Abstract
Introduction
The purpose of this study was to determine whether prolonged oral therapy with sitaxsentan, a potent selective ETA endothelin receptor antagonist, normalizes systolic blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive hamsters, a new rodent model of high-renin genetic hypertension.
Materials and Methods
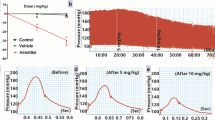
Spontaneously hypertensive hamsters received either oral sitaxsentan (15 mg kg−1 day−1) dissolved in high purity water or saline for 7 weeks. Systolic blood pressure was monitored in lightly anesthetized animals using the leg-cuff method.
Results
We found that sitaxsentan elicited a significant decrease in systolic blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive hamsters from 175 ± 6 mmHg at baseline to 109 ± 7 mmHg after 7 weeks (p < 0.05). Although treatment of spontaneously hypertensive hamsters with saline was also associated with a significant decrease in systolic blood pressure from baseline, the magnitude of response was significantly less than that observed with sitaxsentan (p < 0.05).
Discussion
Collectively, these proof-of-principle data indicate that prolonged oral sitaxsentan therapy normalizes systolic blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive hamsters. We suggest that selective ETA endothelin receptor blockade could be beneficial in the treatment of essential hypertension associated with high renin plasma levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, et al. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA 2003;289:2560–72.
Spranger CB, Ries AJ, Berge CA, Radford NB, Victor RG. Identifying gaps between guidelines and clinical practice in the evaluation and treatment of patients with hypertension. Am J Med 2004;117:14–8.
Wang Y, Wang QJ. The prevalence of prehypertension and hypertension among US adults according to the new joint national committee guidelines: new challenges of the old problem. Arch Intern Med 2004;164:2126–34.
Falkner B. Differences in blacks and whites with essential hypertension: biochemistry and endocrine. Hypertension 1990;15:681–6.
Lindpaintner K, Kreutz R, Ganten D. Genetic variation in hypertensive and ‘control’ strains: what are we controlling for anyway? Hypertension 1992;19:428–30.
Weir MR. Population characteristics and the modulation of renin–angiotensin system in the treatment of hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 1997;11:17–21.
Goraca A. New views on the role of endothelin (minireview). Endocr Regul 2002;36:161–7.
Yanagisawa M, Kurihara H, Kimura S, Tomobe Y, Kobayashi M, Mitsui Y, et al. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature 1988;332:411–5.
Schiffrin EL. State-of-the-art lecture. Role of endothelin-1 in hypertension. Hypertension 1999;34:876–81.
Taddei S, Virdis A, Ghiadoni L, Sudano I, Notari M, Salvetti A. Vasoconstriction to endogenous endothelin-1 is increased in the peripheral circulation of patients with essential hypertension. Circulation 1999;100:1680–3.
Krum H, Viskoper RJ, Lacourciere Y, Budde M, Charlon V. The effect of an endothelin-receptor antagonist, bosentan, on blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension. Bosentan hypertension investigators. N Engl J Med 1998;338:784–90.
Krum H, Liew D. Current status of endothelin blockade for the treatment of cardiovascular and pulmonary vascular disease. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2003;4:298–302.
Li JS, Schiffrin EL. Chronic Endothelin receptor antagonist treatment of young spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens 1995;13:647–52.
Spieker LE, Noll G, Luscher TF. Therapeutic potential for endothelin receptor antagonists in cardiovascular disorders. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs 2001;1:293–303.
Campia U, Cardillo C, Panza JA. Ethnic differences in the vasoconstrictor activity of endogenous endothelin-1 in hypertensive patients. Circulation 2004;109:3191–5.
Koletsky S, Shook P, Rivera-Velze J. Lack of increased renin–angiotensin activity in rats with spontaneous hypertension. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 1970;134:1187–90.
Gulati A, Artwohl JE, Kumar A, Gao X-p, Rubinstein I. Endothelin-1-like immunoreactivity in a new rodent model of spontaneous hypertension. Am J Hypertens 1998;11:866–9.
Rubinstein I, Houmsse M, Davis RG, Vishwanatha JK. Tissue angiotensin I-converting enzyme activity in spontaneously hypertensive hamsters. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1992;183:1117–23.
Suzuki H, Noda Y, Gao X-p, Séjourné F, Alkan-Önyüksel H, Paul S, et al. Encapsulation of vasoactive intestinal peptide into liposomes restores vasorelaxation in hypertension in situ. Am J Physiol 1996;271:H282–7.
Suzuki H, Ikezaki H, Hong D, Rubinstein I. PGH2–TXA2 receptor blockade restores vasoreactivity in a new rodent model of genetic hypertension. J Appl Physiol 2000;88:1983–8.
Thomas CL, Artwohl JE, Suzuki H, Gao X-p, White E, Saroli A, et al. Initial characterization of hamsters with spontaneous hypertension. Hypertension 1997;30 [part 1]:301–4.
Vishwanatha JK, Davis RG, Blumberg S, Gao X-p, Rubinstein I. Tissue neutral endopeptidase 24.11 activity in hamsters with spontaneous hypertension. Am J Hypertens 1998;11:585–90.
Kurjiaka DT. The conduction of dilation along an arteriole is diminished in the cremaster muscle of hypertensive hamsters. J Vasc Res 2004;41:517–24.
Kurjiaka DT, Bender SB, Nye DD, Wiehler WB, Welsh DG. Hypertension attenuates cell-to-cell communication in hamster retractor muscle feed arteries. Am J Physiol 2005;288:H861–70.
Jesmin S, Zaedi S, Maeda S, Togashi H, Yamaguchi I, Goto K, et al. Endothelin antagonism suppresses plasma and cardiac endothelin-1 levels in SHRSPs at the typical hypertensive stage. Exp Biol Med 2006;231:919–24.
Wu-Wong JR. Sitaxsentan (ICOS-Texas Biotechnology). Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2001;2:531–6.
Elmarkaby AA, Babbs Loomis E, Pollock JS, Pollock DM. ETA receptor blockade attenuates hypertension and decreases reactive oxygen species in ETB receptor-deficient rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2004;44:S7–10.
Nakov R, Pfarr E, Eberle S, HEAT Investigators. Darusentan: an effective endothelin A receptor antagonist for treatment of hypertension. Am J Hypertens 2002;15:583–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubinstein, I. Prolonged Anti-Hypertensive Effects of Oral Sitaxsentan, a Selective ETA Endothelin Receptor Antagonist, in Spontaneoulsy Hypertensive Hamsters. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 20, 387–390 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-006-0293-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-006-0293-1