Abstract
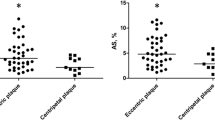
Intravascular ultrasound elastography (IVUSE) is a promising imaging technique for early investigation of vulnerable plaques. Compared to radiofrequency signal processing, digital B-mode analysis is simple and of higher portability. However, rare studies have been reported validating the latter technique in vivo. In this study, we developed an IVUSE computer software system involving semi-automatic border delineation and block-matching algorithm and validated the system in vivo. Seven minipigs were fed with atherogenic diet for 40 weeks. For each pig, the endothelium of one side of the renal arteries was denuded at the fifth week. With cross-correlation analysis, Lagrangian strain was calculated from two intravascular ultrasound images acquired in situ. Sixty regions of interests were selected from 35 elastograms matched well with the corresponding histological slices. Plaque types within these regions were classified as fibrous, fibro-fatty or fatty on Masson’s trichrome and Oil-red O staining. Macrophage infiltration was also evaluated with immunohistology. Comparison between the mean strain value of the region of interest and the histological results revealed significant differences in strain values among different plaque types and non-diseased artery walls. The extent of macrophage infiltration was found to be correlated positively with strain values. For identification of fibro-fatty and fibrous plaques and macrophage infiltration, the system showed high sensitivity (93, 96 and 92%, respectively) and specificity (89, 76 and 66%, respectively), as revealed by receiver operating characteristic analysis. Our IVUSE system based on B-mode analysis is capable of characterizing fibrous and fibro-fatty plaques and macrophage intensity, thus holds potential for identifying vulnerable plaque.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fuster V, Moreno PR, Fayad ZA, Corti R, Badimon JJ (2005) Atherothrombosis and high-risk plaque: part I: evolving concepts. J Am Coll Cardiol 46:937–954
de Korte CL, Pasterkamp G, van der Steen AF, Woutman HA, Bom N (2000) Characterization of plaque components with intravascular ultrasound elastography in human femoral and coronary arteries in vitro. Circulation 102:617–623
Schaar JA, de Korte CL, Mastik F, Strijder C, Pasterkamp G, Boersma E, Serruys PW, Van der Steen AF (2003) Characterizing vulnerable plaque features with intravascular elastography. Circulation 108:2636–2641
Talhami HE, Wilson LS, Neale ML (1994) Spectral tissue strain: a new technique for imaging tissue strain using intravascular ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol 20:759–772
Ryan LK, Foster FS (1997) Ultrasonic measurement of differential displacement and strain in a vascular model. Ultrason Imaging 19:19–38
Hein IA, O’Brien WR (1993) Current time-domain methods for assessing tissue motion by analysis from reflected ultrasound echoes-a review. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 40:84–102
Wan M, Li Y, Li J, Cui Y, Zhou X (2001) Strain imaging and elasticity reconstruction of arteries based on intravascular ultrasound video images. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 48:116–120
Revell J, Mirmehdi M, McNally D (2005) Computer vision elastography: speckle adaptive motion estimation for elastography using ultrasound sequences. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 24:755–766
Shi H, Varghese T (2007) Two-dimensional multi-level strain estimation for discontinuous tissue. Phys Med Biol 52:389–401
Pellot-Barakat C, Frouin F, Insana MF, Herment AA, Herment A (2004) Ultrasound elastography based on multi scale estimations of regularized displacement fields. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 23:153–163
Ganzalez RC, Woods RE (2002) Digital image processing, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Lobregt S, Viergever MA (1995) A discrete dynamic contour model. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 14:12–24
Céspedes EI, de Korte CL, vab der Steen AFW (2000) Intraluminal ultrasonic palpation: assessment of local and cross-sectional tissue stiffness. Ultrasound Med Biol 26:385–396
Mazzone RW, Kornblau S, Durand CM (1980) Shrinkage of lung after chemical fixation for analysis of pulmonary structure-function relations. J Appl Physiol 48:382–385
Dai D, Ding YH, Danielson MA, Kadirvel R, Lewis DA, Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF (2005) Histopathologic and immunohistochemical comparison of human, rabbit, and swine aneurysms embolized with platinum coils. Am J Neuroradiol 26:2560–2568
Lin HL, Xu XS, Lu HX, Zhang L, Li CJ, Tang MX, Sun HW, Liu Y, Zhang Y (2007) Pathological mechanisms and dose dependency of erythrocyte-induced vulnerability of atherosclerotic plaque. J Mol Cell Cardiol 43:272–280
Malik N, Francis SE, Holt CM, Gunn J, Thomas GL, Shepherd L, Chamberlain J, Newman CMH, Cumberland DC, Crossman DC (1998) Apoptosis and cell proliferation after porcine coronary angioplasty. Circulation 98:1657–1665
Pasterkamp G, Schoneveld AH, van der Wal AC, Haudenschild CC, Clarijs RJ, Becker AE, Hillen B, Borst C (1998) Relation of arterial geometry to luminal narrowing and histological markers for plaque vulnerability: the remodeling paradox. J Am Coll Cardiol 32:655–662
Fung YC (1993) Biomechanics: mechanical properties of living tissues, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Chaturvedi P, Insana MF, Hall TJ (1998) Ultrasonic and elasticity imaging to model disease-induced changes in soft-tissue structure. Med Image Anal 2:325–338
Janssen CRM, de Korte CL, van der Heiden MS, Wapennar CPA, van der Steen AFW (2000) Angle matching in intravascular elastography. Ultrasonics 38:417–423
Shi H, Chen Q, Varghese T (2005) A general solution for catheter position effects for strain estimation in intravascular ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol 31:1509–1526
Yueng F, Levinson SF (1998) Feature-adaptive motion tracking of ultrasound image sequences using a deformable mesh. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 17:945–956
de Korte CL, Carlier SG, Mastik F, Doyley MM, van der Steen AFW, Surruys PW, Bom N (2002) Morphological and mechanical information of coronary arteries obtained with intravascular elastography. Eur Heart J 23:405–413
Kearney PP, Ramo MP, Spencer T, Shaw TRD, Starkey IR, McDicken N, Sutherland GR (1997) A study of quantitative and qualitative impact of catheter shaft angulation in a mechanical intravascular ultrasound system. Ultrasound Med Biol 23:87–93
Band W, Goedhard WJA, Knoop AA (1972) Effects of aging on dynamic viscoelastic properties of the rat’s thoracic aorta. Pflugers Arch 331:357–364
de Korte CL, Sierevogel MJ, Mastik F, Strijder C, Schaar JA, Velema E, Pasterkamp G, Serruys PW, van der Steen AF (2002) Identification of atherosclerotic plaque components with intravascular ultrasound elastography in vivo: a Yucatan pig study. Circulation 105:1627–1630
Hiro T, Leung CY, De Guzman S, Caiozzo VJ, Farvid AR, Karimi H, Helfant RH, Tobis JM (1997) Are soft echoes really soft? Intravascular ultrasound assessment of mechanical properties in human atherosclerotic tissue. Am Heart J 133:1–7
Gijsen FJ, Wentzel JJ, Thury A, Mastik F, Schaar JA, Schuurbiers JC, Slager CJ, van der Giessen WJ, de Feyter PJ, van der Steen AF, Serruys PW (2008) Strain distribution over plaques in human coronary arteries relates to shear stress. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:H1608–H1614
Richardson PD, Davies MJ, Born GV (1989) Influence of plaque configuration and stress distribution on fissuring of coronary atherosclerotic plaques. Lancet 2:941–944
Lee RT, Libby P (1997) The unstable atheroma. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 17:1859–1867
Su HJ, Zhang M, Zhang Y (2004) Mechanical model of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque rupture. Sci China Ser G 47:452–462
Van Mieghem CA, Bruining N, Schaar JA, McFadden E, Mollet N, Cademartiri F, Mastik F, Ligthart JM, Granillo GA, Valgimigli M, Sianos G, van der Giessen WJ, Backx B, Morel MA, Van Es GA, Sawyer JD, Kaplow J, Zalewski A, van der Steen AF, de Feyter P, Serruys PW (2005) Rationale and methods of the integrated biomarker and imaging study (IBIS): combining invasive and non-invasive imaging with biomarkers to detect subclinical atherosclerosis and assess coronary lesion biology. Int J Card Imaging 21:425–441
Saijo Y, Tanaka A, Iwamoto T, dos Santos Filho E, Yoshizawa M, Hirosaka A, Kijima M, Akino Y, Hanadate Y, Yambe T (2006) Intravascular two-dimensional tissue strain imaging. Ultrasonics 44:e147–e151
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the technical assistance provided by Drs. Yan-En Zhang and Xian-Quan Cui. This work was supported by grants from the National 973 Basic Research Program of China (No. 2010CB732605), the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 60402023 and No. 60831003) and National 863 Hi-Tech Research and Development Program of China (No. 2007AA02Z448).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors Peng-Fei Zhang, Hai-Jun Su, Mei Zhang, contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, PF., Su, HJ., Zhang, M. et al. Atherosclerotic plaque components characterization and macrophage infiltration identification by intravascular ultrasound elastography based on b-mode analysis: validation in vivo. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 27, 39–49 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-010-9659-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-010-9659-3