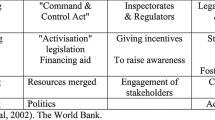
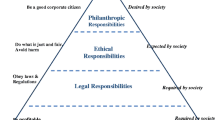
Abstract
This article argues for an extension to the scope of corporate social responsibility (CSR) research to include a contemporary issue of importance to national and global security, critical infrastructure resilience. Rather than extending the multiple perspectives on CSR, this study aimed to identify a method of recognising CSR-related issues, before applying it to two dissimilar case studies on critical infrastructure resilience. One case study was of an international telecommunications company based in the US while the other was of the railway network in Britain during a period of privatisation. The method used was derived from Okoye’s (J Bus Ethics 89(4):613–627, 2009) common reference core for CSR. Both case studies satisfied all the criteria sought which points to critical infrastructure resilience as being an emerging CSR issue. Because ongoing change characterises CSR, the method may have application for identifying future new CSR strands. As the findings suggest that some aspects of national and global security are CSR-related phenomena, the study demonstrates how CSR research may be significant at a societal, national and global level. Implications of the study include a broadening of the value and reach of contributions from CSR researchers and practitioners.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BBC:
-
British Broadcasting Corporation
- CERTs:
-
Community Emergency Response Teams
- CPNI (UK):
-
Centre for the Protection of Critical Infrastructure
- CSR:
-
Corporate social responsibility
- ECC:
-
Essentially contested concept
- PC:
-
Personal computer
- SANS:
-
SysAdmin, Audit, Network, Security
- SRA:
-
Strategic Rail Authority
- UK:
-
United Kingdom
- US:
-
United States
References
Banerjee, S.: 2007, Corporate Social Responsibility: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly, (Edward Elgar, Cheltenham, UK).
BBC News: 2006a, ‘Tories Change Policy on Railways’, 17 July, http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk_politics/5186196.stm. Accessed 30 Dec 2009.
BBC News: 2006b, ‘MPs Raise Rail-franchising Fears’, 5 November, http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk/6117728.stm. Accessed 30 Dec 2009.
Bertels, S. and Vredenburg, H.: 2005, ‘Broadening the Notion of Governance from the Organisation to the domain: A Study of Municipal Water Systems in Canada’, in I. Demirag (ed.), Corporate Social Responsibility, Accountability and Governance: Global Perspectives (Greenleaf Publishing, Sheffield, UK), p. 24-40.
Bradner, S.: 2008, ‘Irrelevant Victories in the World on Spam’, Network World, March 24th, 25(12), 30.
Cabinet Office: 2008, ‘The Pitt Review: Lessons from the 2007 Floods’, http://archive.cabinetoffice.gov.uk/pittreview/thepittreview/final_report.html. Accessed 11 Dec 2009.
Campbell, T.: 2007, ‘The Normative Grounding of Corporate Social Responsibility: A Human Rights Approach’, in D. McBarnet, A., Voiculescu and T. Campbell (eds.), The New Corporate Accountability: Corporate Social Responsibility and the Law (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK), pp. 529-564.
Carroll, A.: 1999, ‘Corporate Social Responsibility Evolution of a Definitional Construct’, Business Society 38(3), 268-295.
Charney, A.: 2005, ‘Combating Cybercrime: A Public-Private Strategy in the Digital Environment', Available:http://web.reed.edu/nwacc/programs/conf05/UNCrimeCongressPaper.doc. Accessed 16 April 2011
Council for Science and Technology: 2009, ‘A National Infrastructure for the 21th Century’, London, UK, http://www.cst.gov.uk/reports/files/national-infrastructure-report.pdf. Accessed 3 Dec 2009.
CPNI (Centre for the Protection of Critical Infrastructure): 2009, ‘What We Do’, http://www.cpni.gov.uk/. Accessed 11 Dec 2009.
Crane, A., McWilliams, A., Matten, D., Moon, J. and Siegel, D.: 2008a, ‘Conclusion’, in A. Crane, A. McWilliams, D. Matten, J. Moon, J. and D. Siegel (eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Corporate Social Responsibility (Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK), pp. 568-575.
Crane, A., McWilliams, A., Matten, D., Moon, J. and Siegel, D.: 2008b, ‘The Corporate Social Responsibility Agenda’, in A. Crane, A. McWilliams, D. Matten, J. Moon, and D. Siegel (eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Corporate Social Responsibility (Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK), pp. 3-15.
Ding, L., Haynes, K. and Liu, Y.: 2008, ‘Telecommunications Infrastructure and Regional Income Convergence in China: Panel Data Approaches’, The Annals of Regional Science 42(4), 843-861.
Economist.com: 2001, ‘A Kinder, Gentler Gorilla?’ April 26, http://www.economist.com/background/displaystory.cfm?story_id=587172. Accessed 2 Jan 2010.
Economist.com: 2009, ‘The End, Sort Of’, December 16, http://www.economist.com/businessfinance/displaystory.cfm?story_id=15108468. Accessed 3 Jan 2010.
Flyvbjerg, B.: 2006, ‘Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research’, Qualitative Inquiry 12(2), 219-245.
Friedman, M.: 1970, ‘The Social Responsibility of Business is to Increase Its Profits’, The New York Times Magazine, 13 September, pp. 124–126.
Gallie, W.: 1955–1956, ‘Essentially Contested Concepts’, in Proceedings of the Aristotelian Society, New Series, Vol. 56, pp. 171–172 (Blackwell Publishing on behalf of The Aristotelian Society), http://www.jstor.org/stable/pdfplus/4544562.pdf. Accessed 17 Dec 2009.
Garriga, E. and Melé, D.: 2004, ‘Corporate Social Responsibility Theories: Mapping the Territory’, Journal of Business Ethics 53(1-2), 51-71.
Harris, C.: 2003, ‘Private Participation in Infrastructure in Developing Countries: Trends, Impacts, and Policy Lessons’, World Bank Working Paper No. 5, The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, Washington DC, USA, http://www.io-base.org/pdf/Private%20Participation%20in%20Infrastructure%20in%20Developing%20Countries-Trends_Impacts_and%20Policy%20Lessons.pdf. Accessed 27 Nov 2009.
Home Office (Office for Security and Counter-Terrorism): 2009, ‘Counter-Terrorism Strategy: Protecting the Critical National Infrastructure’, http://security.homeoffice.gov.uk/counter-terrorism-strategy/working-with-partners1/protect-national-infrastructure/. Accessed 11 Dec 2009.
Keating, P.: 1995, ‘A Framework for Classifying and Evaluating the Theoretical Contributions of Case Research in Management Accounting’, Journal of Management Accounting Research 7, Fall, 66-86.
Kim, J.: 2007, ‘Fears of Foreign Ownership: The Old Face of Economic Nationalism’, SAIS Review 27(2), 167-177.
Leyland, P.: 2005, ‘Back to Government? Reregulating British Railways’, Indiana Journal of Global Legal Studies 12(2), 435-470.
Liddle, R.: 2008, ‘Bring Back British Rail, All is Forgiven’, TIMESONLINE, 6 Jan, http://www.timesonline.co.uk/tol/news/uk/article3136505.ece. Accessed 30 Dec 2009.
Lockett, A., Moon, J. and Visser, W.: 2006, ‘Corporate Social Responsibility in Management Research: Focus, nature, salience and sources of influence’, Journal of Management Studies, Vol. 43(1), pp. 115-136.
McWilliams, A., Siegel, D. and Wright, P.: 2006, ‘Corporate Social Responsibility: Strategic Implications’, Journal of Management Studies 43(1), 1-18.
Melé, D.: 2008, ‘Corporate Social Responsibility Theories’, in A. Crane, A. McWilliams,D. Matten, J. Moon, J. and D. Siegel (eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Corporate Social Responsibility (Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK), pp. 47-82.
Microsoft Corporation: 2009, ‘Microsoft Office 2010 Engineering’, http://blogs.technet.com/office2010/archive/2009/10/07/new-ways-to-try-and-buy-microsoft-office-2010.aspx. Accessed 30 Dec 2009.
Moon, J.; Kang, N.; Gond, J.-P.: 2010, “Corporate Social Responsibility and Government”, in D. Coen; W. Grant; G. Wilson, (eds) Oxford Handbook of Business and Government, (Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK), pp. 512-543.
National Archives: n.d., ‘How did the Railways Change the Lives of People in Victorian Britain?’, http://www.nationalarchives.gov.uk/education/victorianbritain/happy/default.htm. Accessed 2 Jan 2009.
O’Brien, K.: 2009, ‘Managing national security and law enforcement intelligence in a globalised world’, Review of International Studies 35, 903-915.
OECD Statistics Directorate: 2007, Digital Economy Working Papers, L'Elaboration des Politiques pour la Protection des Infrastructurs D'Information Critiques, No. 130, pp. 1–2, 5–79
O’Rourke, T.: 1994, ‘Lifeline Engineering Integrates Infrastructure’, Civil Engineering 64(1), 6.
Okoye, A.: 2009, ‘Theorising Corporate Social Responsibility as an Essentially Contested Concept: Is a Definition Necessary?’ Journal of Business Ethics 89(4), 613-627.
Samaha, K.: 2005, ‘A Systematic View of US Government in Market Governance: Lessons Learned from the California Electricity Crisis’, in I. Demirag (Ed.), Corporate Social Responsibility, Accountability and Governance: Global Perspectives (Greenleaf Publishing, Sheffield, UK), pp. 271-290.
SANS (SysAdmin, Audit, Network, Security) Institute: 2009, September, ‘The Top Cyber Security Risks’, http://www.sans.org/top-cyber-security-risks/. Accessed 2 Jan 2010.
Scherer, A. and Palazzo, G.: 2008, ‘Globalization and Corporate Social Responsibility’, in A. Crane, A. McWilliams, D. Matten, J. Moon, J. and D. Siegel (eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Corporate Social Responsibility (Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK), pp. 413-431.
Sullivan, H. and Skelcher, C.: 2002, Working Across Boundaries: Collaboration in Public Services, (Palgrave, Basingstoke, UK).
Sutherland, J.: 1975, Systems: Analysis, Administration and Architecture, (Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York, USA).
The Economist: 2004, ‘Sir Bill and his Dragons: Past, Present and Future’, 29 Jan, http://www.economist.com/displaystory.cfm?story_id=2384623&source=login_payBarrier. Accessed 23 Dec 2009.
Vaughan, A.: 1997, Railwaymen, Politics and Money: The Great Age of Railways in Britain, (Trafalgar Square Publishing, London, UK).
Waldron, J.: 2002, ‘Is the Rule of Law an Essentially Contested Concept (In Florida)?’ Law and Philosophy 21(2), 137-164.
Whitman, J.: 2005, ‘Disseminative Systems and Global Governance’, Global Governance 11(1), 85-102.
Windsor, D.: 2006, ‘Corporate Social Responsibility: Three key approaches’, Journal of Management Studies; 43(1), pp. 93-114.
Wrigley, C.: 2009, ‘British Railways, 1997–2005: Labour’s Strategic Experiment (Review)’, Business History Review 83(3), 607-609.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ridley, G. National Security as a Corporate Social Responsibility: Critical Infrastructure Resilience. J Bus Ethics 103, 111–125 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-011-0845-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-011-0845-6