Abstract
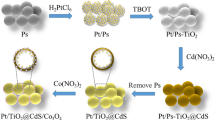
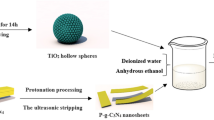
Efficient separation of photogenerated carriers and surface reactions is the crucial factor in achieving successful photocatalytic water splitting. Herein, a novel Pt@Co-T@T@M hollow sphere was prepared by a template-assisted method. Pt was anchored on the inner surface of Co-doped TiO2 shell, serving as electron collectors and active sites for reduction reaction, while MnOX was immobilized on the outer surface of TiO2 shell for oxidation reaction. Under simulated one-sun (AM 1.5G) illumination, the as-prepared Pt@Co-T@T@M hollow spheres exhibited a remarkable hydrogen evolution rate of 7.304 mmol g−1 h−1, which is 114 times higher than that of T@T hollow spheres. The exceptional photocatalytic water-splitting performance is attributed to the synergistic effect between homojunction and spatial dual-cocatalyst, which promotes enhanced spatial separation of photogenerated carriers and reduces recombination. This study highlights the importance of precise and rational control over photocatalyst structure for achieving highly efficient water splitting.
Graphical Abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao S, Piao L (2020) Considerations for a more accurate evaluation method for photocatalytic water splitting. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 59(42):18312–18320
Lin F, Boettcher SW (2014) Adaptive semiconductor/electrocatalyst junctions in water-splitting photoanodes. Nat Mater 13(1):81–86
Ng KH, Lai SY, Cheng CK, Cheng YW, Chong CC (2021) Photocatalytic water splitting for solving energy crisis: myth, fact or busted? Chem Eng J 417:128847
Singla S, Sharma S, Basu S, Shetti NP, Aminabhavi TM (2021) Photocatalytic water splitting hydrogen production via environmental benign carbon based nanomaterials. Int J Hydrogen Energy 46(68):33696–33717
Chen JS, Tan YL, Li CM et al (2010) Constructing hierarchical spheres from large ultrathin anatase TiO2 nanosheets with nearly 100% exposed (001) facets for fast reversible lithium storage. J Am Chem Soc 132(17):6124–6130
Ngaw CK, Xu Q, Tan TTY, Hu P, Cao S, Loo JSC (2014) A strategy for in-situ synthesis of well-defined core–shell Au@TiO2 hollow spheres for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Chem Eng J 257:112–121
Tran PD, Xi L, Batabyal SK, Wong LH, Barber J, Loo JS (2012) Enhancing the photocatalytic efficiency of TiO2 nanopowders for H2 production by using non-noble transition metal co-catalysts. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14(33):11596–11599
Khan H, Charles H, Lee CS (2023) Fabrication of noble-metal-free copper-doped TiO2 nanofibers synergized with acetic acid-treated g-C3N4 nanosheets for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Appl Surf Sci 607:155068
Kudo A, Miseki Y (2009) Heterogeneous photocatalyst materials for water splitting. Chem Soc Rev 38(1):253–278
Li X, Yu J, Low J, Fang Y, Xiao J, Chen X (2015) Engineering heterogeneous semiconductors for solar water splitting. J Mater Chem A 3(6):2485–2534
Hu J, Xie J, Jia W et al (2020) Interesting molecule adsorption strategy induced energy band tuning: boosts 43 times photocatalytic Water splitting ability for commercial TiO2. Appl Catal B 268:118753
Kotesh Kumar M, Naresh G, Vijay Kumar V, Sai Vasista B, Sasikumar B, Venugopal A (2021) Improved H2 yields over Cu-Ni-TiO2 under solar light irradiation: behaviour of alloy nano particles on photocatalytic H2O splitting. Appl Catal B 299:120654
Basavarajappa PS, Patil SB, Ganganagappa N, Reddy KR, Raghu AV, Reddy CV (2020) Recent progress in metal-doped TiO2, non-metal doped/codoped TiO2 and TiO2 nanostructured hybrids for enhanced photocatalysis. Int J Hydrogen Energy 45(13):7764–7778
Zhang K, Wang X, He T, Guo X, Feng Y (2014) Preparation and photocatalytic activity of B-N co-doped mesoporous TiO2. Powder Technol 253:608–613
Ge H, Xu F, Cheng B, Yu J, Ho W (2019) S-scheme heterojunction TiO2/CdS nanocomposite nanofiber as H2-production photocatalyst. ChemCatChem 11(24):6301–6309
Kulmas M, Paterson L, Höflich K et al (2016) Composite nanostructures of TiO2 and ZnO for water splitting application: atomic layer deposition growth and density functional theory investigation. Adv Funct Mater 26(27):4882–4889
Wang X-j, Yang W-y, Li F-t, Xue Y-b, Liu R-h, Hao Y-j (2013) in situ microwave-assisted synthesis of porous N-TiO2/g-C3N4 heterojunctions with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic properties. Ind Eng Chem Res 52(48):17140–17150
Yu X, Zhang J, Zhao Z et al (2015) NiO–TiO2 p–n heterostructured nanocables bridged by zero-bandgap rGO for highly efficient photocatalytic water splitting. Nano Energy 16:207–217
Khan H, Pawar RC, Charles H, Sunyong Lee C (2023) Cu-doped TiO2 nanofibers coated with 1T MoSe2 nanosheets providing a conductive pathway for the electron separation in CO2 photoreduction. Appl Surf Sci 636:157832
Ran J, Zhang J, Yu J, Jaroniec M, Qiao SZ (2014) Earth-abundant cocatalysts for semiconductor-based photocatalytic water splitting. Chem Soc Rev 43(22):7787–7812
Wang Z, Wu W, Xu Q et al (2017) Type-II hetero-junction dual shell hollow spheres loaded with spatially separated cocatalyst for enhancing visible light hydrogen evolution. Nano Energy 38:518–525
Zhang J, Yu Z, Gao Z et al (2017) Porous TiO2 nanotubes with spatially separated platinum and CoO(x) cocatalysts produced by atomic layer deposition for photocatalytic hydrogen production. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 56(3):816–820
Cao B, Li G, Li H (2016) Hollow spherical RuO2 @TiO2 @Pt bifunctional photocatalyst for coupled H2 production and pollutant degradation. Appl Catal B 194:42–49
Liu L, Zou W, Gu X et al (2013) Synthesis of Pt@TiO2@MnOx hollow spheres with high spatial charge separation efficiency for photocatalytic overall water splitting. J Mater Chem A. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta13872k
Han S, Pu Y-C, Zheng L, Zhang JZ, Fang X (2015) Shell-thickness dependent electron transfer and relaxation in type-II core–shell CdS/TiO2 structures with optimized photoelectrochemical performance. J Mater Chem A 3(45):22627–22635
Jiang Z, Wei W, Mao D et al (2015) Silver-loaded nitrogen-doped yolk-shell mesoporous TiO2 hollow microspheres with enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. Nanoscale 7(2):784–797
Qi J, Zhao K, Li G et al (2014) Multi-shelled CeO2 hollow microspheres as superior photocatalysts for water oxidation. Nanoscale 6(8):4072–4077
Xiao M, Wang Z, Lyu M et al (2019) Hollow nanostructures for photocatalysis: advantages and challenges. Adv Mater 31(38):e1801369
Zhang H, Du G, Lu W, Cheng L, Zhu X, Jiao Z (2012) Porous TiO2 hollow nanospheres: synthesis, characterization and enhanced photocatalytic properties. CrystEngComm 14(10):3793–3801
Zhang P, Lou XWD (2019) Design of heterostructured hollow photocatalysts for solar-to-chemical energy conversion. Adv Mater 31(29):e1900281
Wang S, Guan BY, Wang X, Lou XWD (2018) Formation of hierarchical Co9S8@ZnIn2S4 heterostructured cages as an efficient photocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. J Am Chem Soc 140(45):15145–15148
Zheng D, Cao XN, Wang X (2016) Precise formation of a hollow carbon nitride structure with a Janus surface to promote water splitting by photoredox catalysis. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 55(38):11512–11516
Sun X, Li Y (2004) Colloidal carbon spheres and their core/shell structures with noble-metal nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 43(5):597–601
Gao L, Li Y, Ren J et al (2017) Passivation of defect states in anatase TiO2 hollow spheres with Mg doping: realizing efficient photocatalytic overall water splitting. Appl Catal B 202:127–133
Song H, You S, Chen T, Jia X (2015) Controlled preparation of TiO2 hollow microspheres constructed by crosslinked nanochains with high photocatalytic activity. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 26(11):8442–8450
Luo Y, Sun G, Tian B, Zhang J (2022) Facet-heterojunction-based photothermocatalyst CdS-Au-{010}BiVO4{110}-MnOx with excellent synergetic effect for toluene degradation. Chem Eng J 442:135835
Song H, Li C, Lou Z, Ye Z, Zhu L (2017) Effective formation of oxygen vacancies in black TiO2 nanostructures with efficient solar-driven water splitting. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(10):8982–8987
Bai P, Tong X, Gao Y, Guo P (2019) Oxygen-free water-promoted selective photocatalytic oxidative coupling of amines. Catal Sci Technol 9(20):5803–5811
Wang Y, Cai J, Wu M et al (2016) Hydrogenated cagelike titania hollow spherical photocatalysts for hydrogen evolution under simulated solar light irradiation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(35):23006–23014
Jin J, Wang C, Ren X-N et al (2017) Anchoring ultrafine metallic and oxidized Pt nanoclusters on yolk-shell TiO2 for unprecedentedly high photocatalytic hydrogen production. Nano Energy 38:118–126
Sadanandam G, Lalitha K, Kumari VD, Shankar MV, Subrahmanyam M (2013) Cobalt doped TiO2: a stable and efficient photocatalyst for continuous hydrogen production from glycerol: water mixtures under solar light irradiation. Int J Hydrogen Energy 38(23):9655–9664
Li A, Wang T, Chang X et al (2016) Spatial separation of oxidation and reduction co-catalysts for efficient charge separation: Pt@TiO2@MnOx hollow spheres for photocatalytic reactions. Chem Sci 7(2):890–895
Suriya P, Prabhu M, Jagannathan K (2022) Synthesis and structural, optical and photovoltaic characteristics of pure and Ag doped TiO2 nanoparticles for dye sensitized solar cell application. Mater Today Proc 65:100–105
Hu L, Song H, Pan G et al (2007) Photoluminescence properties of samarium-doped TiO2 semiconductor nanocrystalline powders. J Lumin 127(2):371–376
Das K, Sharma SN, Kumar M, De SK (2009) Morphology dependent luminescence properties of Co doped TiO2 nanostructures. J Phys Chem C 113(33):14783–14792
Cruz-Manzo S, Chen R, Greenwood P (2015) An impedance model for analysis of EIS of polymer electrolyte fuel cells under hydrogen peroxide formation in the cathode. J Electroanal Chem 745:28–36
Shiohara M, Isobe T, Matsushita S, Nakajima A (2016) Decomposition of 2-naphthol in water by TiO2 modified with MnO and CeO. Mater Chem Phys 183:37–43
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21878254) and the Projects of Talents Recruitment of Guangdong University of Petrochemical Technology (2018rc49).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FC: conceived the presented idea, conceptualization, methodology, data curation, writing-reviewing, and editing; XH: conducted the experiments, characterizations, and writing-original draft preparation; PJ: conducted the experiments, and characterizations; CZ: conceived the presented idea, writing-reviewing and editing of the revised manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare there are no conflicts of interest related to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, F., Hou, X., Jiao, P. et al. TiO2-Based Double-Shelled Homojunction Hollow Spheres Decorated with Spatially Separated Cocatalyst for Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. Catal Lett (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-024-04611-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-024-04611-3