H, Kodali VK, Littke MH, Munusamy P, et al. All that is silver is not toxic: silver ion and particle kinetics reveals the role of silver ion aging and dosimetry on the toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2018;15:47.
Songu-Mize E, Liu X, Stones JE, Hymel LJ. Regulation of Na+,K+-ATPase alpha-subunit expression by mechanical strain in aortic smooth muscle cells. Hypertension. 1996;27:827–32.
Specht KG, Rodgers MA. Plasma membrane depolarization and calcium influx during cell injury by photodynamic action. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991;1070:60–8.
Sung JH, Ji JH, Park JD, Yoon JU, Kim DS, Jeon KS, et al. Subchronic inhalation toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Toxicol Sci. 2009;108:452–61.
Swamydas M, Luo Y, Dorf ME, Lionakis MS. Isolation of mouse neutrophils. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2015;110:3 20 21–23 20 15.
Takahashi S, Shibata M, Fukuuchi Y. Role of sodium ion influx in depolarization-induced neuronal cell death by high KCI or veratridine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999;372:297–304.
Tonnus W, Meyer C, Paliege A, Belavgeni A, von Massenhausen A, Bornstein SR, et al. The pathological features of regulated necrosis. J Pathol. 2019;247:697–707.
Unal-Cevik I, Kılınç M, Can A, Gürsoy-Özdemir Y, Dalkara T. Apoptotic and necrotic death mechanisms are concomitantly activated in the same cell after cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 2004;35:2189–94.
Venereau E, Ceriotti C, Bianchi ME. DAMPs from cell death to new life. Front Immunol. 2015;6:422.
Villeret B, Dieu A, Straube M, Solhonne B, Miklavc P, Hamadi S, et al. Silver nanoparticles impair retinoic acid-inducible gene I-mediated mitochondrial antiviral immunity by blocking the autophagic flux in lung epithelial cells. ACS Nano. 2018;12:1188–202.
Wang H, Joseph JA. Mechanisms of hydrogen peroxide-induced calcium dysregulation in PC12 cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 2000;28:1222–31.
Wang X, Ji Z, Chang CH, Zhang H, Wang M, Liao YP, et al. Use of coated silver nanoparticles to understand the relationship of particle dissolution and bioavailability to cell and lung toxicological potential. Small. 2014;10:385–98.
Wei X, Shao B, He Z, Ye T, Luo M, Sang Y, et al. Cationic nanocarriers induce cell necrosis through impairment of Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase and cause subsequent inflammatory response. Cell Res. 2015;25:237–53.
West AP, Shadel GS. Mitochondrial DNA in innate immune responses and inflammatory pathology. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017;17:363–75.
Williams KM, Gokulan K, Cerniglia CE, Khare S. Size and dose dependent effects of silver nanoparticle exposure on intestinal permeability in an in vitro model of the human gut epithelium. J Nanobiotechnol. 2016;14:62.
Yu SP. Na(+), K(+)-ATPase: the new face of an old player in pathogenesis and apoptotic/hybrid cell death. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;66:1601–9.
Zhang Q, Itagaki K, Hauser CJ. Mitochondrial DNA is released by shock and activates neutrophils via p38 map kinase. Shock. 2010a;34:55–9.
Zhang Q, Raoof M, Chen Y, Sumi Y, Sursal T, Junger W, et al. Circulating mitochondrial DAMPs cause inflammatory responses to injury. Nature. 2010b;464:104–7.
Zielinska E, Zauszkiewicz-Pawlak A, Wojcik M, Inkielewicz-Stepniak I. Silver nanoparticles of different sizes induce a mixed type of programmed cell death in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget. 2018;9:4675–97.
Zook JM, Long SE, Cleveland D, Geronimo CL, MacCuspie RI. Measuring silver nanoparticle dissolution in complex biological and environmental matrices using UV-visible absorbance. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011;401:1993–2002.
Zorova LD, Popkov VA, Plotnikov EY, Silachev DN, Pevzner IB, Jankauskas SS, et al. Mitochondrial membrane potential. Anal Biochem. 2018;552:50–9.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Major Scientific and Technological Special Project for “Significant New Drugs Development” (No. 2018ZX09733001), National Natural Science Foundation Regional Innovation and Development (U19A2003), the Excellent Youth Foundation of Sichuan Scientific Committe Grant in China (No.2019JDJQ008) and by the Development Program of China (No.2016YFA0201402).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Bi, Z., Hu, Y. et al. Silver nanoparticles and silver ions cause inflammatory response through induction of cell necrosis and the release of mitochondria in vivo and in vitro. Cell Biol Toxicol 37, 177–191 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-020-09526-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-020-09526-4