Abstract
Purpose
Androgen receptor (AR) expression occurs in up to 86% of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive (HER2+) breast cancers. In vitro, AR inhibitors enhance antitumor activity of trastuzumab, an anti-HER2 antibody, in trastuzumab-resistant HER2+ cell lines. This open-label, single-arm, phase II study evaluated the efficacy and safety of enzalutamide, an AR-signaling inhibitor, in patients with advanced HER2+ AR+ breast cancer previously treated with trastuzumab.
Methods
Eligible patients had measurable or non-measurable evaluable disease per Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) v1.1, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group status ≤ 1, no history of brain metastases, and previously received ≥ 1 anti-HER2 regimen for advanced disease. Patients received 160 mg oral enzalutamide daily and 6 mg/kg intravenous trastuzumab every 21 days until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Primary end point was clinical benefit rate at 24 weeks (CBR24); secondary end points included progression-free survival (PFS) and safety.
Results
Overall, 103 women were enrolled [median age 60 years (range 34–83)]; 62% had received ≥ 3 lines of prior anti-HER2 therapy. CBR24, comprising patients with confirmed partial responses (5%) and durable stable disease at 24 weeks (19%), was 24% in the efficacy evaluable set (n = 89). CBR24 did not seem related to AR-expression levels or hormone receptor status. Median PFS was 3.4 months (95% confidence interval 2.0–3.8). Overall, 97 (94%) patients experienced treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs), with fatigue most common (34%). Dyspnea (4%) and malignant neoplasm progression (3%) were the only TEAEs grade ≥ 3 reported in ≥ 3 patients. 22 patients (21%) reported serious TEAEs. Four patients (4%) experienced fatal, non-drug-related TEAEs.
Conclusions
Enzalutamide plus trastuzumab was well tolerated, and a subset of patients in this heavily pretreated population had durable disease control. Determination of biomarkers is needed to identify patients most likely to benefit from this combination.
ClinicalTrials.gov number
NCT02091960
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Breast cancer is among the most frequently diagnosed malignancies and the second most common cause of cancer deaths in women worldwide, with an estimated 1.67 million new cases diagnosed globally in 2012 [1]. Breast cancer, including metastatic breast cancer (MBC), is a heterogeneous disease, making its prognosis and management complex. While the 5-year relative survival rate is 99% for patients presenting with localized disease, it is only 27% for patients with MBC [2]. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) is amplified/overexpressed in approximately 15% of all breast cancer cases [3], making treatment recommendations for MBC highly dependent on hormone receptor (HR) and HER2 status [3, 4]. Survival for patients with HER2-positive (HER2+) MBC has been significantly prolonged due to anti-HER2 therapies [5,6,7,8,9].
The recommended first-line treatment for HER2+ MBC is chemotherapy plus dual HER2 inhibition with trastuzumab and pertuzumab [3, 4]. Trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) is recommended over lapatinib plus capecitabine as standard second-line therapy after trastuzumab-based first-line treatment [4]. In practice, the anti-HER2 agent selected depends on country-specific availability, previous anti-HER2 therapy, and time to relapse [4, 10]. However, even with full access to anti-HER2 agents, the vast majority of patients will eventually experience disease progression. Thus, there remains an unmet medical need in HER2+ MBC treatment for effective new therapies [3, 4].
Androgen receptor (AR) expression is observed in up to 86% of HER2+ breast cancers [11,12,13] and has been investigated as a potential therapeutic target in breast cancer. The AR-signaling inhibitor enzalutamide [14] is either approved or under regulatory consideration for approval for castration-resistant prostate cancer, irrespective of the presence of metastases, and metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (also known as metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer) around the world [15,16,17]. Enzalutamide enhances the in vitro antitumor activity of trastuzumab in trastuzumab-resistant HER2+ cell lines [18], warranting clinical investigation of whether inhibiting AR in HER2+ breast cancers in combination with currently available anti-HER2 therapeutics could improve patient outcomes. We therefore evaluated the efficacy and safety of combining the anti-HER2 therapy trastuzumab with enzalutamide in patients with HER2+ AR+ locally advanced breast cancer or MBC.
Patients and methods
Study design
This was a multinational, multicenter, open-label, single-arm, two-stage, phase II trial evaluating the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of enzalutamide in combination with trastuzumab (NCT02091960). The study was approved by an independent ethics review board at each participating site or by national authorities and was conducted according to the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki and the Good Clinical Practice Guidelines of the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use.
Study population
Eligible patients were women aged ≥ 18 years with histologically or cytologically proven HER2+ AR+ breast carcinoma (see Online Resource 1: Patients and methods). Inclusion in the study could be based on local or central pathology assessment. Patients with locally assessed breast cancer also had their samples sent for central pathology laboratory assessment. Patients were allowed to remain in the study if subsequent central assessment did not confirm locally assessed AR+ breast carcinoma.
Inclusion criteria of the study included the following: (i) metastatic or locally advanced disease that was not amenable to curative treatment and had to have measurable or non-measurable, evaluable disease per Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) v1.1 [19], (ii) previous treatment with ≥ 1 line of anti-HER2 therapy in the metastatic or locally advanced disease setting, (iii) documented progression or discontinued the most recent anti-HER2 therapy due to investigator decision or toxicity other than cardiotoxicity, and (iv) an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status ≤ 1 and a minimum life expectancy of ≥ 6 months. Exclusion criteria included (i) severe concurrent disease, (ii) severe infection or significant comorbidity, (iii) known or suspected brain metastases or active leptomeningeal disease, (iv) a history of a non-breast-cancer malignancy, (v) inadequate marrow, hepatic, and/or renal function, (vi) a history of seizures, and (vii) clinically significant cardiovascular disease.
Analysis sets
The safety analysis set (SAF) included all enrolled patients who received at least one or a partial dose of study treatment. The full analysis set (FAS) was defined as all patients in the SAF who had centrally assessed AR+ breast cancer (defined as ≥ 10% of tumor cells with nuclear expression). The efficacy evaluable set (EES) included all patients in the FAS who had at least one available post-baseline tumor assessment. The primary analysis was performed in the EES, while all efficacy analyses were performed in both the EES and FAS. Patient disposition and safety were based on SAF.
Treatments
Patients received a once-daily oral dose of 160 mg enzalutamide (4 × 40 mg capsules) and trastuzumab, starting with a loading dose (8 mg/kg) followed by either intravenous (6 mg/kg) or subcutaneous (600 mg/5 mL) administration every 21 days. Dose interruptions or modifications of enzalutamide and trastuzumab were permitted due to toxicity, as defined in the study protocol (see Online Resource 1: Patients and methods). Patients continued on treatment until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or any other discontinuation criteria were met.
Study end points
Primary end point was clinical benefit rate at 24 weeks (CBR24), defined as the proportion of evaluable patients with best objective response of confirmed complete response (CR) or partial response (PR) per RECIST v1.1 or prolonged stable disease (SD) ≥ 24 weeks. Key secondary end points were best overall response rate (BORR; CR or PR), overall response rate (ORR; CR or PR) at 24 weeks, progression-free survival (PFS), time to progression (TTP), time to response (TTR), and safety. Prespecified exploratory end points included CBR24 in subgroups by AR-expression levels, hormone receptor (HR) status, and lines of prior therapy.
Assessments
Radiographic disease assessments according to RECIST v1.1 [19] were performed by the investigator at baseline and every 8 weeks up to week 49, then every 12 weeks thereafter. Local AR testing results were confirmed centrally using the Ventana Assay (Ventana Medical Systems, Inc., Tucson, USA) (see Online Resource 1: Patients and methods). Safety assessments throughout the study included the recording of adverse events (AEs). Cardiac safety assessments were required throughout the study to monitor for trastuzumab-associated cardiotoxicity (see Online Resource 1: Patients and methods).
Statistical analysis
The study followed an optimal Simon’s two-stage design to determine sample sizes. A CBR24 of ≥ 3 out of 21 evaluable patients was required in stage I to continue to stage II. In total, approximately 80 patients were planned to be enrolled to achieve a dataset with at least 66 evaluable AR+ patients. The null hypothesis that the true CBR24 is ≤ 10% was tested against a one-sided alternative at a 5% significance level. This design has a statistical power of 90% when the true CBR24 is 25%. Patients in the FAS were included in primary and secondary efficacy analyses. See Online Resource 2: Statistical analysis for descriptive statistics. CBR, BORR, and ORR are summarized, including 95% two-sided exact confidence intervals (CIs) (Clopper–Pearson method). Kaplan–Meier analyses were used to estimate the median PFS, TTP, and TTR.
Results
This trial was conducted in 35 centers in six countries (Belgium, Canada, Italy, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States). Between September 2014 and August 2016, 103 patients were enrolled and received at least one dose of enzalutamide and trastuzumab (see Online Resource 3: Fig. S1). The actual enrollment was greater than the planned enrollment goal of 80 patients due to increased screening and patient recruitment. At the end of stage I, six out of 22 evaluable patients (27%; 95% CI 10.7–50.2) demonstrated CBR24, thus meeting the prespecified requirement for the study to continue to stage II.
Baseline patient demographics and disease characteristics are reported in Table 1. In the efficacy evaluable set, approximately 52% of patients were HR + and 87% were perimenopausal or post menopausal. All patients had been previously treated with trastuzumab, and 62% had received ≥ 3 lines of prior anti-HER2 therapy. HER2 status was locally determined. Local AR testing results were confirmed centrally using the Ventana Assay, with a concordance level of 98.6% (see Online Resource 4: Table S1). AR staining was high (i.e., 50–100% positive cells) in approximately 90% of patients.
The median duration of exposure for enzalutamide was 70 days (range 1–660). Patients received a median of four trastuzumab infusions (see Online Resource 5: Table S2). At the time of data cut-off (February 2017), 12 (12%) patients remained on treatment.
Efficacy
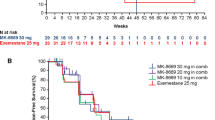
In the primary efficacy analysis set, CBR24 was 24% (21/89 patients) (Table 2). Four (5%) patients had confirmed PR and 17 (19%) patients had durable SD at 24 weeks. Additionally, 42 (47%) patients had a best overall response of SD. BORR was 5% and ORR at 24 weeks was 3%. Median TTR and TTP were 57.0 days (range 57–222) and 108.0 days (95% CI 61–116), respectively. Median PFS was 3.4 months (95% CI 2.0–3.8) (Fig. 1a). A plot of response to treatment for individual patients is shown in Fig. 1b.
a Kaplan–Meier curve of progression-free survivala in the full analysis set; b swimmer plot of response to treatment for individual patients aProgression-free survival is defined as the time from the date of first dose of enzalutamide until the date of disease progression per RECIST v1.1 or death from any cause on study (death within 168 days after treatment discontinuation), whichever occurred first CI confidence interval, RECIST Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors
Exploratory efficacy subgroup analyses
In exploratory analyses of efficacy in subgroups defined by AR-expression level (percentage of tumor cells with nuclear expression) and by HR status (HR + or HR−), CBR24 was similar in all subgroups versus the overall patient population (see Online Resource 6: Table S3). Additionally, efficacy did not appear to be affected by the number of previous lines of antineoplastic therapy or anti-HER2 therapy (see Online Resource 7: Table S4).
Safety
Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) of any grade were reported in 97 (94%) patients; the most common (≥ 10%) included fatigue in 35 (34%) and nausea in 28 (27%) patients (Table 3). Dyspnea (four patients = 4%) and malignant neoplasm progression due to breast cancer (three patients = 3%) were the only TEAEs of grade ≥ 3 reported in ≥ 3 patients. Serious TEAEs were reported in 22 (21%) patients; the most frequent (≥ 2.0%) were malignant neoplasm progression due to breast cancer (five patients = 5%), nausea (three patients = 3%), and vomiting (three patients = 3%). Four patients (4%) experienced fatal TEAEs: (i) two malignant neoplasm progression, (ii) one pulmonary edema, and (iii) one general physical health deterioration associated with concurrent worsening abdominal pain and dyspnea. None of these fatal AEs were assessed as related to a study drug.
Enzalutamide- or trastuzumab-related TEAEs occurred in 78 (76%) patients (Table 3). Eight serious enzalutamide-related TEAEs, nausea (two events), vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia, asthenia, accidental overdose, and dyspnea, were reported in three (3%) patients; no trastuzumab-related serious TEAEs were reported. Drug-related TEAEs necessitating dose reduction of enzalutamide occurred in seven (7%) patients (see Online Resource 5: Table S2), the most frequent being fatigue (three patients = 3%). Study-drug-related TEAEs led to permanent discontinuation of enzalutamide in five (5%) and of trastuzumab in four (4%) patients (Table 3).
Discussion
In this single-arm phase II study of enzalutamide plus trastuzumab in heavily pretreated patients with advanced HER2+ AR+ breast cancer, CBR24 was 24% in the primary analysis set, with a BORR of 5%. Overall, a median PFS of 3.4 months was observed.
Direct comparisons cannot be made across different clinical studies due to the heavily pretreated nature and specific AR+ subset of the HER2+ MBC patient population in this study, for which equivalent data are scarce. In a study with HER2+ locally advanced/MBC patients who had received a median of three trastuzumab regimens, lapatinib in combination with trastuzumab showed an ORR of 10.3% compared to 6.9% for lapatinib alone [6]. In the TH3RESA study of T-DM1 in patients who had previously received ≥ 2 HER2-directed regimens in the advanced setting, including trastuzumab and lapatinib, median PFS (T-DM1 = 6.2 months versus physicians’ choice = 3.3 months) was higher than in the current study for T-DM1, although the patient populations are not directly comparable [20]. Overall, the combination of trastuzumab plus enzalutamide appears to offer durable disease control in a subset of patients with heavily pretreated HER2+ AR+ MBC; however, the clinical impact of this observation is limited because those patients most likely to benefit could not be identified in advance.
The interpretation of these efficacy results should take into account the heavily pretreated patient population in this study (> 60% having received ≥ 3 previous lines of anti-HER2 therapy), although the number of previous lines of anti-HER2 therapy did not appear to be associated with CBR24. In this study, AR-expression levels and HR status did not appear to predict benefit of the combination. However, preclinical data suggest that AR plays a differential role in tumor suppression and oncogenesis within ER+ and ER− breast tissue, respectively [21]. The use of more sophisticated analyses of endocrine signaling may reveal the interaction of HR status and AR in HER2+ MBC in future trials. Current treatments for HER2+ MBC are based on anti-HER2 therapies [3, 4]; however, there remains a need for new targeted treatments with predictive biomarkers to identify patient subgroups that are most likely to respond, including patients with HER2+ AR+ MBC. Indeed, multiple new treatments are being evaluated for HER2+ MBC, including cyclin D-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors, mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors, immunotherapies, antibody drug conjugates, monoclonal antibodies, and therapeutic dendritic cell-based vaccines [22, 23].
In this study, enzalutamide showed a favorable safety profile, consistent with that seen in men with prostate cancer [17] and women with AR-expressing, triple-negative breast cancer [24]. No new safety signals were observed in this female breast cancer population. The frequencies of the most common enzalutamide-related TEAEs in this study, fatigue (30%) and nausea (20%), were in line with those reported in previous enzalutamide trials in men.
This study had limitations. It was a single-arm study consisting of a heterogenous population and, consequently, direct comparison of the efficacy and safety results of enzalutamide plus trastuzumab with other therapies is not possible. Moreover, information that may have assisted in the exploratory analyses to identify predictive biomarkers, such as further details of local genetic testing (e.g., HER2 gene copy number and fluorescence in situ hybridization ratio) and definitions of local estrogen receptor and/or progesterone receptor positivity, were not collected. Importantly, we were unable to centrally assess 24 locally reviewed AR+ cases and 11 HER2+ cases due to a lack of sample material.
Conclusions
The combination of enzalutamide and trastuzumab was well tolerated, and a subset of patients derived durable disease control. Determination of biomarkers to identify patients most likely to benefit from this combination are needed for this intervention to have a meaningful clinical impact.
Data availability
Access to anonymized individual participant level data collected during the study, in addition to supporting clinical documentation, is planned for studies conducted with approved product indications and formulations, as well as compounds terminated during development. Studies conducted with product indications or formulations that remain active in development are assessed after study completion to determine if Individual Participant Data can be shared. Conditions and exceptions are described under the Sponsor Specific Details for Astellas on www.clinicalstudydatarequest.com. Study-related supporting documentation is redacted and provided if available, such as the protocol and amendments, statistical analysis plan, and clinical study report. Access to participant level data is offered to researchers after publication of the primary manuscript (if applicable) and is available as long as Astellas has legal authority to provide the data. Researchers must submit a proposal to conduct a scientifically relevant analysis of the study data. The research proposal is reviewed by an Independent Research Panel. If the proposal is approved, access to the study data is provided in a secure data sharing environment after receipt of a signed Data Sharing Agreement.
Abbreviations
- AE:
-
Adverse event
- AR:
-
Androgen receptor
- AR+:
-
Androgen receptor-positive
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- BORR:
-
Best overall response rate
- CBR24:
-
Clinical benefit rate at 24 weeks
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CR:
-
Complete response
- ECOG:
-
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group
- EES:
-
Efficacy evaluable set
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- FAS:
-
Full analysis set
- FISH:
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridization
- HER2:
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
- HER2+:
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive
- HR:
-
Hormone receptor
- MBC:
-
Metastatic breast cancer
- NA:
-
Data not available
- NCI CTCAE:
-
National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events
- ORR:
-
Overall response rate
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- PgR:
-
Progesterone receptor
- PR:
-
Partial response
- RECIST:
-
Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors
- SAF:
-
Safety analysis set
- SD:
-
Stable disease
- T-DM1:
-
Trastuzumab emtansine
- TEAE:
-
Treatment-emergent adverse event
- TTP:
-
Time to progression
- TTR:
-
Time to response
References
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F (2015) Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 136(5):E359–E386. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29210
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2019) Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin 69(1):7–34. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21551
Giordano SH, Temin S, Chandarlapaty S, Crews JR, Esteva FJ, Kirshner JJ, Krop IE, Levinson J, Lin NU, Modi S, Patt DA, Perlmutter J, Ramakrishna N, Winer EP, Davidson NE (2018) Systemic therapy for patients with advanced human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer: ASCO clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol 36(26):2736–2740. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2018.79.2697
Cardoso F, Costa A, Senkus E et al (2017) 3rd ESO–ESMO international consensus guidelines for Advanced Breast Cancer (ABC 3). Breast 31:244–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.breast.2016.10.001
Swain SM, Baselga J, Kim SB, Ro J, Semiglazov V, Campone M, Ciruelos E, Ferrero JM, Schneeweiss A, Heeson S, Clark E, Ross G, Benyunes MC, Cortés J, CLEOPATRA Study Group (2015) Pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med 372(8):724–734. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1413513
Blackwell KL, Burstein HJ, Storniolo AM, Rugo H, Sledge G, Koehler M, Ellis C, Casey M, Vukelja S, Bischoff J, Baselga J, O’Shaughnessy J (2010) Randomized study of lapatinib alone or in combination with trastuzumab in women with ErbB2-positive, trastuzumab-refractory metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 28(7):1124–1130. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2008.21.4437
Krop IE, Kim SB, Martin AG, LoRusso PM, Ferrero JM, Badovinac-Crnjevic T, Hoersch S, Smitt M, Wildiers H (2017) Trastuzumab emtansine versus treatment of physician’s choice in patients with previously treated HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (TH3RESA): final overall survival results from a randomised open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 18(6):743–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30313-3
Verma S, Miles D, Gianni L, Krop IE, Welslau M, Baselga J, Pegram M, Oh DY, Diéras V, Guardino E, Fang L, Lu MW, Olsen S, Blackwell K, EMILIA Study Group (2012) Trastuzumab emtansine for HER2-positive advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 367(19):1783–1791. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1209124
Swain SM, Kim SB, Cortés J, Ro J, Semiglazov V, Campone M, Ciruelos E, Ferrero JM, Schneeweiss A, Knott A, Clark E, Ross G, Benyunes MC, Baselga J (2013) Pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (CLEOPATRA study): overall survival results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 14(6):461–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(13)70130-x
Giordano SH, Temin S, Kirshner JJ et al (2014) Systemic therapy for patients with advanced human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol 32(19):2078–2099. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2013.54.0948
Micello D, Marando A, Sahnane N, Riva C, Capella C, Sessa F (2010) Androgen receptor is frequently expressed in HER2-positive, ER/PR-negative breast cancers. Virchows Arch 457(4):467–476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-010-0964-y
Park S, Koo J, Park HS, Kim JH, Choi SY, Lee JH, Park BW, Lee KS (2010) Expression of androgen receptors in primary breast cancer. Ann Oncol 21(3):488–492. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdp510
Qi JP, Yang YL, Zhu H, Wang J, Jia Y, Liu N, Song YJ, Zan LK, Zhang X, Zhou M, Gu YH, Liu T, Hicks DG, Tang P (2012) Expression of the androgen receptor and its correlation with molecular subtypes in 980 Chinese breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer (Auckl) 6:1–8. https://doi.org/10.4137/BCBCR.S8323
Tran C, Ouk S, Clegg NJ et al (2009) Development of a second-generation antiandrogen for treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Science 324(5928):787–790. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1168175
European Medicines Agency (2018) Summary of opinion (post authorization) -Xtandi. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/smop/chmp-post-authorisation-summary-positive-opinion-xtandi-ii-39-g_en.pdf. Accessed 2 Feb 2020
Astellas Pharma US Inc., Medivation Inc. (2019) XTANDI US Prescribing Information. https://www.astellas.us/docs/us/12A005-ENZ-WPI.pdf. Accessed 19 Mar 2020
US Food and Drug Administration (2019) XTANDI highlights of prescribing information. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/203415s015lbl.pdf. Accessed 30 Mar 2020
D'Amato NC, Cochrane DR, Barton VN, Bolin L, Edgerton SM, Bernales S, Gu H, Thor AD, Richer JK (2013) Targeting the androgen receptor in multiple breast cancer subtypes. Mol Cancer Res 11 (10 suppl): Abstract IA18.
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J et al (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45(2):228–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
Krop IE, Kim SB, González-Martín A, LoRusso PM, Ferrero JM, Smitt M, Yu R, Leung ACF, Wildiers H, TH3RESA Study Collaborators (2014) Trastuzumab emtansine versus treatment of physician’s choice for pretreated HER2-positive advanced breast cancer (TH3RESA): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 15(7):689–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70178-0
Hickey TE, Robinson JL, Carroll JS, Tilley WD (2012) Minireview: the androgen receptor in breast tissues: growth inhibitor, tumor suppressor, oncogene? Mol Endocrinol 26(8):1252–1267. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2012-1107
Wagner R, Ayoub L, Kahnamoui S, Li H, Patel D, Liu D, Del Bigio MR, Stefanovici C, Lacher M, Keijzer R (2019) Establishment of a biobank for human lung tissues of congenital diaphragmatic hernia and congenital pulmonary airway malformation. J Pediatr Surg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2019.05.003
Larionov AA (2018) Current therapies for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastatic breast cancer patients. Front Oncol 8:89. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00089
Traina TA, Miller K, Yardley DA et al (2018) Enzalutamide for the treatment of androgen receptor-expressing triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 36(9):884–890. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2016.71.3495
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by Astellas Pharma Inc. and Pfizer Inc., the co-developers of enzalutamide. The study sponsors were involved in the design and conduct of the study, the collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data, and the review and approval of the manuscript. Medical writing and editorial assistance were provided by Beatrice Vetter-Ceriotti, PhD, and Jane Beck from Complete HealthVizion, funded by the study sponsors. In Manchester, UK, this study was supported by, and carried out at, the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Manchester Clinical Research Facility at The Christie NHS Foundation Trust.
Funding
This work was supported by Astellas Pharma Inc. and Pfizer Inc., the co-developers of enzalutamide (no grant number is applicable).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AW, J Steinberg, J Sugg, ICT, and IEK contributed to the study conception and design. Data collection was performed by AW, JC, LP, KM, AJC, HSR, MH, RY, VA, RB, LH, SC, DC, GSW, M-PG, PN, AR, SR, and IEK. Data interpretation and analysis were performed by all authors. Statistical analysis was performed by J Sugg. Original draft preparation was conducted by AW and IEK. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
AW reports a role as study investigator with Astellas during the conduct of this study, consulting/advisory roles with, and research funding from, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche outside the submitted work, consulting/advisory roles with Athenex, Coleman Research, Gerson Lehrman, and Guidepoint outside the submitted work, director of Andrew Wardley Limited and the Manchester Cancer Academy, honoraria from AstraZeneca, Athenex, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche, speaker’s bureau fees from AstraZeneca, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche, travel expenses from Daiichi Sankyo, MSD, and Roche, and research funding from Seattle Genetics. JC reports a role as study investigator with Astellas during the conduct of this study and consulting/advisory roles with AstraZeneca, Biothera, Celgene, Cellestia, Eisai, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche outside the submitted work. LP reports a consulting/advisory role with, and research funding from, Astellas and Medivation during the conduct of this study, a consulting/advisory role with Lilly outside the submitted work, consulting/advisory roles and research funding from Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche outside the submitted work and research funding from GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Odonate outside the submitted work. KM, AJC, ICT, MH, RY, RB, LH, SC, PG, PN, and SR report a role as study investigator with Astellas during the conduct of this study. HSR received research funding from Astellas during the conduct of this study. J Steinberg and J Sugg are full-time employees of Astellas. VA reports a role as study investigator with Astellas during the conduct of this study, research funding from Genentech outside the submitted work, and consulting/advisory roles for AbbVie, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, and Novartis outside the submitted work. DC reports a role as study investigator with Astellas during the conduct of this study and consulting/advisory roles for Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and Syntheon outside the submitted work. GSW reports a consulting/advisory role with, and research funding from, Astellas during the conduct of the study and research funding from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Lilly, G1 Therapeutics, Genentech, Incyte, Janssen, MacroGenics, Medivation, Merrimack, Novartis, Pfizer, and Tesaro outside the submitted work and stock holdings from Puma and Roche outside the submitted work. M-PG reports a role as study investigator with Astellas during the conduct of this study and consulting/advisory roles with Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche outside the submitted work. IEK reports research funding from Pfizer during the conduct of the study, a consulting/advisory role with Astellas during the conduct of this study, a consulting/advisory role with, and research funding from, Genentech/Roche outside the submitted work, and consulting/advisory roles with Context, Daiichi Sankyo, MacroGenics, Novartis, and Taiho outside the submitted work.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Wardley, A., Cortes, J., Provencher, L. et al. The efficacy and safety of enzalutamide with trastuzumab in patients with HER2+ and androgen receptor-positive metastatic or locally advanced breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 187, 155–165 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-021-06109-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-021-06109-7