Abstract
Purpose
CYP4Z1 is a human cytochrome P450 enzyme involved in breast cancer progression and prognosis, but its functional role in these processes is not understood. In order to gain more insight into CYP4Z1’s properties it was recombinantly expressed in a host animal that does not have an endogenous homologue.
Methods
We generated a transgenic mouse model that specifically expresses human CYP4Z1 in breast tissue under the control of the whey acidic protein promoter. Complementary experiments were done using cell lines derived from human breast cell.
Results
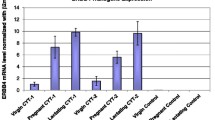
Induction of CYP4Z1 expression led to reduction of body weight, activity, and birth rates. Histological analysis revealed no evidence for tumor formation. However, a strong increase in estrogen receptor alpha was observed by immunohistochemistry; weaker but significantly increased immunoreactivity was also detected for collagen I and fibronectin. Overexpression of CYP4Z1 in the human breast cancer cell line MCF7 also led to increased ERα expression. Moreover, increased expression of both CYP4Z1 and ERα was observed in MCF-10A normal breast cells upon cocultivation with MCF-7 cells (with or without overexpression of CYP4Z1).
Conclusion
These data suggest that CYP4Z1 facilitates breast cancer development by induction of ERα expression via an as yet undefined mechanism.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AI:
-
Aromatase inhibitor
- BC:
-
Breast cancer
- CYP:
-
Human cytochrome P450 enzyme
- Cyp:
-
Mouse cytochrome P450 enzyme
- E2:
-
Estradiol
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SERD:
-
Selective estrogen receptor degrader
- SERM:
-
Selective estrogen receptor modulator
- WAP:
-
Whey acidic protein
References
Means GD, Mahendroo MS, Corbin CJ, Mathis JM, Powell FE, Mendelson CR, Simpson ER (1989) Structural analysis of the gene encoding human aromatase cytochrome P-450, the enzyme responsible for estrogen biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 264(32):19385–19391
Rosenfeld CS, Shay DA, Vieira-Potter VJ (2018) Cognitive effects of aromatase and possible role in memory disorders. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 9:610
Patel HK, Bihani T (2018) Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) and selective estrogen receptor degraders (SERDs) in cancer treatment. Pharmacol Ther 186:1–24
Durairaj P, Fan L, Du W, Ahmad S, Mebrahtu D, Sharma S, Ashraf RA, Liu J, Liu Q, Bureik M (2019) Functional expression and activity screening of all human cytochrome P450 enzymes in fission yeast. FEBS Lett 593(12):1372–1380
Hrycay EG, Bandiera SM (2015) Involvement of cytochrome P450 in reactive oxygen species formation and cancer. Adv Pharmacol 74:35–84
Rieger MA, Ebner R, Bell DR, Kiessling A, Rohayem J, Schmitz M, Temme A, Rieber EP, Weigle B (2004) Identification of a novel mammary-restricted cytochrome P450, CYP4Z1, with overexpression in breast carcinoma. Cancer Res 64(7):2357–2364
Zöllner A, Dragan CA, Pistorius D, Muller R, Bode HB, Peters FT, Maurer HH, Bureik M (2009) Human CYP4Z1 catalyzes the in-chain hydroxylation of lauric acid and myristic acid. Biol Chem 390(4):313–317
McDonald MG, Ray S, Amorosi CJ, Sitko KA, Kowalski JP, Paco L, Nath A, Gallis B, Totah RA, Dunham MJ, Fowler DM, Rettie AE (2017) Expression and functional characterization of breast cancer-associated cytochrome P450 4Z1 in saccharomyces cerevisiae. Drug Metab Dispos 45(12):1364–1371
Kowalski JP, McDonald MG, Pelletier RD, Hanenberg H, Wiek C, Rettie AE (2020) Design and characterization of the first selective and potent mechanism-based inhibitor of cytochrome P450 4Z1. J Med Chem 63(9):4824–4836
Machalz D, Li H, Du W, Sharma S, Liu S, Bureik M, Wolber G (2021) Discovery of a novel potent cytochrome P450 CYP4Z1 inhibitor. Eur J Med Chem 215: 113255.
Yang X, Hutter M, Goh WW, Bureik M (2017) CYP4Z1 - a human cytochrome P450 enzyme that might hold the key to curing breast cancer. Curr Pharm Des 23(14):2060–2064
Sato M, Inada E, Saitoh I, Watanabe S, Nakamura S (2020) piggyBac-based non-viral in vivo gene delivery useful for production of genetically modified animals and organs. Pharmaceutics 12(3):277
Ding S, Wu X, Li G, Han M, Zhuang Y, Xu T (2005) Efficient transposition of the piggyBac (PB) transposon in mammalian cells and mice. Cell 122(3):473–483
Kim A, Pyykko I (2011) Size matters: versatile use of PiggyBac transposons as a genetic manipulation tool. Mol Cell Biochem 354(1–2):301–309
Ittner LM, Götz J (2007) Pronuclear injection for the production of transgenic mice. Nature Protocols 2(5):1206
Pittius CW, Hennighausen L, Lee E, Westphal H, Nicols E, Vitale J, Gordon K (1988) A milk protein gene promoter directs the expression of human tissue plasminogen activator cDNA to the mammary gland in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 85(16):5874–5878
Nukumi N, Ikeda K, Osawa M, Iwamori T, Naito K, Tojo H (2004) Regulatory function of whey acidic protein in the proliferation of mouse mammary epithelial cells in vivo and in vitro. Dev Biol 274(1):31–44
Jonkers J, Derksen PW (2007) Modeling metastatic breast cancer in mice. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 12(2–3):191–203
Fantozzi A, Christofori G (2006) Mouse models of breast cancer metastasis. Breast Cancer Res 8(4):1–11
Caligioni CS (2009) Assessing reproductive status/stages in mice. Curr Protocols Neurosci 48(1):A. 4I. 1-A. 4I. 8
Riddle O (1940) Lactogenic and mammogenic hormones. J Am Med Assoc 115(26):2276–2281
Lloyd-Lewis B, Sargeant TJ, Kreuzaler PA, Resemann HK, Pensa S, Watson CJ (2017) Analysis of the involuting mouse mammary gland: an in vivo model for cell death. Springer, In Mammary Gland Development, pp 165–186
Charan J, Kantharia N (2013) How to calculate sample size in animal studies? J Pharmacol Pharmacother 4(4):303
Festing MF, Altman DG (2002) Guidelines for the design and statistical analysis of experiments using laboratory animals. ILAR J 43(4):244–258
Festing MF (2006) Design and statistical methods in studies using animal models of development. ILAR J 47(1):5–14
Paster EV, Villines KA, Hickman DL (2009) Endpoints for mouse abdominal tumor models: refinement of current criteria. Comp Med 59(3):234–241
Foltz CJ, Ullman-Cullere M (1999) Guidelines for assessing the health and condition of mice. Lab Anim 28(5).
Morton DB (2000) A systematic approach for establishing humane endpoints. ILAR J 41(2):80–86
Burkholder T, Foltz C, Karlsson E, Linton CG, Smith JM (2012) Health evaluation of experimental laboratory mice. Curr Protocols Mouse Biol 2(2):145–165
Thompson C, Keck K, Hielscher A (2017) Isolation of intact, whole mouse mammary glands for analysis of extracellular matrix expression and gland morphology. JoVE(128), e56512.
Sampias C, Rolls G (2019) H&E staining overview: a guide to best practices. Wetzlar: Leica Biosystems
Phillips PG, Birnby LM, Narendran A, Milonovich WL (2001) Nitric oxide modulates capillary formation at the endothelial cell-tumor cell interface. Am J Physiol-Lung Cell Mol Physiol 281(1):L278–L290
Lincoln DW, Phillips PG, Bove K (2003) Estrogen-induced Ets-1 promotes capillary formation in an in vitro tumor angiogenesis model. Breast Cancer Res Treat 78(2):167–178
Khayeka-Wandabwa C, Ma X, Cao X, Nunna V, Pathak JL, Bernhardt R, Cai P, Bureik M (2019) Plasma membrane localization of CYP4Z1 and CYP19A1 and the detection of anti-CYP19A1 autoantibodies in humans. Int Immunopharmacol 73:64–71
Nunna V, Jalal N, Bureik M (2017) Anti-CYP4Z1 autoantibodies detected in breast cancer patients. Cell Mol Immunol.
Murray GI, Patimalla S, Stewart KN, Miller ID, Heys SD (2010) Profiling the expression of cytochrome P450 in breast cancer. Histopathology 57(2):202–211
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Lu Xinran and Li Futian of the Institute of Radiation Medicine of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Tianjin, for technical support in rearing and monitoring of the animals used in this study. We also thank Wu Che-lin of Beijing Maid Conner Biotechnology for technical assistance in the pathology work of this study.
Funding
No funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: CKW, JLP, HW, and MB; experimental work: CKW and JZ; formal analysis and visualization: CKW and MB; writing: CKW, JLP, HW, and MB. The authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures for handling of animals were approved by the institutional animal research ethical committee (protocol number IRM20180503).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khayeka-Wandabwa, C., Zhao, J., Pathak, J.L. et al. Upregulation of estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) expression in transgenic mice expressing human CYP4Z1. Breast Cancer Res Treat 191, 319–326 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-021-06435-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-021-06435-w