Abstract
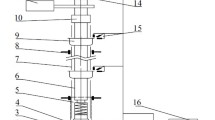
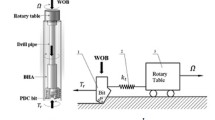
During drilling into hard rocks, the vibration of telescopic drillstring for the rotary drilling rig becomes more severe, which not only leads to the fracture of drillstring, but also reduces the rock-breaking efficiency, the service life, and the reliability of the rotary drilling rig. A drillstring vibration absorber for the rotary drill rig was proposed based on nonlinear targeted energy transfer technology, and the theoretical model of the absorber was adopted. By applying the instantaneous nonlinear energy absorption rate of the absorber, the vibration responses of the system were predicted on different structure parameters and impact amplitudes. To evaluate the feasibility of the absorber, experiments were carried out. Moreover, the amplitude decrease rate was generated for various working conditions. Furthermore, the analytical results were verified by the experiment. The results indicate that the absorber has a distinct effect on vibration reduction.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, Z.Y.; Jiao, S.J.; Wu, F.X.: Rotary Drilling Rig and Construction Technology. Beijing, China (2010)
Thomas Busuyi AFENI: Optimization of drilling and blasting operations in an open pit mine_the SOMAIR experience. Min. Sci. Technol. 19(6), 736–739 (2009)
Sapsis, T.P.; Vakakis, A.F.; Gendelman, O.V.; Bergman, L.A.; Kerschen, G.; Quinn, D.D.: Efficiency of targeted energy transfers in coupled nonlinear oscillators associated with 1:1 resonance captures: part II, analytical study. J. Sound Vib. 325(1–2), 297–320 (2009)
Zhang, Z.; Lu, Z.Q.; Ding, H.; Chen, L.Q.: An inertial nonlinear energy sink. J. Sound Vib. 450, 199–213 (2019)
Gendelman, O.V.; Starosvetsky, Y.; Feldman, M.: Attractors of harmonically forced linear oscillator with attached nonlinear energy sink I: description of response regimes. Nonlinear Dyn. 51, 31–46 (2008)
Avramov, K.V.; Mikhlin, Y.V.: Review of applications of nonlinear normal modes for vibrating mechanical systems. Appl. Mech. Rev. 65(2), 1010–1029 (2013)
Javidialesaadi, A.; Wierschem, N.E.: An inerter-enhanced nonlinear energy sink. Mech. Syst. Signal Process.129, 449–454 (2019)
Hubbard, S.A.; McFarland, D.M.; Bergman, L.A.; Vakakis, A.F.; Andersen, G.: Targeted energy transfer between a swept wing and winglet-housed nonlinear energy sink. AIAA J. 52(12), 2633–2651 (2014)
Lin, D.C.; Oguamanam, D.C.D.: Targeted energy transfer efficiency in a low-dimensional mechanical system with an essentially nonlinear attachment. Nonlinear Dyn. 82, 971–986 (2015)
AL-Shudeifat, M.A.; Vakakis, A.F.; Bergman, L.A.: Shock mitigation by means of low- to high-frequency nonlinear targeted energy transfers in a large-scale structure. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 11(2), 1015–1025 (2016)
Zhang, W.F.; Liu, Y.; Cao, S.L.; Chen, J.H.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhang, J.Z.: Targeted energy transfer between 2-D wing and nonlinear energy sinks and their dynamic behaviors. Nonlinear Dyn.90(3), 1841–1850 (2017)
Dolatabadi, N.; Theodossiades, S.; Rothberg, S.J.: Passive control of piston secondary motion using nonlinear energy absorbers. J. Vib. Acoust. 139(5), 1462–1473 (2017)
Georgiades, F.; Vakakis, A.F.: Dynamics of a linear beam with an attached local nonlinear energy sink. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 12(5), 643–651 (2007)
Huang, X.C.; Su, Z.W.; Hua, H.X.: Optimal parameters for dynamic vibration absorber with negative stiffness in controlling force transmission to a rigid foundation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 152, 88–98 (2019)
Qiu, D.H.; Seguy, S.; Paredes, M.: Tuned nonlinear energy sink with conical spring: design theory and sensitivity analysis. J. Mech. Des. 140(1), 1500–1509 (2018)
Taleshi, M.; Dardel, M.; Pashaie, M.H.: Passive targeted energy transfer in the steady state dynamics of a nonlinear plate with nonlinear absorber. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 92, 56–72 (2016)
Yao, H.L.; Cao, Y.B.; Ding, Z.Y.; Wen, B.C.: Using grounded nonlinear energy sinks to suppress lateral vibration in rotor systems. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 124, 237–253 (2019)
Wei, Y.M.; Dong, X.J.; Guo, P.F.; Feng, Z.K.; Zhang, W.M.: Enhanced targeted energy transfer by vibro impact cubic nonlinear energy sink. Int. J. Appl. Mech. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1142/S1758825118500618
Gendelman, O.V.; Gourdon, E.; Lamarque, C.H.: Quasiperiodic energy pumping in coupled oscillators under periodic forcing. J. Sound Vib. 294(4–5), 651–662 (2006)
Starosvetsky, Y.; Gendelman, O.V.: Response regimes in forced system with nonlinear energy sink: quasi-periodic and random forcing. Nonlinear Dyn. 64(1–2), 177–195 (2011)
Lo Feudo, S.; Touze, C.; Boisson, J.; Cumunel, G.: Nonlinear magnetic vibration absorber for passive control of a multi-storey structure. J. Sound Vib. 438, 33–53 (2019)
Zang, J.; Zhang, Y.W.; Ding, H.; Yang, T.Z.; Chen, L.Q.: The evaluation of a nonlinear energy sink absorber based on the transmissibility. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 125, 99–122 (2019)
Qiu, D.; Seguy, S.; Paredes, M.: Design criteria for optimally tuned vibro-impact nonlinear energy sink. J. Sound Vib. 442, 497–513 (2019)
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank the financial support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51805041, 51774320) and The National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFC0808204) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Nos. 300102259204, 310825152011) and the Scientific Planning Project of Henan Provincial Department of Transportation (Nos. 2018J1, 2019J3) and the Key Technological Special Project of Xinxiang city (No. ZD19007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Gu, H., Kan, Z. et al. Properties of Drillstring Vibration Absorber for Rotary Drilling Rig. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 5849–5858 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04562-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04562-y