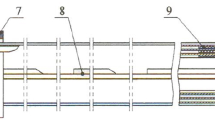
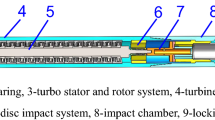
The vibration of a drill string can cause multiple hazards in the process of drilling operations. The conversion of excessive vibration energy of the drill string into the rock breaking energy can provide the dual effect of reducing the risks and improving the rock breaking efficiency of drilling. To address the task, a drill string absorption & hydraulic supercharging device has been developed. However, the design and exploitation of the drill string absorption & hydraulic supercharging device needs a comprehensive understanding of the characteristics of conversion of the drill string’s vibration energy. Based on the drill string dynamics experimental device, a simulation test platform has been developed to evaluate the efficiency of conversion of the vibration energy. The analysis of the test results is used to evaluate the conversion characteristics of the vibration energy of the bottom hole drill string. The results show that the energy conversion efficiency depends on the elastic stiffness and installation position of the drill string absorption & hydraulic supercharging device, the overall rotational speed, and the WOB (weight on bit) of the conversion device. With increase in the elastic stiffness, the conversion efficiency of the vibration energy first increases and then decreases. The closer the installation position of the drill string absorption & hydraulic supercharging device is to the bit, the better the conversion efficiency. With increase in the rotational speed, the conversion efficiency of the vibration energy increases. With increase in the WOB, the conversion efficiency of the vibration energy first increases and then decreases. The research results provide the background for the development and application of speed raising tools based on conversion of the drill string vibration.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Gao, Z. Liu, and X. Guo, “Calculation and measurement of the natural frequency of axial drilling string vibration,” J. Xi’an Pet. Ins., 15(1), 39-43 (2000).
Z. Han, F. Li, L. Yang et al., “Investigation of longitudinal free vibration of drill rod,” J. Gansu Univ. Technol., 28(2), 50-53 (2002).
Y. Zhang and Z. Xiao, “Experimental study severe down hole vibration of drill string and its control,” Oil Field Equip., 28(3), 6-10 (1999).
H. Shi, G. Li, X. Wang, et al., “Improving the rate of penetration by hydraulic pulsating-cavitating water jet under-balance pressure drilling,” Pet. Explor. Dev., 37(1), 111-115 (2010).
Z. Wang, “Discussion on theory & methodology of suction pulse drilling technique,” Oil Drill. Prod. Technol., 27(6), 13215 (2005).
C. Liu, M. Xu, and P. Tang, “Present situation and development trend of downhole electromotive drill,” Drill. Prod. Technol., 31(5), 115-117 (2008).
C. Lu, H. Lu, and F. Li, “Study on a new electric percussive-rotary drilling tool,” Pet. Drill. Techniq., 38(1), 77-79 (2010).
L. Liu, G. Jiang, H. Lu, et al., “Study on the electric percussive drill and its performance test,” Min. Machin., 38(5), 4-7 (2010).
Y. Liu, “Design research on drill string absorption & downhole hydraulic pressurizing system,” Dissertation, Dongying China University of Petroleum (2007).
Z. Guan, Y. Liu, H. Zhang, et al., “Drilling string absorption & hydraulic pulsed jet generator system and drilling method,” China National Patent 201310047969.X.
Z. Guan, H. Zhang, and Y. Liu, “Downhole full displacement pressurizing system,” China National Patent 201320133787.X.
Z. Guan, Y. Liu, W. Wei, et al., “A downhole supercharger system to increase drilling speed,” China Invention Patent ZL 2012 1 0207320.5. 2012.10.3.
Y. Liu and Z. Guan, “A device to increase drilling speed of oil and gas well,” China Invention Patent 201410153115.4. 2014.7.2.
Z. Guan, W. Wei, and Y. Liu, “Downhole device to decrease drilling string vibration and increase pressure,” China Invention Patent ZL 2010 1 0119842.0. 2010.7.28.
Z. Guan, Y. Liu, W. Wei, H. Bo, Y. Xu, and Y. Shi, “Downhole drill string absorption & hydraulic supercharging device working principle and analysis of speed-increasing effect,” Pet. Drill. Techniq., 40(2), 8-13 (2012).
H. Zhang, Z. Guan, Y. Liu, D. Liang, and Y. Xu, “A novel tool to improve the rate of penetration by transferring drilling string vibration energy to hydraulic energy,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., 146, 318-325 (2016).
Y. Liu, Z. Guan, H. Zhang, and B. Zhang, “Development and application of the downhole drilling string shock-absorption and hydraulic supercharging device,” Shock Vibrat., 2016, 2041671 (2016).
Z. Guan, Y. Jin, and Y. Wang, “Experimental research on motion behavior of bottom drill string in straight hole” Acta Pet. Sin., 24(5), 102-106 (2003).
H. Zhang, Z. Guan, H. Wang, et al., “Evaluation test for drilling string vibration energy conversion efficiency,” Chin. Pet. Machin., 24(5), 102-106 (2003).
Y. Shi, Y. Yuan, and C. Wu, “Setting up a simulate device on motion behavior of bottom-hole assembly according to similitude principles,” J. Guangxi Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed., 31(1), 159-162 (2006).
Acknowledgments
The study was funded by the National Major Science and Technology Project (2016ZX05022-002) and the Special Fund Project of the Central Universities Fundamental Research Fund (19CX02065A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 2, pp. 57–60 March– April, 2022.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yongwang, L., Zhichuan, G., Hongning, Z. et al. Study on Vibration Energy Conversion Efficiency of the Drill String Absorption & Hydraulic Supercharging Device. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 58, 340–348 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-022-01390-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-022-01390-8