Abstract
Tumor suppressor genes and proto-oncogenes comprise most of the complex genomic landscape associated with cancer, with a minimal number of genes exhibiting dual-context-dependent functions. The transcription factor cellular promoter 2 (TFCP2), a pivotal transcription factor encoded by the alpha globin transcription factor CP2 gene, is a constituent of the TFCP2/grainyhead family of transcription factors. While grainyhead members have been extensively studied for their crucial roles in developmental processes, embryogenesis, and multiple cancers, the TFCP2 subfamily has been relatively less explored. The molecular mechanisms underlying TFCP2's involvement in carcinogenesis are still unclear even though it is a desirable target for cancer treatment and a therapeutic marker. This comprehensive literature review summarizes the molecular functions of TFCP2, emphasizing its involvement in cancer pathophysiology, particularly in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. It highlights TFCP2's critical function as a regulatory target and explores its potential as a prognostic marker for survival and inflammation in carcinomas. Its ambiguous association with carcinomas underlines the urgent need for an in-depth understanding to facilitate the development of more efficacious targeted therapeutic modality and diagnostic tools. This study aims to elucidate the multifaceted effects of TFCP2 regulation, through a comprehensive integration of the existing knowledge in cancer therapeutics. Furthermore, the clinical relevance and the inherent challenges encountered in investigating its intricate role in cancer pathogenesis have been discussed in this review.
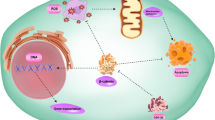
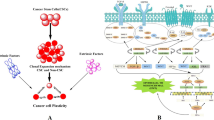
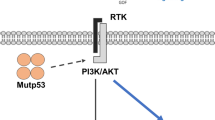
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data has been included in the manuscript. If required, it can be available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- TFCP2:
-
Transcription factor CP2
- TFCP2L1:
-
Transcription factor CP2 like 1
- UBP1:
-
Upstream Binding Protein 1
- DBD:
-
DNA binding domains
- GRH:
-
Grainyhead family
- SAM:
-
Sterile alpha motif
- DAPK:
-
Death-associated protein kinase
- NF-E2:
-
Nuclear Factor, Erythroid 2
- HIV:
-
Human immunodeficiency virus
- (hESCs)/ESCs:
-
Embryonic stem cells
- GRHL :
-
Grainyhead like
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- YY1:
-
Yin-Yang 1
- CYP11A1:
-
Cytochrome P450 family 11 subfamily A member 1
- CPEB1:
-
Cytoplasmic Polyadenylation Element Binding Protein 1
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- ASIC2:
-
Acid-sensing ion channel subunit 2
- miR:
-
MiRNA
- circITCH:
-
Circular RNA Itchy E3 Ubiquitin Protein Ligase
- YAP1:
-
Yes1 Associated Transcriptional Regulator
- DAPK:
-
Death-associated protein kinase
- TS:
-
Thymidylate synthase
- TFCP2dn:
-
Dominant-negative TFCP2
- SCC:
-
Squamous cell carcinoma
- TCF:
-
T cell factor
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
- AKT:
-
AKT Serine/Threonine Kinase
- ChIP:
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- VEGF:
-
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
- MMPs:
-
Matrix Metallopeptidase
- IL-8:
-
Interleukin
- 5-FU:
-
5-Fluorouracil
- AEG-1:
-
Astrocyte Elevated Gene-1
- CSCs:
-
Cancer stem cells
- MET:
-
Mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition
- GRP78:
-
Glucose-regulated protein
- NOTCH1:
-
Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1
- DNMT1:
-
DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1
- FQl1:
-
Factor quinolinone inhibitor 1
- OPN:
-
Osteopontin
- TJP1:
-
Tight junction protein 1
- CCT3:
-
Chaperonin containing TCP1 subunit 3
- YAP:
-
Yes associated transcriptional regulator
- YY1:
-
Yin yang 1 transcription factor
- TCF:
-
T cell factor
- SREBP2:
-
Sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 2
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor β
- PI3K:
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- SMAD2:
-
SMAD family member 2
- SULF1:
-
Sulfatase 1
- EWSR1:
-
EWS RNA binding protein 1
- FUS:
-
FUS RNA binding protein
- MAGE-A11:
-
Melanoma-associated antigen 11
- ZEB1:
-
Zinc finger E-Box binding homeobox 1
- TSG101:
-
Tumor susceptibility gene 101
- ATF3:
-
Activating transcription factor 3
References
Kotarba, G., Krzywinska, E., Grabowska, A. I., Taracha, A., & Wilanowski, T. (2018). TFCP2/TFCP2L1/UBP1 transcription factors in cancer. Cancer Letters, 420, 72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CANLET.2018.01.078
Cunningham, J. M., Vanin, E. F., Tran, N., Valentine, M., & Jane, S. M. (1995). The human transcription factor CP2 (TFCP2), a component of the human gamma-globin stage selector protein, maps to chromosome region 12q13 and is within 250 kb of the NF-E2 gene. Genomics, 30(2), 398–399.
Swendeman, S. L., Spielholz, C., Jenkins, N. A., Gilbert, D. J., Copeland, N. G., & Sheffery, M. (1994). Characterization of the genomic structure, chromosomal location, promoter, and development expression of the alpha-globin transcription factor CP2. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 269(15), 11663–11671.
Kent, W. J., Sugnet, C. W., Furey, T. S., Roskin, K. M., Pringle, T. H., Zahler, A. M., & Haussler, D. (2002). The Human Genome Browser at UCSC. Genome Research, 12(6), 996–1006. https://doi.org/10.1101/GR.229102
Kokoszynska, K., Ostrowski, J., Rychlewski, L., & Wyrwicz, L. S. (2008). The fold recognition of CP2 transcription factors gives new insights into the function and evolution of tumor suppressor protein p53. Cell Cycle, 7(18), 2907–2915. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.7.18.6680
Shirra, M. K., & Hansen, U. (1998). LSF and NTF-1 share a conserved DNA recognition motif yet require different oligomerization states to form a stable protein-DNA complex. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273(30), 19260–19268.
Hansen, U., Owens, L., & Saxena, U. (2009). Transcription factors LSF and E2Fs: Tandem cyclists driving G0 to S? Cell Cycle, 8(14), 2146–2151.
Ming, Q., Roske, Y., Schuetz, A., Walentin, K., Ibraimi, I., Schmidt-Ott, K. M., & Heinemann, U. (2018). Structural basis of gene regulation by the Grainyhead/CP2 transcription factor family. Nucleic Acids Research, 46(4), 2082–2095. https://doi.org/10.1093/NAR/GKX1299
Murata, T., Nitta, M., & Yasuda, K. (1998). Transcription factor CP2 is essential for lens-specific expression of the chicken $α$A-crystallin gene. Genes to Cells, 3(7), 443–457.
Frith, M. C., Hansen, U., & Weng, Z. (2001). Detection of cis-element clusters in higher eukaryotic DNA. Bioinformatics, 17(10), 878–889.
Drouin, E. E., Schrader, C. E., Stavnezer, J., & Hansen, U. (2002). The ubiquitously expressed DNA-binding protein late SV40 factor binds Ig switch regions and represses class switching to IgA. The Journal of Immunology, 168(6), 2847–2856.
Jane, S. M., Nienhuis, A. W., & Cunningham, J. M. (1995). Hemoglobin switching in man and chicken is mediated by a heteromeric complex between the ubiquitous transcription factor CP2 and a developmentally specific protein. The EMBO Journal, 14(1), 97–105.
Shirra, M. K., Zhu, Q., Huang, H.-C., Pallas, D., & Hansen, U. (1994). One exon of the human LSF gene includes conserved regions involved in novel DNA-binding and dimerization motifs. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 14(8), 5076–5087. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.14.8.5076-5087.1994
Uv, A. E., Thompson, C. R. L., & Bray, S. J. (1994). The Drosophila tissue-specific factor Grainyhead contains novel DNA-binding and dimerization domains which are conserved in the human protein CP2. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 14(6), 4020–4031. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.14.6.4020-4031.1994
Tuckfield, A., Clouston, D. R., Wilanowski, T. M., Zhao, L.-L., Cunningham, J. M., & Jane, S. M. (2002). Binding of the RING Polycomb Proteins to Specific Target Genes in Complex with the grainyhead-Like Family of Developmental Transcription Factors. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 22(6), 1936. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.22.6.1936-1946.2002
Shao, K., Pu, W., Zhang, J., Guo, S., Qian, F., Glurich, I., … Ding, W. (2021). DNA hypermethylation contributes to colorectal cancer metastasis by regulating the binding of CEBPB and TFCP2 to the CPEB1 promoter. Clinical Epigenetics, 13(1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/S13148-021-01071-Z/FIGURES/7
Zhang, J., Cai, Y., Sheng, S., Zhao, C., & Jiang, B. (2022). circITCH suppresses cell proliferation and metastasis through miR-660/TFCP2 pathway in melanoma. Cancer Medicine, 11(12), 2405–2413. https://doi.org/10.1002/CAM4.4627
Shen, Y., Ye, Y. F., Ruan, L. W., Bao, L., Wu, M. W., & Zhou, Y. (2017). Inhibition of miR-660–5p expression suppresses tumor development and metastasis in human breast cancer. Genetics and molecular research : GMR, 16(1). https://doi.org/10.4238/GMR16019479
Zhang, J., Zhao, X., Zhang, J., Zheng, X., & Li, F. (2018). Circular RNA hsa_circ_0023404 exerts an oncogenic role in cervical cancer through regulating miR-136/TFCP2/YAP pathway. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 501(2), 428–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BBRC.2018.05.006
Bray, S. J., & Kafatos, F. C. (1991). Developmental function of Elf-1: An essential transcription factor during embryogenesis in Drosophila. Genes & Development, 5(9), 1672–1683. https://doi.org/10.1101/GAD.5.9.1672
Cieply, B., Riley IV, P., Pifer, P. M., Widmeyer, J., Addison, J. B., Ivanov, A. V., … Frisch, S. M. (2012). Suppression of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by Grainyhead-like-2. Cancer research, 72(9), 2440–2453. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-4038
Gao, X., Vockley, C. M., Pauli, F., Newberry, K. M., Xue, Y., Randell, S. H., … Hogan, B. L. M. (2013). Evidence for multiple roles for grainyhead-like 2 in the establishment and maintenance of human mucociliary airway epithelium.[corrected]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(23), 9356–9361. https://doi.org/10.1073/PNAS.1307589110
Peyrard-Janvid, M., Leslie, E. J., Kousa, Y. A., Smith, T. L., Dunnwald, M., Magnusson, M., … Schutte, B. C. (2014). Dominant mutations in GRHL3 cause Van der Woude Syndrome and disrupt oral periderm development. American journal of human genetics, 94(1), 23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AJHG.2013.11.009
Huang, H. C., Sundseth, R., & Hansen, U. (1990). Transcription factor LSF binds two variant bipartite sites within the SV40 late promoter. Genes & Development, 4(2), 287–298. https://doi.org/10.1101/GAD.4.2.287
Kim, C. H., Heath, C., Bertuch, A., & Hansen, U. (1987). Specific stimulation of simian virus 40 late transcription in vitro by a cellular factor binding the simian virus 40 21-base-pair repeat promoter element. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 84(17), 6025–6029. https://doi.org/10.1073/PNAS.84.17.6025
Wu, F. K., Garcia, J. A., Harrich, D., & Gaynor, R. B. (1988). Purification of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 enhancer and TAR binding proteins EBP-1 and UBP-1. The EMBO Journal, 7(7), 2117–2130. https://doi.org/10.1002/J.1460-2075.1988.TB03051.X
Huang, N., & Miller, W. L. (2000). Cloning of Factors Related to HIV-inducible LBP Proteins That Regulate Steroidogenic Factor-1-independent Human Placental Transcription of the Cholesterol Side-chain Cleavage Enzyme, P450scc. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275(4), 2852–2858. https://doi.org/10.1074/JBC.275.4.2852
Rodda, S., Sharma, S., Scherer, M., Chapman, G., & Rathjen, P. (2001). CRTR-1, a Developmentally Regulated Transcriptional Repressor Related to the CP2 Family of Transcription Factors. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276(5), 3324–3332. https://doi.org/10.1074/JBC.M008167200
Kim, C. M., Jang, T., & Park, H. H. (2016). Functional Analysis of CP2-Like Domain and SAM-Like Domain in TFCP2L1, Novel Pluripotency Factor of Embryonic Stem Cells. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 179(4), 650–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12010-016-2021-Z/METRICS
Liu, K., Zhang, Y., Liu, D., Ying, Q. L., & Ye, S. (2017). TFCP2L1 represses multiple lineage commitment of mouse embryonic stem cells through MTA1 and LEF1. Journal of Cell Science, 130(22), 3809–3817. https://doi.org/10.1242/JCS.206532/265431/AM/TFCP2L1-REPRESSES-MULTIPLE-LINEAGE-COMMITMENT-OF
Wang, X., Wang, X., Zhang, S., Sun, H., Li, S., Ding, H., … Ye, S. D. (2019). The transcription factor TFCP2L1 induces expression of distinct target genes and promotes self-renewal of mouse and human embryonic stem cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 294(15), 6007–6016. https://doi.org/10.1074/JBC.RA118.006341
Taracha, A., Kotarba, G., & Wilanowski, T. (2018). Neglected Functions of TFCP2/TFCP2L1/UBP1 Transcription Factors May Offer Valuable Insights into Their Mechanisms of Action. International journal of molecular sciences, 19(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS19102852
Chen, A. F., Liu, A. J., Krishnakumar, R., Freimer, J. W., DeVeale, B., & Blelloch, R. (2018). GRHL2-Dependent Enhancer Switching Maintains a Pluripotent Stem Cell Transcriptional Subnetwork after Exit from Naive Pluripotency. Cell Stem Cell, 23(2), 226-238.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.STEM.2018.06.005
Caddy, J., Wilanowski, T., Darido, C., Dworkin, S., Ting, S. B., Zhao, Q., … Jane, S. M. (2010). Epidermal Wound Repair Is Regulated by the Planar Cell Polarity Signaling Pathway. Developmental Cell, 19(1), 138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DEVCEL.2010.06.008
Deng, Z., Cangkrama, M., Butt, T., Jane, S. M., & Carpinelli, M. R. (2021). Grainyhead-like transcription factors: Guardians of the skin barrier. Veterinary Dermatology, 32(6), 553-e152. https://doi.org/10.1111/VDE.12956
Liu, J., Fu, N., Yang, Z., Li, A., Wu, H., Jin, Y., … Zhang, X. (2023). The genetic and epigenetic regulation of CD55 and its pathway analysis in colon cancer. Frontiers in Immunology, 13, 947136. https://doi.org/10.3389/FIMMU.2022.947136/BIBTEX
Ren, Y., YaneYang, Lu., Wang, Q., Lu, Q., Lu, G., Wei, Y., & Zhou, J. (2023). Transcription factor cellular promoter 2 is required for upstream binding protein 1 -mediated angiogenesis. Gene Expression Patterns, 48, 119308. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GEP.2023.119308
Basu, A., Champagne, R. N., Patel, N. G., Nicholson, E. D., & Weiss, R. J. (2023). TFCP2 is a transcriptional regulator of heparan sulfate assembly and melanoma cell growth. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 299(6). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104713
Beckmann, A., Ramirez, P., Gamez, M., Gonzalez, E., De Mange, J., Bieniek, K. F., … Frost, B. (2023). Moesin is an effector of tau-induced actin overstabilization, cell cycle activation, and neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. iScience, 26(3), 106152. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ISCI.2023.106152
Cardenas-Diaz, F. L., Liberti, D. C., Leach, J. P., Babu, A., Barasch, J., Shen, T., … Morrisey, E. E. (2023). Temporal and spatial staging of lung alveolar regeneration is determined by the grainyhead transcription factor Tfcp2l1. Cell Reports, 42(5), 112451. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CELREP.2023.112451
Yang, Z., Jia, X., Deng, Q., Luo, M., Hou, Y., Yue, J., … Shan, N. (2023). Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles loaded with TFCP2 activate Wnt/β-catenin signaling to alleviate preeclampsia. International Immunopharmacology, 115, 109732. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.INTIMP.2023.109732
Zhou, W., Clouston, D. R., Wang, X., Cerruti, L., Cunningham, J. M., & Jane, S. M. (2000). Induction of Human Fetal Globin Gene Expression by a Novel Erythroid Factor, NF-E4. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 20(20), 7662–7672. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.20.20.7662-7672.2000
Casolaro, V., Keane-Myers, A. M., Swendeman, S. L., Steindler, C., Zhong, F., Sheffery, M., … Ono, S. J. (2000). Identification and characterization of a critical CP2-binding element in the human interleukin-4 promoter. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275(47), 36605–36611. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M007086200
Powell, C. M. H. (2000). Inhibition of the mammalian transcription factor LSF induces S-phase-dependent apoptosis by downregulating thymidylate synthase expression. The EMBO Journal, 19(17), 4665–4675. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/19.17.4665
Solis, C., Aizencang, G. I., Astrin, K. H., Bishop, D. F., & Desnick, R. J. (2001). Uroporphyrinogen III synthase erythroid promoter mutations in adjacent GATA1 and CP2 elements cause congenital erythropoietic porphyria. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 107(6), 753–762. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI10642
Xu, X., Liu, Z., Zhou, L., Xie, H., Cheng, J., Ling, Q., … Zheng, S. (2015). Characterization of genome-wide TFCP2 targets in hepatocellular carcinoma: implication of targets FN1 and TJP1 in metastasis. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research : CR, 34(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/S13046-015-0121-1
Jung, J., & Yoo, S. (2023). Identification of Breast Cancer Metastasis Markers from Gene Expression Profiles Using Machine Learning Approaches. Genes, 14(9), 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/GENES14091820/S1
Song, J., Yan, S., & Ren, X. (2023). IDDF2023-ABS-0024 TFCP2 promotes EMT, invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer by regulating the expression of CIP2A. Gut, 72(Suppl 1), A61–A62. https://doi.org/10.1136/GUTJNL-2023-IDDF.52
Santhekadur, P. K., Rajasekaran, D., Siddiq, A., Gredler, R., Chen, D., Schaus, S. E., … Sarkar, D. (2012). The transcription factor LSF: a novel oncogene for hepatocellular carcinoma. American journal of cancer research, 2(3), 269–85.
Goto, Y., Yajima, I., Kumasaka, M., Ohgami, N., Tanaka, A., Tsuzuki, T., … Kato, M. (2016). Transcription factor LSF (TFCP2) inhibits melanoma growth. Oncotarget, 7(3), 2379–2390. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6230
Son, S. H., Kim, M. Y., Jo, E., Uversky, V. N., & Kim, C. G. (2022). Structural and Functional Insights into CP2c Transcription Factor Complexes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(12), 6369. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS23126369/S1
Whitmarsh, A. J., & Davis, R. J. (2000). Regulation of transcription factor function by phosphorylation. Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS, 57(8–9), 1172–1183. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00000757
Sundseth, R., & Hansen, U. (1992). Activation of RNA polymerase II transcription by the specific DNA-binding protein LSF. Increased rate of binding of the basal promoter factor TFIIB. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 267(11), 7845–7855. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)42591-4
Romerio, F., Gabriel, M. N., Margolis, D. M., Chun, -W, Finzi, D., Margolick, J., … Siliciano, R. F. (1997). Repression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through the novel cooperation of human factors YY1 and LSF. Journal of Virology, 71(12), 9375–9382. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.71.12.9375-9382.1997
Volker, J. L., Rameh, L. E., Zhu, Q., DeCaprio, J., & Hansen, U. (1997). Mitogenic stimulation of resting T cells causes rapid phosphorylation of the transcription factor LSF and increased DNA-binding activity. Genes & Development, 11(11), 1435–1446. https://doi.org/10.1101/GAD.11.11.1435
Pagon, Z., Volker, J., Cooper, G. M., & Hansen, U. (2003). Mammalian transcription factor LSF is a target of ERK signaling. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 89(4), 733–746. https://doi.org/10.1002/JCB.10549
Sun, H., You, Y., Guo, M., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., & Ye, S. (2018). Tfcp2l1 safeguards the maintenance of human embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 233(9), 6944–6951. https://doi.org/10.1002/JCP.26483
Sarkar, P., Mischler, A., Randall, S. M., Collier, T. S., Dorman, K. F., Boggess, K. A., … Rao, B. M. (2016). Identification of epigenetic factor proteins expressed in human embryonic stem cell-derived trophoblasts and in human placental trophoblasts. Journal of Proteome Research, 15(8), 2433–2444. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.JPROTEOME.5B01118/ASSET/IMAGES/LARGE/PR-2015-01118Y_0004.JPEG
Miller, W. L. (1988). Molecular Biology of Steroid Hormone Synthesis. Endocrine Reviews, 9(3), 295–318. https://doi.org/10.1210/EDRV-9-3-295
Morohashi, K., Sogawa, K., Omura, T., & Fujii-kuriyama, Y. (1987). Gene Structure of Human Cytochrome P-450(SCC), Cholesterol Desmolase. The Journal of Biochemistry, 101(4), 879–887. https://doi.org/10.1093/OXFORDJOURNALS.JBCHEM.A121955
Nebert, D. W., Nelson, D. R., Coon, M. J., Estabrook, R. W., Feyereisen, R., Fujii-Kuriyama, Y., … Waxman, D. J. (2009). The P450 Superfamily: Update on New Sequences, Gene Mapping, and Recommended Nomenclature. https://home.liebertpub.com/dna, 10(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1089/DNA.1991.10.1
Koutnikova, H., Laakso, M., Lu, L., Combe, R., Paananen, J., Kuulasmaa, T., … Auwerx, J. (2009). Identification of the UBP1 Locus as a Critical Blood Pressure Determinant Using a Combination of Mouse and Human Genetics. PLOS Genetics, 5(8), e1000591. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PGEN.1000591
Xia, J., Zhou, Z. H., Bubien, J. K., Fuller, C. M., Markert, J. M., Mapstone, T. B., … Benos, D. J. (2003). Molecular cloning and characterization of human acid sensing ion channel (ASIC)2 gene promoter. Gene, 313(1–2), 91–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1119(03)00633-4
Pulling, L. C., Grimes, M. J., Damiani, L. A., Juri, D. E., Do, K., Tellez, C. S., & Belinsky, S. A. (2009). Dual promoter regulation of death-associated protein kinase gene leads to differentially silenced transcripts by methylation in cancer. Carcinogenesis, 30(12), 2023–2030.
Yoo, B. K., Emdad, L., Gredler, R., Fuller, C., Dumur, C. I., Jones, K. H., … Sarkar, D. (2010). Transcription factor Late SV40 Factor (LSF) functions as an oncogene in hepatocellular carcinoma. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(18), 8357–8362. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1000374107
Yoo, B. K., Emdad, L., Gredler, R., Fuller, C., Dumur, C. I., Jones, K. H., … others. (2010). Transcription factor Late SV40 Factor (LSF) functions as an oncogene in hepatocellular carcinoma. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 107(18), 8357–8362.
Yuedi, D., Yuankun, C., Jiaying, Z., Han, L., Yueqi, W., Houbao, L., & Dexiang, Z. (2017). TFCP2 activates beta-catenin/TCF signaling in the progression of pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget, 8(41), 70538–70549. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19741
Chen, C.-H., Tsai, H.-T., Chuang, H.-C., Shiu, L.-Y., Su, L.-J., Chiu, T.-J., … Chien, C.-Y. (2017). Metformin disrupts malignant behavior of oral squamous cell carcinoma via a novel signaling involving Late SV40 factor/Aurora-A. Scientific reports, 7(1), 1–15.
Jiang, H., Du, J., Jin, J., Qi, X., Pu, Y., & Fei, B. (2014). LSF expression and its prognostic implication in colorectal cancer. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology, 7(9), 6024.
Broniarczyk, J. K., Warowicka, A., Kwaśniewska, A., Wolun-Cholewa, M., Kwaśniewski, W., & Goździcka-Józefiak, A. (2014). Expression of TSG101 protein and LSF transcription factor in HPV-positive cervical cancer cells. Oncology Letters, 7(5), 1409–1413.
Kaur, M., MacPherson, C. R., Schmeier, S., Narasimhan, K., Choolani, M., & Bajic, V. B. (2011). In Silico discovery of transcription factors as potential diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. BMC Systems Biology, 5(1), 1–13.
Li, X.-P., Xu, Q.-Y., Wang, J.-L., Wang, S., Zhao, Y., & Wei, L. (2012). Evaluation of whether serum tumor markers in patients with epithelial ovarian carcinoma change following chemotherapy. Chinese Medical Journal, 125(03), 410–415.
Dong, L., Cui, H., Li, X. P., Sun, L. F., Chang, X. H., Liang, X. D., & Zhu, H. L. (2008). Clinical value of serum CA19-9, CA125 and CP2 in mucinous ovarian tumor: A retrospective study of 273 patients. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi, 43(1), 5–8.
Pozzesi, N., Pierangeli, S., Vacca, C., Falchi, L., Pettorossi, V., Martelli, M. P., … others. (2011). Maesopsin 4-O-$β$-D-glucoside, a natural compound isolated from the leaves of artocarpus tonkinensis, inhibits proliferation and up-regulates HMOX1, SRXN1 and BCAS3 in acute myeloid leukemia. Journal of Chemotherapy, 23(3), 150–157.
Luo, X., Li, N., Zhong, J., Tan, Z., Liu, Y., Dong, X., … others. (2016). Grifolin inhibits tumor cells adhesion and migration via suppressing interplay between PGC1$α$ and Fra-1/LSF-MMP2/CD44 axes. Oncotarget, 7(42), 68708.
Qin, C., Samudio, I., Ngwenya, S., & Safe, S. (2004). Estrogen-dependent regulation of ornithine decarboxylase in breast cancer cells through activation of nongenomic cAMP-dependent pathways. Molecular Carcinogenesis: Published in cooperation with the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, 40(3), 160–170.
Zhao, Y., Kaushik, N., Kang, J. H., Kaushik, N. K., Son, S. H., Uddin, N., … Lee, S. J. (2020). A feedback loop comprising EGF/TGFa sustains TFCP2-mediated breast cancer progression. Cancer Research, 80(11), 2217–2229. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-2908/653989/AM/A-FEEDBACK-LOOP-COMPRISING-EGF-TGF-SUSTAINS-TFCP2
Liu, Y., Zhang, X., Lin, J., Chen, Y., Qiao, Y., Guo, S., … Sun, F. (2019). CCT3 acts upstream of YAP and TFCP2 as a potential target and tumour biomarker in liver cancer. Cell Death & Disease 2019 10:9, 10(9), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1894-5
Cai, H., Guo, F., Wen, S., Jin, X., Wu, H., & Ren, D. (2022). Overexpressed integrin alpha 2 inhibits the activation of the transforming growth factor β pathway in pancreatic cancer via the TFCP2-SMAD2 axis. Journal of Experimental and Clinical Cancer Research, 41(1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/S13046-022-02286-5/FIGURES/8
Kashour, T., Burton, T., Dibrov, A., & Amara, F. M. (2003). Late Simian virus 40 transcription factor is a target of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway in anti-apoptotic Alzheimers amyloid precursor protein signalling. Biochemical Journal, 370(3), 1063–1075.
Saxena, U. H., Powell, C. M. H., Fecko, J. K., Cacioppo, R., Chou, H. S., Cooper, G. M., & Hansen, U. (2009). Phosphorylation by cyclin C/cyclin-dependent kinase 2 following mitogenic stimulation of murine fibroblasts inhibits transcriptional activity of LSF during G1 progression. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 29(9), 2335–2345.
Lamouille, S., Xu, J., & Derynck, R. (2014). Molecular mechanisms of epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology, 15(3), 178–196.
Porta-De-La-Riva, M., Stanisavljevic, J., Curto, J., Francí, C., Díaz, V. M., de Herreros, A., & Baulida, J. (2011). TFCP2c/LSF/LBP-1c is required for Snail1-induced fibronectin gene expression. Biochemical Journal, 435(3), 563–568.
Wang, H., & Unternaehrer, J. J. (2019). Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Stem Cells: At the Crossroads of Differentiation and Dedifferentiation. Developmental Dynamics, 248(1), 10–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/DVDY.24678
Roy, S., Sunkara, R. R., Parmar, M. Y., Shaikh, S., & Waghmare, S. K. (2021). EMT imparts cancer stemness and plasticity: New perspectives and therapeutic potential. Frontiers in Bioscience - Landmark, 26(2), 238–265. https://doi.org/10.2741/4893/4893/FIG3.JPG
Kim, J. S., Son, S. H., Kim, M. Y., Choi, D., Jang, I.-S., Paik, S. S., … Geun Kim, C. (2017). Diagnostic and prognostic relevance of CP2c and YY1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget, 8(15), 24389–24400. https://doi.org/10.18632/ONCOTARGET.15462
Yoo, B. K., Gredler, R., Chen, D., Santhekadur, P. K., Fisher, P. B., & Sarkar, D. (2011). c-Met activation through a novel pathway involving osteopontin mediates oncogenesis by the transcription factor LSF. Journal of Hepatology, 55(6), 1317–1324. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHEP.2011.02.036
Santhekadur, P. K., Gredler, R., Chen, D., Siddiq, A., Shen, X.-N., Das, S. K., … Sarkar, D. (2012). Late SV40 factor (LSF) enhances angiogenesis by transcriptionally up-regulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287(5), 3425–3432.
Seol, H. S., Lee, S. E., Song, J. S., Rhee, J. K., Singh, S. R., Chang, S., & Jang, S. J. (2016). Complement proteins C7 and CFH control the stemness of liver cancer cells via LSF-1. Cancer Letters, 372(1), 24–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CANLET.2015.12.005
Zhang, D., Lu, P., Zhu, K., Wu, H., & Dai, Y. (2021). TFCP2 Overcomes Senescence by Cooperating With SREBP2 to Activate Cholesterol Synthesis in Pancreatic Cancer. Frontiers in Oncology, 11, 724437. https://doi.org/10.3389/FONC.2021.724437/BIBTEX
Cha, C. D., Son, S. H., Kim, C. G., Park, H., & Chung, M. S. (2023). Prognostic Implication of YY1 and CP2c Expression in Patients with Primary Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, Vol. 15, Page 3495, 15(13), 3495. https://doi.org/10.3390/CANCERS15133495
Liu, X., Wang, L., Han, Y., Tsai, H., Shu, F., Xu, Z., … Cheng, F. (2022). TRAF6 modulates PD-L1 expression through YAP1-TFCP2 signaling in melanoma. bioRxiv, 2022.09.28.509909. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.09.28.509909
Le Loarer, F., Cleven, A. H. G., Bouvier, C., Castex, M. P., Romagosa, C., Moreau, A., … Tirode, F. (2020). A subset of epithelioid and spindle cell rhabdomyosarcomas is associated with TFCP2 fusions and common ALK upregulation. Modern Pathology, 33(3), 404–419. https://doi.org/10.1038/S41379-019-0323-8
Koutlas, I. G., Olson, D. R., & Rawwas, J. (2021). FET(EWSR1)-TFCP2 Rhabdomyosarcoma: An Additional Example of this Aggressive Variant with Predilection for the Gnathic Bones. Head and Neck Pathology, 15(1), 374–380. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12105-020-01189-1/METRICS
Xu, B., Suurmeijer, A. J. H., Agaram, N. P., Zhang, L., & Antonescu, C. R. (2021). Head and neck rhabdomyosarcoma with TFCP2 fusions and ALK overexpression: A clinicopathological and molecular analysis of 11 cases. Histopathology, 79(3), 347–357. https://doi.org/10.1111/HIS.14323
Chrisinger, J. S. A., Wehrli, B., Dickson, B. C., Fasih, S., Hirbe, A. C., Shultz, D. B., … Demicco, E. G. (2020). Epithelioid and spindle cell rhabdomyosarcoma with FUS-TFCP2 or EWSR1-TFCP2 fusion: report of two cases. Virchows Archiv, 477(5), 725–732. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00428-020-02870-0/METRICS
Gallagher, K. P. D., Roza, A. L. O. C., Tager, E. M. J. R., Mariz, B. A. L. A., Soares, C. D., Rocha, A. C., … Santos-Silva, A. R. (2023). Rhabdomyosarcoma with TFCP2 Rearrangement or Typical Co-expression of AE1/AE3 and ALK: Report of Three New Cases in the Head and Neck Region and Literature Review. Head and neck pathology, 17(2), 546–561. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12105-022-01507-9
Gu, L., Sang, M., Li, J., Liu, F., Wu, Y., Liu, S., … Shan, B. (2019). Expression and prognostic significance of MAGE-A11 and transcription factors (SP1,TFCP2 and ZEB1) in ESCC tissues. Pathology - Research and Practice, 215(7), 152446. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PRP.2019.152446
Lotfollahzadeh, S., Lo, D., York, E. A., Napoleon, M. A., Yin, W., Elzinad, N., … Chitalia, V. C. (2022). Pharmacologic Manipulation of Late SV40 Factor Suppresses Wnt Signaling and Inhibits Growth of Allogeneic and Syngeneic Colon Cancer Xenografts. The American Journal of Pathology, 192(8), 1167–1185. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AJPATH.2022.04.006
Hsu, W. H., Labella, K. A., Lin, Y., Xu, P., Lee, R., Hsieh, C. E., … Depinho, R. A. (2023). Oncogenic KRAS Drives Lipofibrogenesis to Promote Angiogenesis and Colon Cancer Progression. Cancer discovery, 13(12), 2652–2673. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-22-1467
Luo, X., Ge, J., Liu, J., Liu, Z., Bi, C., & Lan, S. (2022). TFCP2, a binding protein of ATF3, promotes the progression of glioma by activating the synthesis of serine. Experimental Cell Research, 416(1), 113136. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.YEXCR.2022.113136
Tsagiopoulou, M., Chapaprieta, V., Duran-Ferrer, M., Moysiadi, T., Psomopoulos, F., Kollia, P., … Martin-Subero, J. I. (2020). Chronic lymphocytic leukemias with trisomy 12 show a distinct DNA methylation profile linked to altered chromatin activation. Haematologica, 105(12), 2864–2867. https://doi.org/10.3324/HAEMATOL.2019.240721
Klintman, J., consortium, on behalf of the O., Appleby, N., consortium, on behalf of the O., Stamatopoulos, B., consortium, on behalf of the O., … consortium, on behalf of the O. (2021). Genomic and transcriptomic correlates of Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood, 137(20), 2800–2816https://doi.org/10.1182/BLOOD.2020005650
Harper, J., & Moses, M. A. (2006). Molecular regulation of tumor angiogenesis: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. In: Cancer: Cell Structures, Carcinogens and Genomic Instability. Experientia Supplementum, vol 96. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-7643-7378-4_10. Birkhäuser Basel
Parekh, V., McEwen, A., Barbour, V., Takahashi, Y., Rehg, J. E., Jane, S. M., & Cunningham, J. M. (2004). Defective extraembryonic angiogenesis in mice lacking LBP-1a, a member of the grainyhead family of transcription factors. Molecular and cellular biology, 24(16), 7113–7129.
Deryugina, E. I., & Quigley, J. P. (2006). Matrix metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer and metastasis reviews, 25(1), 9–34.
Deryugina, E. I., & Quigley, J. P. (2015). Tumor angiogenesis: MMP-mediated induction of intravasation-and metastasis-sustaining neovasculature. Matrix Biology, 44, 94–112.
Rundhaug, J. E. (2005). Matrix metalloproteinases and angiogenesis. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine, 9(2), 267–285.
Rundhaug, J. E., & Fischer, S. M. (2010). Molecular mechanisms of mouse skin tumor promotion. Cancers, 2(2), 436–482.
Bergers, G., Brekken, R., McMahon, G., Vu, T. H., Itoh, T., Tamaki, K., … others. (2000). Matrix metalloproteinase-9 triggers the angiogenic switch during carcinogenesis. Nature cell biology, 2(10), 737–744.
Hanahan, D., & Weinberg, R. A. (2000). The hallmarks of cancer. cell, 100(1), 57–70.
Hanahan, D., & Weinberg, R. A. (2011). Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell, 144(5), 646–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CELL.2011.02.013
Yeo, W., Mok, T. S., Zee, B., Leung, T. W. T., Lai, P. B. S., Lau, W. Y., … others. (2005). A randomized phase III study of doxorubicin versus cisplatin/interferon $α$-2b/doxorubicin/fluorouracil (PIAF) combination chemotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 97(20), 1532–1538.
Showalter, S. L., Showalter, T. N., Witkiewicz, A., Havens, R., Kennedy, E. P., Hucl, T., … Brody, J. R. (2008). Evaluating the drug-target relationship between thymidylate synthase expression and tumor response to 5-fluorouracil: Is it time to move forward? Cancer biology \& therapy, 7(7), 986–994.
Yoshinare, K., Kubota, T., Watanabe, M., Wada, N., Nishibori, H., Hasegawa, H., … Fukushima, M. (2003). Gene expression in colorectal cancer and in vitro chemosensitivity to 5-fluorouracil: A study of 88 surgical specimens. Cancer science, 94(7), 633–638.
Oguri, T., Achiwa, H., Bessho, Y., Muramatsu, H., Maeda, H., Niimi, T., … Ueda, R. (2005). The role of thymidylate synthase and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase in resistance to 5-fluorouracil in human lung cancer cells. Lung cancer, 49(3), 345–351.
Yoo, B. K., Gredler, R., Vozhilla, N., Su, Z., Chen, D., Forcier, T., … others. (2009). Identification of genes conferring resistance to 5-fluorouracil. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106(31), 12938–12943.
Yoo, B. K., Chen, D., Su, Z., Gredler, R., Yoo, J., Shah, K., … Sarkar, D. (2010). Molecular Mechanism of Chemoresistance by Astrocyte Elevated Gene-1AEG-1 Confers Chemoresistance. Cancer research, 70(8), 3249–3258.
Li, Y., Mo, N., Yang, D., Lin, Q., Huang, W., & Wang, R. (2023). Predictive value of DNA methylation in the efficacy of chemotherapy for gastric cancer. Frontiers in Oncology, 13, 1238310. https://doi.org/10.3389/FONC.2023.1238310/BIBTEX
Shen, Y., Ye, Y. F., Ruan, L. W., Bao, L., Wu, M. W., & Zhou, Y. (2017). Inhibition of miR-660-5p expression suppresses tumor development and metastasis in human breast cancer. Genetics and Molecular Research, 16(1), 1–11.
Tian, Y., Bresenitz, P., Reska, A., El Moussaoui, L., Beier, C. P., & Gründer, S. (2017). Glioblastoma cancer stem cell lines express functional acid sensing ion channels ASIC1a and ASIC3. Scientific reports, 7(1), 1–14.
Xia, J., Zhou, Z.-H., Bubien, J. K., Fuller, C. M., Markert, J. M., Mapstone, T. B., … Benos, D. J. (2003). Molecular cloning and characterization of human acid sensing ion channel (ASIC) 2 gene promoter. Gene, 313, 91–101.
Jiang, H., Du, J., Jin, J., Qi, X., Pu, Y., & Fei, B. (2014). LSF expression and its prognostic implication in colorectal cancer. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology, 7(9), 6024. Retrieved from /pmc/articles/PMC4203218/.
Kaur, M., MacPherson, C. R., Schmeier, S., Narasimhan, K., Choolani, M., & Bajic, V. B. (2011). In Silico discovery of transcription factors as potential diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. BMC Systems Biology 2011 5:1, 5(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-5-144
Wang, H., Luo, J., Tian, X., Xu, L., Zhai, Z., Cheng, M., … Luo, S. (2021). DNAJC5 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cells proliferation though regulating SKP2 mediated p27 degradation. Biochimica et biophysica acta. Molecular cell research, 1868(6). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BBAMCR.2021.118994
Willoughby, J. L. S., George, K., Roberto, M. P., Chin, H. G., Stoiber, P., Shin, H., … Hansen, U. (2020). Targeting the oncogene LSF with either the small molecule inhibitor FQI1 or siRNA causes mitotic delays with unaligned chromosomes, resulting in cell death or senescence. BMC Cancer 2020 20:1, 20(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12885-020-07039-1
Li, T., Fu, J., Zeng, Z., Cohen, D., Li, J., Chen, Q., … Liu, X. S. (2020). TIMER2.0 for analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Nucleic acids research, 48(W1), W509–W514. https://doi.org/10.1093/NAR/GKAA407
Grant, T. J., Bishop, J. A., Christadore, L. M., Barot, G., Chin, H. G., Woodson, S., … Hansen, U. (2012). Antiproliferative small-molecule inhibitors of transcription factor LSF reveal oncogene addiction to LSF in hepatocellular carcinoma. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109(12), 4503–4508. https://doi.org/10.1073/PNAS.1121601109
Chin, H. G., Ponnaluri, V. k. C., Zhang, G., Estève, P.-O., Schaus, S. E., Hansen, U., … Pradhan, S. (2016). Transcription factor LSF-DNMT1 complex dissociation by FQI1 leads to aberrant DNA methylation and gene expression. Oncotarget, 7(50), 83627–83640. https://doi.org/10.18632/ONCOTARGET.13271
Funding
This research was funded by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea, funded by the Korean government (2021R1C1C1013875, 2021R1A6A1A03038785, 2021R1F1A1055694).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: NK; writing original draft: NK, AJ, and PB; writing, review, and editing: NK and AJ; funding acquisition: NK, NKK, and EHC; supervision: NKK and EHC. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaushik, N., Jaiswal, A., Bhartiya, P. et al. TFCP2 as a therapeutic nexus: unveiling molecular signatures in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-024-10175-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-024-10175-w