Abstract
Purpose
Coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) has, to date, been diagnosed in over 130 million persons worldwide and is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Several variants of concern have emerged including those in the United Kingdom, South Africa, and Brazil. SARS-CoV-2 can cause a dysregulated inflammatory response known as a cytokine storm, which can progress rapidly to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), multi-organ failure, and death. Suppressing these cytokine elevations may be key to improving outcomes. Remote ischemic conditioning (RIC) is a simple, non-invasive procedure whereby a blood pressure cuff is inflated and deflated on the upper arm for several cycles. “RIC in COVID-19” is a pilot, multi-center, randomized clinical trial, designed to ascertain whether RIC suppresses inflammatory cytokine production.
Methods
A minimum of 55 adult patients with diagnosed COVID-19, but not of critical status, will be enrolled from centers in the United Kingdom, Brazil, and South Africa. RIC will be administered daily for up to 15 days. The primary outcome is the level of inflammatory cytokines that are involved in the cytokine storm that can occur following SARS-CoV-2 infection. The secondary endpoint is the time between admission and until intensive care admission or death. The in vitro cytotoxicity of patient blood will also be assessed using primary human cardiac endothelial cells.
Conclusions
The results of this pilot study will provide initial evidence on the ability of RIC to suppress the production of inflammatory cytokines in the setting of COVID-19.
Trial Registration
NCT04699227, registered January 7th, 2021.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) emerged in late 2019 and has since been diagnosed in well-over 100 million persons worldwide and resulted in over 3 million deaths. It is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The case fatality varies fairly widely from < 0.1 to > 20% according to country but averages ~ 4% worldwide [1]. The disparity may be partly explained by variants of SARS-CoV-2 that have arisen in certain countries, including the (20I/501Y.V1) variant in the United Kingdom, which increases viral transmissibility [2], and the South African (20H/501Y.V2) and Brazilian (20 J/501Y.V3) variants harboring the E484K mutation, which appears to confer heightened resistance to antibody neutralization [3].
Inflammatory Response and ARDS
SARS-CoV-2 infection can cause a dysregulated inflammatory response known as a cytokine storm, which can progress rapidly to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), multi-organ failure, and death [4]. Suppressing these cytokine elevations may therefore be key to improving outcomes.
SARS-CoV-2 can cause marked cardiac injury. An elevated plasma level of troponin (cTn) is seen in 20–30% of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 and is associated with greater disease severity and worse outcome [5]. However, despite some evidence that it is possible for SARS-CoV-2 to infect cardiomyocytes [6], fulminant myocarditis is relatively rare in COVID-19. On the other hand, the presence of ARDS is associated with greater cardiac injury [5], which suggests that excess levels of cytokines may be causally involved in the cardiac injury. It is not well understood whether high levels of inflammatory cytokines are markers, mediators, or both, of COVID-19 severity and if these pathways account for cardiovascular impairment [7]. This knowledge may be relevant to the prevention of cardiovascular pathophysiology in SARS-CoV-2 infection.
In addition to cardiac effects, the vasculature is also affected in COVID-19, both directly by the SARS-CoV-2 virus and indirectly as a result of a systemic inflammatory cytokine storm [8]. A hyperinflammatory and pro-coagulatory state is characteristic of COVID-19, which suggests that there is a critical role for the endothelium, both as an effector contributing to inflammation and thrombosis and as a target organ, whose dysfunction may contribute to poor outcome [8]. Therefore, measurements of endothelial dysfunction could be useful in the risk stratification of COVID-19 patients [8].
Developing new methods to reduce the heightened inflammatory response is essential to halting progression of COVID-19 in patients and reducing the severity of damage [4]. Tocilizumab and other IL-6-neutralizing agents can be useful in interrupting the cytokine storm. However, their benefit in hospitalized COVID-19 patients is often modest [9]. Alternative approaches are therefore required that can suppress the cytokine response more broadly.
Remote Ischemic Conditioning
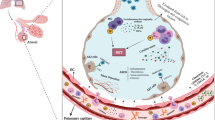
Remote ischemic conditioning (RIC) is a simple, non-invasive procedure in which a blood pressure cuff is applied to the upper arm for repeated cycles of inflation and deflation (typically 3–5 cycles of 5 min each) [10, 11]. This process activates pro-survival mechanisms in the body to protect vital organs and improve the immune system [11,12,13,14]. Therefore, we believe it represents a promising strategy to protect organs against reduced blood flow and heightened immune response, as seen in patients with COVID-19 infections [13]. Several studies suggest that RIC can suppress cytokine induction in the setting of cardiac surgery or sepsis [12, 13, 15, 16].
The above observations that cytokine storm contributes to COVID-19 morbidity and mortality and that RIC can suppress the inflammatory response led us to propose that RIC could provide benefit in patients with COVID-19 [4, 13]. The rationale of this study is thus that RIC will supress cytokine induction in patients with COVID-19, leading to less cytokine-induced cardiac injury.
Study Hypothesis
We propose to test the hypothesis that RIC, via repeated cycles of inflation and deflation of a peripheral arm blood pressure cuff, administered daily, reduces inflammation in COVID-19 patients.
Study Objectives
The “RIC in COVID-19” study will be a proof-of-concept study to investigate the effect of RIC in COVID-19 patients. The study objective is to determine whether RIC reduces the level of inflammatory cytokines in non-critically ill patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19. Primary and secondary outcome measures are detailed in the “Study Endpoints” section.
Methods
Study Design
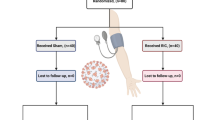
“RIC in COVID-19” is a pilot, multi-center, randomized study designed to ascertain whether RIC decreases the severity of inflammatory markers associated with a “cytokine storm” score.
The study has been reviewed and approved with a favorable opinion from the United Kingdom National Research Ethics Service (NRES) (South Central – Berkshire Research Ethics Committee reference: 20/SC/0192). The study protocol is registered on the public trials database clinicaltrials.gov NCT04699227. This study has also received approval by the Ethics Committee of the State University of Campinas (CAAE: 33,709,320.4.0000.5404) and by the Human Research Ethics Committee, University of Cape Town, South Africa (HREC 407/2020).
Study Population
A minimum of 55 non-critical adult patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 will be consecutively enrolled into the study. The patients will be identified as those admitted to either The Royal Free (London UK), The Lister Hospital (Stevenage, UK), Hospital Estadual Sumaré (Sumaré, Brazil), or Groote Schuur Hospital (Cape Town, South Africa). After enrolment, patients will be randomized (n = 30 per group) in a 1:1 fashion to receive either RIC or sham-control intervention.
Patients will be included according to the following criteria:
-
Adult patients (≥ 18 to 80 years of age) with a diagnosis of COVID-19 infection, confirmed by positive PCR reaction.
-
Clinical features of respiratory distress, i.e., with respiratory rate > 30 bpm or use of accessory muscles; or
-
Peripheral oxygen saturation SaO2 < 95% or requiring oxygen supplementation, or
-
Clinically unwell with reduced mobility, raised temperature/heart rate, and/or deranged biochemical laboratory results.
Patients will be excluded on the basis of any of the following exclusion criteria:
-
Contraindication for the use of a brachial cuff on either arm;
-
Intercurrent disease with an expected life expectancy of less than 24 h;
-
Cardiac arrest;
-
Pregnant or breastfeeding women;
-
Bleeding disorder or platelet count below 50;
-
Currently enrolled in another research study;
-
End-stage renal disease requiring renal replacement therapy;
-
Chronic liver disease and/or ALT and AST ≥ 5 times the normal upper reference limit;
-
Significant immunodeficiency states: AIDS/HIV not on antiretroviral agents, solid organ transplants, bone marrow transplants, chronic use of immunomodulating therapy such as anti-TNF-α or corticosteroids with prednisone-equivalent dose ≥ 20 mg/day prior to COVID diagnosis;
-
Any active underlying malignancy;
-
Baseline stage C chronic heart failure or symptomatic chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
-
Critical illness requiring invasive ventilation, including patients with:
-
- Hemodynamic instability or
-
- Signs of severe hypoxemic respiratory failure despite non-invasive ventilation as defined by the following:
-
Respiratory rate > 40 breaths per minute, and
-
Pulse oximetry (SpO2) less than 90%, or
-
Arterial blood sample with PaO2 < 8.0 kPa, or
-
Heart rate > 120 beats per minute
-
-
Trial Intervention
The RIC protocol will consist of 3–4 cycles of cuff inflations to at least 20 mmHg above systolic blood pressure for 5 min with deflation to 0 mmHg for a further 5 min, which will be automatically administered by the pre-programmed CellAegis (Canada), or Segall (Denmark) autoRIC pneumatic device.
Patients randomized to the sham-control group will have 3–4 cycles of automated low-pressure cuff inflation to 20 mmHg for 5 min and deflation to 0 mmHg for a further 5 min, by a visually identical pneumatic device as used in the RIC protocol. Trial intervention will be performed daily up to 15 days or until either patient discharge or deterioration requiring critical care. The trial intervention will not delay or affect the patient’s clinical management in accordance with local center policies.
Randomization and Blinding
After enrolment, patients will be randomized 1:1 to receive either RIC or sham-control intervention. The research team who will perform the trial intervention will be unblinded as they will need to be informed of which protocol to administer to the patient. All subsequent analysis will be performed blinded to treatment.
Study Endpoints
The primary outcome is the level of inflammatory cytokines that are involved in the cytokine storm that can occur following SARS-CoV-2 infection. Venous blood will be collected following RIC administration (on the day of admission and every other day subsequently, when possible) and saved for the subsequent measurement of inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP), TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and D-dimer, in addition to cardiac biomarkers troponin T and NTpro-BNP.
Secondary endpoints include the following: [i] time to clinical deterioration (defined as time from randomization to mortality or worsening of the World Health Organization (WHO) Clinical Progression Scale — assessed by the increase of 2 points in this scale), [ii] serum IL-6 ≥ 80 pg/mL as a biomarker of severe clinical outcomes in COVID-19 infection, and [iii] cytokine storm score measured by area under the curve (AUC) serum TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and CRP. The effect of plasma from COVID-19 patients on cardiac endothelial cells will also be evaluated as a secondary endpoint by measuring the survival of primary cardiac endothelial cells incubated with patient plasma [17].
Sample Size Calculations
Since there are no data available on the effect of RIC on the inflammatory response in COVID-19 patients and the objective of this pilot study is not to provide a formal assessment of efficacy, the sample size was established empirically in 55 individuals in a conservative expectation of a small standardized effect size (0.2).
Statistical Analysis
Summary statistics will be provided by treatment group for demographic and baseline characteristics, which will be compared among treatment groups for the ITT population. Between-group differences in demographic and baseline characteristic will be tested using a chi-square test (for categorical variables) or a 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) model with treatment as a factor (for continuous variables). The significance of these tests will be used as an initial assessment for satisfactoriness of randomization. For continuous variables, changes from baseline to subsequent days of follow up will be considered outcomes. These outcomes will be compared according to the treatment groups adjusted to the baseline values using covariance analysis models (ANCOVA) or by rank analysis of covariance (RANCOVA) according to their distribution. The normality distribution will be investigated using normality tests such as histograms, kurtosis, asymmetry, Kolmogorov–Smirnov, and Shapiro–Wilk in order to select the appropriate tests to compare the data.
Data Management, Governance, and Funding
The trial is funded by the Thomson Family Charitable Trust and the Hatter Cardiovascular Institute and sponsored by University College London and by the Fundação de Apoio a Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP). Data will be collected on a case report form (CRF) and managed using REDCap electronic data capture tools. REDCap [18] is a secure, web-based application designed to support validated and audited data capture for research studies. An independent data monitoring committee will be convened to monitor the progress and safety of the study.
Discussion
While the immune response is clearly essential in the host response to infection, an extreme immune response leading to a cytokine storm can cause collateral damage to the host, that is greater than the immediate benefit of the immune response [19]. Monocytes and macrophages are particularly enriched in the lungs of COVID-19 patients and appear to be important in the pathogenicity of the disease. SARS-CoV-2 infection alters monocyte metabolism leading to inhibition of the T-cell response and reduction of epithelial cell survival [20].
There is no single cytokine that can provide a specific indication of a cytokine storm, and the precise response can vary depending on the infective agent. The first-line host defense to viral infections such as SARS-CoV-2 is provided by the innate immune system. This produces type I interferon, proinflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-6 and TNF-α), and chemokines. Stimulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome further activates caspase-1, which cleaves pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 into active proinflammatory cytokines. These can activate NF-κB to augment IL-6 and TNF-α expression. Thus, interferon-γ, interleukin-1, interleukin-6, TNF-α, and interleukin-18 are key cytokines that are often found to be elevated in cytokine storm situations and are believed to have central immunopathologic roles [19]. Both IL-1 and IL-6 are critical in regulating CRP levels, which has been found to be prognostic with regard poor outcome in patients with COVID-19 [21]. In terms of the response to SARS-CoV-2 infection, an in-depth transcriptomic analysis revealed an imbalanced inflammatory response defined by low levels of type I and III interferons with elevated chemokines and high expression of IL-6 [22]. This would suggest that controlling inflammation is more important than targeting the IFN response in treatments for COVID-19.
The primary aim of this study is to investigate the effect of RIC on cytokine production and inflammatory responses in COVID-19. Several animal studies have shown that RIC suppresses cytokine induction via downregulation of NF-κB, a central transcription factor mediating proinflammatory gene induction in both innate and adaptive immune cells, and myeloperoxidase (MPO) pathways (reviewed in [13]). Two of the largest clinical trials to measure cytokines in patients who had been administered RIC (with n = 65, n = 90 participants) demonstrated cytokine attenuation in the treatment group undergoing RIC prior to off-pump CABG and colorectal surgery, respectively. In the latter study, levels of IL-1β and TNF-α were significantly reduced [13].
A cytokine storm-like response with excessive cytokine release can also occur in other setting such as sepsis [19]. Acute and chronic (repeated daily) RIC has been shown to provide benefit following LPS-induced sepsis in animal models [12, 15]. In these studies, RIC reduced the levels the proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, as well as suppressing the sepsis-induced increase in plasma cardiac troponin I [12, 15]. Furthermore, mortality was significantly reduced following chronic RIC administration as opposed to acute RIC administration [12, 15]. RIC has also been seen to improve survival in sheep with sepsis [16]. RIC has not been extensively evaluated in patients with sepsis, but a small clinical trial saw an improvement in microcirculatory flow in septic patients administered RIC [23].
Measurements of endothelial dysfunction could be useful in the risk stratification of COVID-19 patients [8]. Plasma from critically ill COVID-19 patients causes rapid and direct cytotoxicity in an in vitro assay using human primary pulmonary endothelial cells [17]. Endotheliopathy is a central part of the pathological response to severe COVID-19 and may contribute to cardiac injury [24]. In the “RIC in COVID-19” study, the effect of plasma from COVID-19 patients will also be evaluated on primary cardiac endothelial cells incubated with patient plasma with the aim of determining whether the endothelium may be directly affected in COVID-19.
In conclusion, this pilot study will allow us to ascertain whether RIC has a part to play in reducing the overall markers of inflammation and secondary outcomes.
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
Change history
07 July 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-021-07223-w
Abbreviations
- ARDS:
-
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
- COVID-19:
-
Coronavirus 2019
- CRF:
-
Case report form
- cTn:
-
Troponin
- RIC:
-
Remote ischemic conditioning
- SARS-CoV-2:
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
References
Sorci G, Faivre B, Morand S. Explaining among-country variation in COVID-19 case fatality rate. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):18909. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-75848-2.
Leung K, Shum MH, Leung GM, Lam TT, Wu JT. Early transmissibility assessment of the N501Y mutant strains of SARS-CoV-2 in the United Kingdom, October to November 2020. Euro Surveill. 2021;26(1). https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.26.1.2002106.
Greaney AJ, Loes AN, Crawford KHD, Starr TN, Malone KD, Chu HY, et al. Comprehensive mapping of mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain that affect recognition by polyclonal human plasma antibodies. Cell Host Microbe. 2021;29(3):463-76.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2021.02.003.
Pearce L, Davidson SM, Yellon DM. The cytokine storm of COVID-19: a spotlight on prevention and protection. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020;24(8):723–30. https://doi.org/10.1080/14728222.2020.1783243.
Shi S, Qin M, Shen B, Cai Y, Liu T, Yang F, et al. Association of cardiac injury with mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan. China JAMA Cardiol. 2020;5(7):802–10. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamacardio.2020.0950.
Bojkova D, Wagner JUG, Shumliakivska M, Aslan GS, Saleem U, Hansen A, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infects and induces cytotoxic effects in human cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Res. 2020;116(14):2207–15. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvaa267.
Chung MK, Zidar DA, Bristow MR, Cameron SJ, Chan T, Harding CV 3rd, et al. COVID-19 and cardiovascular disease: from bench to bedside. Circ Res. 2021;128(8):1214–36. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.317997.
Evans PC, Rainger GE, Mason JC, Guzik TJ, Osto E, Stamataki Z, et al. Endothelial dysfunction in COVID-19: a position paper of the ESC Working Group for Atherosclerosis and Vascular Biology, and the ESC Council of Basic Cardiovascular Science. Cardiovasc Res. 2020;116(14):2177–84. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvaa230.
Salama C, Han J, Yau L, Reiss WG, Kramer B, Neidhart JD, et al. Tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with Covid-19 pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(1):20–30. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2030340.
Pickard JM, Botker HE, Crimi G, Davidson B, Davidson SM, Dutka D, et al. Remote ischemic conditioning: from experimental observation to clinical application: report from the 8th Biennial Hatter Cardiovascular Institute Workshop. Basic Res Cardiol. 2015;110(1):453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-014-0453-6.
Heusch G, Botker HE, Przyklenk K, Redington A, Yellon D. Remote ischemic conditioning. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65(2):177–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2014.10.031.
Honda T, He Q, Wang F, Redington AN. Acute and chronic remote ischemic conditioning attenuate septic cardiomyopathy, improve cardiac output, protect systemic organs, and improve mortality in a lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis model. Basic Res Cardiol. 2019;114(3):15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-019-0724-3.
Pearce L, Davidson SM, Yellon DM. Does remote ischaemic conditioning reduce inflammation? A focus on innate immunity and cytokine response. Basic Res Cardiol. 2021;116(1):12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-021-00852-0.
Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM. The therapeutic potential of ischemic conditioning: an update. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2011;8(11):619–29. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2011.85.
Joseph B, Khalil M, Hashmi A, Hecker L, Kulvatunyou N, Tang A, et al. Survival benefits of remote ischemic conditioning in sepsis. J Surg Res. 2017;213:131–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2016.01.033.
Orbegozo Cortes D, Su F, Santacruz C, Hosokawa K, Donadello K, Creteur J, et al. Ischemic conditioning protects the microcirculation, preserves organ function, and prolongs survival in sepsis. Shock. 2016;45(4):419–27. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000000526.
Rauch A, Dupont A, Goutay J, Caplan M, Staessens S, Moussa M, et al. Endotheliopathy is induced by plasma from critically ill patients and associated with organ failure in severe COVID-19. Circulation. 2020;142(19):1881–4. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.050907.
Harris PA, Taylor R, Thielke R, Payne J, Gonzalez N, Conde JG. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform. 2009;42(2):377–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2008.08.010.
Fajgenbaum DC, June CH. Cytokine storm. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(23):2255–73. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra2026131.
Codo AC, Davanzo GG, Monteiro LB, de Souza GF, Muraro SP, Virgilio-da-Silva JV, et al. Elevated glucose levels favor SARS-CoV-2 infection and monocyte response through a HIF-1alpha/glycolysis-dependent axis. Cell Metab. 2020;32(3):437-46.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2020.07.007.
Smilowitz NR, Kunichoff D, Garshick M, Shah B, Pillinger M, Hochman JS, et al. C-reactive protein and clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19. Eur Heart J. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa1103.
Blanco-Melo D, Nilsson-Payant BE, Liu WC, Uhl S, Hoagland D, Moller R, et al. Imbalanced host response to SARS-CoV-2 drives development of COVID-19. Cell. 2020;181(5):1036-45.e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.026.
Kiudulaite I, Belousoviene E, Vitkauskiene A, Pranskunas A. Effects of remote ischemic conditioning on microcirculatory alterations in patients with sepsis: a single-arm clinical trial. Ann Intensive Care. 2021;11(1):55. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13613-021-00848-y.
Gladka MM, Maack C. The endothelium as Achilles’ heel in COVID-19 patients. Cardiovasc Res. 2020;116(14):e195–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvaa327.
Funding
Funding for this study was provided by grants from the Thompson Family Trust, The Hatter Cardiovascular Institute, Mancherje-Potash Foundation, and the Fundação de Apoio a Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Derek Yellon conceived the study. Derek Yellon and Andrei Sposito designed the study. Sean Davidson and Derek Yellon drafted the paper. All authors provide comments on the draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The study was approved by South Central – Berkshire Research Ethics Committee reference: 20/SC/0192; State University of Campinas: CAAE: 33709320.4.0000.5404, and Human Research Ethics Committee, University of Cape Town: HREC407/2020 and was performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Consent forms will be approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) and participants will have the opportunity to carefully review the written consent form, discuss the study with their family or substitutes, and ask questions of the investigator before signing it. Participants will be informed that participation is voluntary and that they can withdraw from the study at any time, without prejudice. The informed consent process will be conducted and documented in the source document (including the date), and the signed form, before the participant is subjected to any specific study procedures. One version of this document will be kept at the research centers and another will be given to the participants for their records. Participants’ rights and well-being will be protected by emphasizing that the quality of their medical care will not be adversely affected if they refuse to participate in this study.
Consent for Publication
This study will comply with the Data Sharing Policy and as such, this trial was registered with ClinicalTrials.gov. In addition, all attempts will be made to publish the results in peer-reviewed journals. The Steering Committee is responsible for reporting and publishing the results of the study. The results of the study will be submitted for publication regardless of whether the study outcomes are achieved.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
See “Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate.”
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Sean M. Davidson and Kishal Lukhna are joint first authors.
Mpiko Ntsekhe, Andrei C. Sposito, and Derek M. Yellon are joint senior authors.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Davidson, S.M., Lukhna, K., Gorog, D.A. et al. RIC in COVID-19—a Clinical Trial to Investigate Whether Remote Ischemic Conditioning (RIC) Can Prevent Deterioration to Critical Care in Patients with COVID-19. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 36, 925–930 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-021-07221-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-021-07221-y