Abstract
Purpose
Limited knowledge exists on the detection of breast cancer stem cell (BCSC)-related mutations in circulating free DNA (cfDNA) from patients with advanced cancers. Identification of new cancer biomarkers may allow for earlier detection of disease progression and treatment strategy modifications.
Methods
We conducted a prospective study to determine the feasibility and prognostic utility of droplet digital polymerase chain reaction (ddPCR)-based BCSC gene mutation analysis of cfDNA in patients with breast cancer.
Results
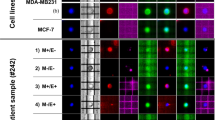
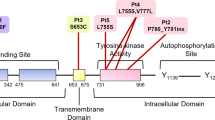
Detection of quantitative BCSC gene mutation in cfDNA by ddPCR mirrors disease progression and thus may represent a valuable and cost-effective measure of tumor burden. We have previously shown that hematological and neurological expressed 1-like (HN1L), ribosomal protein L39 (RPL39), and myeloid leukemia factor 2 (MLF2) are novel targets for BCSC self-renewal, and targeting these genetic alterations could be useful for personalized genomic-based therapy.
Conclusion
BCSC mutation detection in cfDNA may have important implications for diagnosis, prognosis, and serial monitoring.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets supporting the conclusions for the current study are stored in secured shared drive and will be shared by the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- BCSC:
-
Breast cancer stem cell
- cfDNA:
-
Circulating free DNA
- ddPCR:
-
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction
- HN1L:
-
Hematological and neurological expressed 1-like
- RPL39:
-
Ribosomal protein L39
- MLF2:
-
Myeloid leukemia factor 2
- RNA-Seq:
-
RNA deep sequencing
- SIFT:
-
Sorting intolerant from tolerant
- HER2:
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
- TTM:
-
Time-to-metastasis
- NOS:
-
Nitric oxide synthase
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
References
Dawson SJ, Tsui DW, Murtaza M, Biggs H, Rueda OM, Chin SF, Dunning MJ, Gale D, Forshew T, Mahler-Araujo B, Rajan S, Humphray S, Becq J, Halsall D, Wallis M, Bentley D, Caldas C, Rosenfeld N (2013) Analysis of circulating tumor DNA to monitor metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med 368(13):1199–1209. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1213261
Smalley M, Ashworth A (2003) Stem cells and breast cancer: a field in transit. Nat Rev Cancer 3(11):832–844. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1212
Li X, Lewis MT, Huang J, Gutierrez C, Osborne CK, Wu MF, Hilsenbeck SG, Pavlick A, Zhang X, Chamness GC, Wong H, Rosen J, Chang JC (2008) Intrinsic resistance of tumorigenic breast cancer cells to chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst 100(9):672–679
Creighton CJ, Li X, Landis M, Dixon JM, Neumeister VM, Sjolund A, Rimm DL, Wong H, Rodriguez A, Herschkowitz JI, Fan C, Zhang X, He X, Pavlick A, Gutierrez MC, Renshaw L, Larionov AA, Faratian D, Hilsenbeck SG, Perou CM, Lewis MT, Rosen JM, Chang JC (2009) Residual breast cancers after conventional therapy display mesenchymal as well as tumor-initiating features. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(33):13820–13825. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0905718106
Luo M, Clouthier SG, Deol Y, Liu S, Nagrath S, Azizi E, Wicha MS (2015) Breast cancer stem cells: current advances and clinical implications. Methods Mol Biol 1293:1–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2519-3_1
Dave B, Granados-Principal S, Zhu R, Benz S, Rabizadeh S, Soon-Shiong P, Yu KD, Shao Z, Li X, Gilcrease M, Lai Z, Chen Y, Huang TH, Shen H, Liu X, Ferrari M, Zhan M, Wong ST, Kumaraswami M, Mittal V, Chen X, Gross SS, Chang JC (2014) Targeting RPL39 and MLF2 reduces tumor initiation and metastasis in breast cancer by inhibiting nitric oxide synthase signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(24):8838–8843. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1320769111
Liu Y, Choi DS, Sheng J, Ensor JE, Liang DH, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Polley A, Benz S, Elemento O, Verma A, Cong Y, Wong H, Qian W, Li Z, Granados-Principal S, Lopez-Berestein G, Landis MD, Rosato RR, Dave B, Wong S, Marchetti D, Sood AK, Chang JC (2018) HN1L promotes triple-negative breast cancer stem cells through LEPR-STAT3 pathway. Stem cell Rep 10(1):212–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.11.010
Dave B, Gonzalez DD, Liu ZB, Li X, Wong H, Granados S, Ezzedine NE, Sieglaff DH, Ensor JE, Miller KD, Radovich M, KarinaEtrovic A, Gross SS, Elemento O, Mills GB, Gilcrease MZ, Chang JC (2017) Role of RPL39 in Metaplastic Breast Cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djw292
Robinson DR, Wu YM, Lonigro RJ, Vats P, Cobain E, Everett J, Cao X, Rabban E, Kumar-Sinha C, Raymond V, Schuetze S, Alva A, Siddiqui J, Chugh R, Worden F, Zalupski MM, Innis J, Mody RJ, Tomlins SA, Lucas D, Baker LH, Ramnath N, Schott AF, Hayes DF, Vijai J, Offit K, Stoffel EM, Roberts JS, Smith DC, Kunju LP, Talpaz M, Cieslik M, Chinnaiyan AM (2017) Integrative clinical genomics of metastatic cancer. Nature 548(7667):297–303. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23306
Schwarzenbach H, Hoon DS, Pantel K (2011) Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients. Nat Rev Cancer 11(6):426–437. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3066
Murtaza M, Dawson SJ, Tsui DW, Gale D, Forshew T, Piskorz AM, Parkinson C, Chin SF, Kingsbury Z, Wong AS, Marass F, Humphray S, Hadfield J, Bentley D, Chin TM, Brenton JD, Caldas C, Rosenfeld N (2013) Non-invasive analysis of acquired resistance to cancer therapy by sequencing of plasma DNA. Nature 497(7447):108–112. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12065
Kimura H, Kasahara K, Kawaishi M, Kunitoh H, Tamura T, Holloway B, Nishio K (2006) Detection of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in serum as a predictor of the response to gefitinib in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12(13):3915–3921. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2324
Sorenson GD (2000) Detection of mutated KRAS2 sequences as tumor markers in plasma/serum of patients with gastrointestinal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 6(6):2129–2137
Diehl F, Li M, Dressman D, He Y, Shen D, Szabo S, Diaz LA Jr, Goodman SN, David KA, Juhl H, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (2005) Detection and quantification of mutations in the plasma of patients with colorectal tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(45):16368–16373. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0507904102
Hindson CM, Chevillet JR, Briggs HA, Gallichotte EN, Ruf IK, Hindson BJ, Vessella RL, Tewari M (2013) Absolute quantification by droplet digital PCR versus analog real-time PCR. Nat Methods 10(10):1003–1005. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2633
Sanmamed MF, Fernandez-Landazuri S, Rodriguez C, Zarate R, Lozano MD, Zubiri L, Perez-Gracia JL, Martin-Algarra S, Gonzalez A (2015) Quantitative cell-free circulating BRAFV600E mutation analysis by use of droplet digital PCR in the follow-up of patients with melanoma being treated with BRAF inhibitors. Clin Chem 61(1):297–304. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2014.230235
Chu D, Paoletti C, Gersch C, VanDenBerg DA, Zabransky DJ, Cochran RL, Wong HY, Toro PV, Cidado J, Croessmann S, Erlanger B, Cravero K, Kyker-Snowman K, Button B, Parsons HA, Dalton WB, Gillani R, Medford A, Aung K, Tokudome N, Chinnaiyan AM, Schott A, Robinson D, Jacks KS, Lauring J, Hurley PJ, Hayes DF, Rae JM, Park BH (2016) ESR1 mutations in circulating plasma tumor DNA from metastatic breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 22(4):993–999. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0943
Garcia-Murillas I, Schiavon G, Weigelt B, Ng C, Hrebien S, Cutts RJ, Cheang M, Osin P, Nerurkar A, Kozarewa I, Garrido JA, Dowsett M, Reis-Filho JS, Smith IE, Turner NC (2015) Mutation tracking in circulating tumor DNA predicts relapse in early breast cancer. Science translational medicine 7(302):302ra133. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aab0021
Gerlinger M, Rowan AJ, Horswell S, Larkin J, Endesfelder D, Gronroos E, Martinez P, Matthews N, Stewart A, Tarpey P, Varela I, Phillimore B, Begum S, McDonald NQ, Butler A, Jones D, Raine K, Latimer C, Santos CR, Nohadani M, Eklund AC, Spencer-Dene B, Clark G, Pickering L, Stamp G, Gore M, Szallasi Z, Downward J, Futreal PA, Swanton C (2012) Intratumor heterogeneity and branched evolution revealed by multiregion sequencing. N Engl J Med 366(10):883–892. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1113205
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, Gion M, Clark GM, Statistics Subcommittee of NCIEWGoCD (2006) REporting recommendations for tumor MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK). Breast Cancer Res Treat 100(2):229–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9242-8
Acknowledgements
Any opinions, findings, and conclusions expressed in this materials are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect those of the American Society of Clinical Oncology® or the Conquer Cancer Foundation, or The Breast Cancer Research Foundation. We would like to thank Dr. Ana María González-Angulo from MD Anderson Hospital who identified the samples from GEICAM investigators.
Funding
This work was supported by a 2013 Conquer Cancer Foundation of ASCO Long-term International Fellowship (LIFe) in Breast Cancer, supported by The Breast Cancer Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, ZBL, BD, and JCC; Methodology, ZBL, NEE, AKE, BD, HW, and JCC; Investigation, ZBL, DSC, YL, HW, and BD; Formal Analysis, ZBL, NEE, JEE, and BD.; Resources, AKE, HJH, ZMS, JGD, GBM, and JCC; Writing—Original Draft, ZBL; Writing—Review and Editing, ZBL, JGD, DK, BD, and JCC; Supervision, BD and JCC; Funding Acquisition, JCC.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with the material reported in this manuscript and have no financial relationship with the organization that funded this study. Individual conflict of interest unrelated to the data presented here are listed in the conflict of interest form.
Research involving human participants and informed consent
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board at the Houston Methodist Hospital (IRB protocol numbers 0908-0265, 0811-0147, and 0208-0033) and written informed consent was obtained from all patients before sample and data collection.
Animal subjects
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, ZB., Ezzedine, N.E., Eterovic, A.K. et al. Detection of breast cancer stem cell gene mutations in circulating free DNA during the evolution of metastases. Breast Cancer Res Treat 178, 251–261 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-019-05374-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-019-05374-x