Abstract
In this work, ceria-based nanocatalysts mixed with copper and manganese were studied. All the catalysts were synthesized via the hydrothermal procedure. Four samples were prepared here denoted through the atomic ratios of the metals in the mixed oxide: Ce0.95Mn0.05, Ce0.95Cu0.05, Ce0.95Mn0.025Cu0.025 and CeO2. The samples were tested for the CO and soot oxidation reactions with different gas-phase oxygen concentrations (10, 1.0, 0.5 and 0.02 vol% O2). As a whole, the most promising catalysts for the CO oxidation reaction are the Ce0.95Cu0.05 and Ce0.95Mn0.025Cu0.025 samples. Indeed, the presence of Cu species in the solid enhances the surface redox mechanism for the CO oxidation. High vol% O2 values lead to competitive CO and O2 adsorption on the catalyst surface thus reducing the catalytic performances for binary and ternary oxides. On the other hand, the CO oxidation reaction over the CeO2 catalyst appears favored with 10 vol% O2. For the soot oxidation reaction, the most active catalyst (in terms of soot conversion %) is the CeO2 sample likely due to the unique feature of presenting well-defined and highly reactive nanocubic structures. Moreover, the presence of 10 vol% O2 in the mixture appears to be the best condition to oxidize the soot particles.
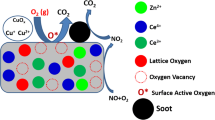
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jost K (2002) Spark ignition engine trends. Automotive Engineering
Nagai K, Seko T (2000) Trends of motor fuel quality in Japan. JSAE Rev 21:457–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0389-4304(00)00070-9
Sakaguchi T (2000) Influence of diffusion of fuel-efficient motor vehicles on gasoline demand for individual user owned passenger cars. Energy Policy 28:895–903. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4215(00)00071-9
Batmaz I, Balc M, Salman S, Erdiller B (1997) Experimental analysis of fuel economy and exhaust emissions at petrol engine vehicles. In: First Automotive Technology Congress with International Participation. Adana, Turkey, pp 95–103
Korkmaz I (1996) A study on the performance and emission characteristics of gasoline and methanol fuelled spark-ignition engines. Istanbul Technical University, Turkey
Bayraktar H (1997) Theoretical investigation of the effect of gasoline-ethanol blends on spark-ignition engine combustion and cycles. Karadeniz Technical University, Turkey
Heywood JB (1988) Internal combustion engine fundamentals. Mcgraw-hill, New York
Mogi K (1998) Analysis and avoidance of pre-ignition in S.I. gasoline engines. JSAE Rev 19:9–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0389-4304(97)00045-3
Lox ESJ, Engler BH, Frennet A, Bastin JM (1999) Environmental catalysis–mobile sources. In: Ertl G, Knozinger H, Weitkamp J (eds) Environmental catalysis, Wiley, Weinheim, pp 1–117
Moldovan M, Palacios MA, Gómez MM et al (2002) Environmental risk of particulate and soluble platinum group elements released from gasoline and diesel engine catalytic converters. Sci Total Environ 296:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00087-6
Neeft JPA, Van Pruissen OP, Makkee M, Moulijn JA (1997) Catalysts for the oxidation of soot from diesel exhaust gases. II. Contact between soot and catalyst under practical conditions. Appl Catal B Environ 12:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-3373(96)00060-4
Govinda Rao B, Jampaiah D, Venkataswamy P, Reddy BM (2016) Enhanced catalytic performance of manganese and cobalt Co-doped CeO2 catalysts for diesel soot oxidation. Chem Sel 1:6681–6691. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201601297
Sudarsanam P, Hillary B, Mallesham B et al (2016) Designing CuOx nanoparticle-decorated CeO2 nanocubes for catalytic soot oxidation: role of the nanointerface in the catalytic performance of heterostructured nanomaterials. Langmuir 32:2208–2215. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b04590
Piumetti M, Bensaid S, Russo N, Fino D (2015) Nanostructured ceria-based catalysts for soot combustion: investigations on the surface sensitivity. Appl Catal B Environ 165:742–751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.10.062
Fino D, Bensaid S, Piumetti M, Russo N (2016) A review on the catalytic combustion of soot in diesel particulate filters for automotive applications: from powder catalysts to structured reactors. Appl Catal A Gen 509:75–96
Andana T, Piumetti M, Bensaid S et al (2016) CO and soot oxidation over Ce–Zr–Pr oxide catalysts. Nanoscale Res Lett 11:278. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1494-6
Neeft J, Makkee M, Moulijn J (1996) Catalysts for the oxidation of soot from diesel exhaust gases. I. An exploratory study. Appl Catal B Environ 8:57. https://doi.org/10.1016/0926-3373(95)00057-7
Pérez VR, Bueno-López A (2015) Catalytic regeneration of diesel particulate filters: comparison of Pt and CePr active phases. Chem Eng J 279:79–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.05.004
Piumetti M, Andana T, Bensaid S et al (2017) Ceria-based nanomaterials as catalysts for CO oxidation and soot combustion: effect of Zr-Pr doping and structural properties on the catalytic activity. AIChE J 63:216–225. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.15548
Piumetti M, Bensaid S, Fino D, Russo N (2015) Catalysis in diesel engine NO x aftertreatment: a review. Catal Struct React 1:155–173. https://doi.org/10.1080/2055074X.2015.1105615
Andana T, Piumetti M, Bensaid S et al (2017) Ceria-supported small Pt and Pt3Sn nanoparticles for NOx-assisted soot oxidation. Appl Catal B Environ 209:295–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.03.010
Setiabudi A, Chen J, Mul G et al (2004) CeO2 catalysed soot oxidation: the role of active oxygen to accelerate the oxidation conversion. Appl Catal B Environ 51:9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APCATB.2004.01.005
Arena F, Di Chio R, Fazio B et al (2017) Probing the functionality of nanostructured MnCeOx catalysts in the carbon monoxide oxidation: part I. Influence of cerium addition on structure and CO oxidation activity. Appl Catal B Environ 210:14–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.03.049
Bueno-López A (2014) Diesel soot combustion ceria catalysts. Appl Catal B Environ 146:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.02.033
Aneggi E, Wiater D, De Leitenburg C et al (2014) Shape-dependent activity of ceria in soot combustion. ACS Catal 4:172–181. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs400850r
Aneggi E, Llorca J, Boaro M, Trovarelli A (2005) Surface-structure sensitivity of CO oxidation over polycrystalline ceria powders. J Catal 234:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2005.06.008
Trovarelli A (1996) Catalytic properties of ceria and CeO2-containing materials. Catal Rev 38:439–520. https://doi.org/10.1080/01614949608006464
Di Sarli V, Landi G, Lisi L, Di Benedetto A (2017) Ceria-coated diesel particulate filters for continuous regeneration. AIChE J 63:3442–3449. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.15688
Gupta A, Waghmare UV, Hegde MS (2010) Correlation of oxygen storage capacity and structural distortion in transition-metal-, noble-metal-, and rare-earth-ion-substituted CeO2 from first principles calculation. Chem Mater 22:5184–5198. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm101145d
Doornkamp C, Ponec V (2000) The universal character of the Mars and Van Krevelen mechanism. J Mol Catal A Chem 162:19–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1381-1169(00)00319-8
Piumetti M, Bensaid S, Andana T et al (2017) Nanostructured ceria-based materials: effect of the hydrothermal synthesis conditions on the structural properties and catalytic activity. Catalysts 7:174. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7060174
Mai HX, Sun LD, Zhang YW et al (2005) Shape-selective synthesis and oxygen storage behavior of ceria nanopolyhedra, nanorods, and nanocubes. J Phys Chem B 109:24380–24385. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp055584b
Yang Z, Zhou K, Liu X et al (2007) Single-crystalline ceria nanocubes: size-controlled synthesis, characterization and redox property. Nanotechnology 18:185606. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/18/18/185606
Dosa M, Piumetti M, Bensaid S et al (2017) Novel Mn–Cu-containing CeO2 nanopolyhedra for the oxidation of CO and diesel soot: effect of dopants on the nanostructure and catalytic activity. Catal Lett 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-017-2226-y
Venkataswamy P, Jampaiah D, Mukherjee D et al (2016) Mn-doped ceria solid solutions for CO oxidation at lower temperatures. Catal Lett 146:2105–2118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-016-1811-9
Andana T, Piumetti M, Bensaid S et al (2016) Nanostructured ceria-praseodymia catalysts for diesel soot combustion. Appl Catal B Environ 197:125–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.12.030
Piumetti M, Andana T, Bensaid S et al (2016) Study on the CO oxidation over ceria-based nanocatalysts. Nanoscale Res Lett 11:165. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1375-z
Jansson J (2000) Low-temperature CO oxidation over Co3O4/Al2O3. J Catal 194:55–60. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcat.2000.2924
Royer S, Duprez D (2011) Catalytic oxidation of carbon monoxide over transition metal oxides. ChemCatChem 3:24–65. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201000378
Freund HJ, Meijer G, Scheffler M et al (2011) CO oxidation as a prototypical reaction for heterogeneous processes. Angew Chemie—Int Ed 50:10064–10094
Engel T, Ertl G (1978) A molecular beam investigation of the catalytic oxidation of CO on Pd(111). J Chem Phys 69:1267. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.436666
Akhter S, White JM (1986) The effect of oxygen islanding on Co and H2 oxidation on Pt(111). Surf Sci 171:527–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-6028(86)91058-7
Libuda J, Meusel I, Hoffmann J et al (2001) The CO oxidation kinetics on supported Pd model catalysts: a molecular beam/in situ time-resolved infrared reflection absorption spectroscopy study. J Chem Phys 114:4669–4684. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1342240
Conner WC, Falconer JL (2002) Spillover in heterogeneous catalysis spillover in heterogeneous catalysis. Society 95:759–788. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00035a014
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dosa, M., Piumetti, M., Bensaid, S. et al. Novel Mn–Cu-Containing CeO2 Nanopolyhedra for the Oxidation of CO and Diesel Soot (Part II): Effect of Oxygen Concentration on the Catalytic Activity. Catal Lett 149, 107–118 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-018-2591-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-018-2591-1