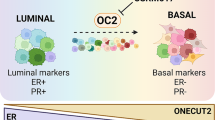
Abstract
Activation of oncogenes to sustain proliferative signaling and initiate metastasis are important hallmarks of cancer. Oncogenes are amplified or overexpressed in cancer cells and overexpression is often controlled at the level of transcription. Gene expression is tightly controlled by many cis-regulatory elements and trans-acting factors. Large clusters of enhancers known as “super-enhancers” drive robust expression of cell-fate determining transcription factors in cell identity. Cancer cells can take advantage of super-enhancers and become transcriptionally addicted to them leading to tumorigenesis and metastasis. Additionally, the cis-regulatory landscape of cancer includes aberrant super-enhancers that are not present in normal cells. The landscape of super-enhancers in cancer is characterized by high levels of histone H3K27 acetylation and bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4), and Mediator complex. These chromatin features facilitate the identification of cancer type-specific and cell-type-specific super-enhancers that control the expression of important oncogenes to stimulate their growth. Disruption of super-enhancers via inhibiting BRD4 or other epigenetic proteins is a potential therapeutic option. Here, we will describe the discovery of super-enhancers and their unique characteristics compared to typical enhancers. Then, we will highlight how super-enhancer-associated genes contribute to cancer progression in different solid tumor types. Lastly, we will cover therapeutic targets and their epigenetic modulators.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
B Lu C Zou M Yang Y He J He C Zhang W Zhao (2021) Pharmacological inhibition of core regulatory circuitry liquid–liquid phase separation suppresses metastasis and chemoresistance in osteosarcoma Advanced Science 8 (20) https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202101895
Heintzman, N. D., Hon, G. C., Hawkins, R. D., Kheradpour, P., Stark, A., Harp, L. F., & Ren, B. (2009). Histone modifications at human enhancers reflect global cell-type-specific gene expression. Nature, 459(7243), 108–112. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07829
Whyte, W. A., Orlando, D. A., Hnisz, D., Abraham, B. J., Lin, C. Y., Kagey, M. H., & Young, R. A. (2013). Master transcription factors and mediator establish super-enhancers at key cell identity genes. Cell, 153(2), 307–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.03.035
Hnisz, D., Schuijers, J., Lin, C. Y., Weintraub, A. S., Abraham, B. J., Lee, T. I., & Young, R. A. (2015). Convergence of developmental and oncogenic signaling pathways at transcriptional super-enhancers. Molecular Cell, 58(2), 362–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.02.014
RW Zhou J Xu TC Martin AL Zachem J He S Ozturk RE Parsons (2022) A local tumor microenvironment acquired super-enhancer induces an oncogenic driver in colorectal carcinoma Nature Communications 13 (1) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33377-8
M Wiese FH Hamdan K Kubiak C Diederichs GH Gielen G Nussbaumer CM Kramm (2020) Combined treatment with CBP and BET inhibitors reverses inadvertent activation of detrimental super enhancer programs in DIPG cells Cell Death and Disease 11 (8) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-02800-7
JE Lee YK Park S Park Y Jang N Waring A Dey K Ge (2017) Brd4 binds to active enhancers to control cell identity gene induction in adipogenesis and myogenesis Nature Communications 8 (1) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02403-5
Alver, B. H., Kim, K. H., Lu, P., Wang, X., Manchester, H. E., Wang, W., … Roberts, C. W. M. (2017). The SWI/SNF chromatin remodelling complex is required for maintenance of lineage specific enhancers. Nature Communications, 8 https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14648
BR Sabari Dall’Agnese, A., Boija, A., Klein, I. A., Coffey, E. L., Shrinivas, K., … Young, R. A. (2018) Coactivator condensation at super-enhancers links phase separation and gene control Science 361 (6400) https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar3958
Mediator condensates localize signaling factors to key cell identity genes (n.d.)
Wang, W., Qiao, S., Li, G., Cheng, J., Yang, C., Zhong, C., & Sui, G. (2022). A histidine cluster determines YY1-compartmentalized coactivators and chromatin elements in phase-separated enhancer clusters. Nucleic acids research, 50(9), 4917–4937. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac233
Boija, A., Klein, I. A., Sabari, B. R., & Dall’Agnese, A., Coffey, E. L., Zamudio, A. v., … Young, R. A. (2018). Transcription factors activate genes through the phase-separation capacity of their activation domains. Cell, 175(7), 1842-1855.e16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.10.042
Y Gong C Lazaris T Sakellaropoulos A Lozano P Kambadur P Ntziachristos A Tsirigos (2018) Stratification of TAD boundaries reveals preferential insulation of super-enhancers by strong boundaries Nature Communications 9 (1) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03017-1
Kloetgen, A., Thandapani, P., Ntziachristos, P., Ghebrechristos, Y., Nomikou, S., Lazaris, C., & Tsirigos, A. (2020). Three-dimensional chromatin landscapes in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nature Genetics, 52(4), 388–400. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-020-0602-9
C Fang Z Wang C Han SL Safgren KA Helmin ER Adelman C Zang (2020) Cancer-specific CTCF binding facilitates oncogenic transcriptional dysregulation Genome Biology 21 (1) https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-020-02152-7
Merkenschlager, M., & Nora, E. P. (2016). CTCF and cohesin in genome folding and transcriptional gene regulation. Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics. Annual Reviews Inc. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genom-083115-022339
T Zhang X Song Z Zhang Q Mao W Xia L Xu G Dong (2020) Aberrant super-enhancer landscape reveals core transcriptional regulatory circuitry in lung adenocarcinoma Oncogenesis 9 (10) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41389-020-00277-9
Tsang, F. H. C., Law, C. T., Tang, T. C. C., Cheng, C. L. H., Chin, D. W. C., Tam, W. S. V., & Wong, C. M. (2019). Aberrant super-enhancer landscape in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology, 69(6), 2502–2517. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30544
Roe, J. S., Hwang, C., & il, Somerville, T. D. D., Milazzo, J. P., Lee, E. J., da Silva, B., …Vakoc, C. R. (2017). Enhancer reprogramming promotes pancreatic cancer metastasis. Cell, 170(5), 875-888.e20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.007
H-R Kim J Yim H-B Yoo SE Lee S Oh S Jung J-S Roe (2021) EVI1 activates tumor-promoting transcriptional enhancers in pancreatic cancer NAR Cancer 3 (2) https://doi.org/10.1093/narcan/zcab023
Wu, F., Xu, L., Tu, Y., Cheung, O. K., Szeto, L. L., Mok, M. T., & To, K. F. (2022). Sirtuin 7 super-enhancer drives epigenomic reprogramming in hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Letters, 525, 115–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2021.10.039
Wen, S., He, Y., Wang, L., Zhang, J., Quan, C., Niu, Y., & Huang, H. (2020). Aberrant activation of super enhancer and choline metabolism drive antiandrogen therapy resistance in prostate cancer. Oncogene, 39(42), 6556–6571. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-01456-z
Yu, D., Yang, X., Lin, J., Cao, Z., Lu, C., Yang, Z., …Cai, W. (2021). Super-enhancer induced IL-20RA promotes proliferation/metastasis and immune evasion in colorectal cancer. Frontiers in Oncology, 11 https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.724655
Jiang, X., Qin, N., Hua, T., Wei, X., Li, Y., Chen, C., & Ma, H. (2022). Functional characterization and clinical significance of super-enhancers in lung adenocarcinoma. Molecular Carcinogenesis, 61(8), 776–786. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.23419
Tatsumi, G., Kawahara, M., Yamamoto, R., Hishizawa, M., Kito, K., Suzuki, T., & Andoh, A. (2020). LSD1-mediated repression of GFI1 super-enhancer plays an essential role in erythroleukemia. Leukemia, 34(3), 746–758. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-019-0614-6
Ying, Y., Wang, Y., Huang, X., Sun, Y., Zhang, J., Li, M., Shu, X., & sheng. (2020). Oncogenic HOXB8 is driven by MYC-regulated super-enhancer and potentiates colorectal cancer invasiveness via BACH1. Oncogene, 39(5), 1004–1017. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-1013-1
H Huang J Hu A Maryam Q Huang Y Zhang S Ramakrishnan YR Chin (2021) Defining super-enhancer landscape in triple-negative breast cancer by multiomic profiling Nature Communications 12 (1) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-22445-0
Patel, S. A., Rodrigues, P., Wesolowski, L., & Vanharanta, S. (2021, January 5). Genomic control of metastasis. British Journal of Cancer. Springer Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-020-01127-6
McDonald, O. G., Li, X., Saunders, T., Tryggvadottir, R., Mentch, S. J., Warmoes, M. O., & Feinberg, A. P. (2017). Epigenomic reprogramming during pancreatic cancer progression links anabolic glucose metabolism to distant metastasis. Nature Genetics, 49(3), 367–376. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3753
Teng, S., Li, Y. E., Yang, M., Qi, R., Huang, Y., Wang, Q., & Wang, D. (2020). Tissue-specific transcription reprogramming promotes liver metastasis of colorectal cancer. Cell Research, 30(1), 34–49. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-019-0259-z
Andricovich, J., Perkail, S., Kai, Y., Casasanta, N., Peng, W., & Tzatsos, A. (2018). Loss of KDM6A activates super-enhancers to induce gender-specific squamous-like pancreatic cancer and confers sensitivity to BET inhibitors. Cancer Cell, 33(3), 512-526.e8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2018.02.003
J Dong J Li Y Li Z Ma Y Yu CY Wang (2021) Transcriptional super-enhancers control cancer stemness and metastasis genes in squamous cell carcinoma Nature Communications 12 (1) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24137-1
Zhang, M., Hoyle, R. G., Ma, Z., Sun, B., Cai, W., Cai, H., & Li, J. (2021). FOSL1 promotes metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through super-enhancer-driven transcription program. Molecular Therapy, 29(8), 2583–2600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.03.024
Zhang, C., Wei, S., Sun, W. P., Teng, K., Dai, M. M., Wang, F. W., & Xie, D. (2020). Super-enhancer-driven AJUBA is activated by TCF4 and involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Theranostics, 10(20), 9066–9082. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.45349
Kim, E. J., Liu, P., Zhang, S., Donahue, K., Wang, Y., Schehr, J. L., & Xu, W. (2021). BAF155 methylation drives metastasis by hijacking super-enhancers and subverting anti-tumor immunity. Nucleic Acids Research, 49(21), 12211–12233. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab1122
Filippakopoulos, P., Qi, J., Picaud, S., Shen, Y., Smith, W. B., Fedorov, O., & Bradner, J. E. (2010). Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains. Nature, 468(7327), 1067–1073. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09504
Shi, J., & Vakoc, C. R. (2014, June 5). The mechanisms behind the therapeutic activity of BET bromodomain inhibition. Molecular Cell. Cell Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.05.016
Nakamura, Y., Hattori, N., Iida, N., Yamashita, S., Mori, A., Kimura, K., & Ushijima, T. (2017). Targeting of super-enhancers and mutant BRAF can suppress growth of BRAF-mutant colon cancer cells via repression of MAPK signaling pathway. Cancer Letters, 402, 100–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.05.017
Gryder, B. E., Yohe, M. E., Chou, H. C., Zhang, X., Marques, J., Wachtel, M., & Khan, J. (2017). PAX3-FOXO1 establishes myogenic super enhancers and confers BET bromodomain vulnerability. Cancer Discovery, 7(8), 884–899. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-1297
BE Gryder L Wu GM Woldemichael S Pomella TR Quinn PMC Park J Khan (2019) Chemical genomics reveals histone deacetylases are required for core regulatory transcription Nature Communications 10 (1) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11046-7
Caslini, C., Hong, S., Ban, Y. J., Chen, X. S., & Ince, T. A. (2019). HDAC7 regulates histone 3 lysine 27 acetylation and transcriptional activity at super-enhancer-associated genes in breast cancer stem cells. Oncogene, 38(39), 6599–6614. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-0897-0
Nguyen, T. T. T., Zhang, Y., Shang, E., Shu, C., Torrini, C., Zhao, J., … Siegelin, M. D. (2020). HDAC inhibitors elicit metabolic reprogramming by targeting super-enhancers in glioblastoma models. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 130(7), 3699–3716. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI129049
C Zhang X Lu J Huang H He L Chen Y Liu D Xu (2021) Epigenome screening highlights that JMJD6 confers an epigenetic vulnerability and mediates sunitinib sensitivity in renal cell carcinoma Clinical and Translational Medicine 11 (2) https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.328
Xiao, L., Parolia, A., Qiao, Y., Bawa, P., Eyunni, S., Mannan, R., & Chinnaiyan, A. M. (2022). Targeting SWI/SNF ATPases in enhancer-addicted prostate cancer. Nature, 601(7893), 434–439. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04246-z
L Li N Wang M Zhu Y Xiong F Wang G Guo Y Gu (2021) Aberrant super-enhancer-driven oncogene ENC1 promotes the radio-resistance of breast carcinoma Cell Death and Disease 12 (8) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-04060-5
B Ye D Fan W Xiong M Li J Yuan Q Jiang Y Qiao (2021) Oncogenic enhancers drive esophageal squamous cell carcinogenesis and metastasis Nature Communications 12 (1) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24813-2
Zhu, X., Zhang, T., Zhang, Y., Chen, H., Shen, J., Jin, X., … Zhou, G. (2020). A super-enhancer controls TGF- β signaling in pancreatic cancer through downregulation of TGFBR2. Cellular Signalling, 66 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2019.109470
Sun, Y., Han, J., Wang, Z., Li, X., Sun, Y., & Hu, Z. (2021, January 26). Safety and efficacy of bromodomain and extra-terminal inhibitors for the treatment of hematological malignancies and solid tumors: A systematic study of clinical trials. Frontiers in Pharmacology. Frontiers Media S.A. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.621093
Jiang, Y. Y., Lin, D. C., Mayakonda, A., Hazawa, M., Ding, L. W., Chien, W. W., & Koeffler, H. P. (2017). Targeting super-enhancer-Associated oncogenes in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gut, 66(8), 1358–1368. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2016-311818
Zhang, J., Liu, W., Zou, C., Zhao, Z., Lai, Y., Shi, Z., & Shen, J. (2020). Targeting super-enhancer–associated oncogenes in osteosarcoma with THZ2, a Covalent CDK7 Inhibitor. Clinical Cancer Research, 26(11), 2681–2692. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1418
Garcia-Martinez, L., Zhang, Y., Nakata, Y., Chan, H. L., & Morey, L. (2021, December 1). Epigenetic mechanisms in breast cancer therapy and resistance. Nature Communications. Nature Research. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-22024-3
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Elise Wright for her help in illustrating the figures.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Institutes of Health R01 CA236356, R01 CA268183, R01 CA281024 to W.X. and the National Cancer Institute NRSA award T32 CA009135 to M.B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.B. and W.X. conceived the idea for this manuscript. M.B. performed the literature search and drafted the manuscript. W.X. critically revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests. We apologize to the authors whose work was not cited due to space limitations.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bacabac, M., Xu, W. Oncogenic super-enhancers in cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Cancer Metastasis Rev 42, 471–480 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-023-10103-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-023-10103-4