Summary
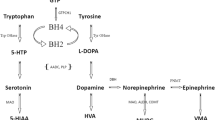
Paediatric neurotransmitter diseases consist of a group of inherited neurometabolic diseases in children, and include disorders related to γ-amino butyric acid (GABA) metabolism, monoamine biosynthesis, etc. The diagnosis of paediatric neurotransmitter diseases remain a great challenge for paediatricians and child neurologists. In addition to clinical manifestations and CSF neurotransmitter measurement, neuroimaging findings can also be very informative for the diagnosis and evaluation of the patients. For patients with monoamine biosynthesis disorders, the functional evaluation of dopaminergic transmission also plays an important role. Understanding of the possible neuroimaging changes in paediatric neurotransmitter diseases is therefore of great value for the investigation of these patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 5-HIAA:
-
5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid
- AADC:
-
aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase
- GABA:
-
γ-amino butyric acid
- GTPCH I:
-
GTP cyclohydrolase I
- HVA:
-
homovanillic acid
- MAO:
-
monoamine oxidase
- NAA:
-
N-acetylaspartate
- PET:
-
positron emission tomography
- SPECT:
-
single-photon-emission computed tomography
- SR:
-
sepiapterin reductase
- SSADH:
-
succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase
- TH:
-
tyrosine hydroxylase
References
Abeling NG, Duran M, Bakker HD, et al (2006) Sepiapterin reductase deficiency an autosomal recessive DOPA-responsive dystonia. Mol Genet Metab 89:116–120. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2006.03.010
Akaboshi S, Hogema BM, Novelletto A, et al (2003) Mutational spectrum of the succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH5A1) gene and functional analysis of 27 novel disease-causing mutations in patients with SSADH deficiency. Hum Mutat 22:442–450
Al-Essa MA, Bakheet SM, Patay ZJ, Powe JE, Ozand PT (2000) Clinical, FDG PET, MRI of the brain and biochemical observations in a patient with 4-hydroxybutyric aciduria: a progressive neurometabolic disease. Brain Dev 22:127–131. doi:10.1016/S0387-7604(99)00121-7
Anselm IA, Darras BT (2006) Catecholamine toxicity in aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency. Pediatr Neurol 35:142–144. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2006.01.008
Asanuma M, Miyazaki I, Ogawa N (2003) Dopamine- or l-DOPA-induced neurotoxicity: the role of dopamine quinone formation and tyrosinase in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotox Res 5:165–176.
Booij J, Halraken JBA, Bergmans P, et al (1998) Imaging of dopamine transporter with iodine-123-FP-CIT SPECT in healthy controls and patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Nucl Med 39:1879–1884.
Bräutigam C, Wevers RA, Jansen RJ, et al (1998) Biochemical hallmarks of tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency. Clin Chem 44:1897–1904.
Bräutigam C, Hyland K, Wevers R, et al (2002) Clinical and laboratory findings in twins with neonatal epileptic encephalopathy mimicking aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency. Neuropediatrics 33:113–117. doi:10.1055/s-2002-33673
Breit S, Reimold M, Reischl G, Klockgether T, Wüllner U (2006) [11C]d-threo-methylphenidate PET in patients with Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor. J Neural Transm 113:187–193. doi:10.1007/s00702-005-0311-7
Buu NT (1989) Vesicular accumulation of dopamine following l-DOPA administration. Biochem Pharmacol 38:1787–1792. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(89)90413-9
Chan AS, Ng LW, Poon LS, Chan WW, Wong YH (2007) Dopaminergic and adrenergic toxicities on SK-N-MC human neuroblastoma cells are mediated through G protein signaling and oxidative stress. Apoptosis 12:167–179. doi:10.1007/s10495-006-0524-8
De Lonlay P, Nassogne MC, van Gennip AH, et al (2000) Tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency unresponsive to l-dopa treatment with unusual clinical and biochemical presentation. J Inherit Metab Dis 23:819–825. doi:10.1023/A:1026760602577
Dionisi-Vici C, Hoffmann GF, Leuzzi V, et al (2000) Tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency with severe clinical course: clinical and biochemical investigations and optimization of therapy. J Pediatr 136:560–562. doi:10.1016/S0022-3476(00)90027-1
de Rijk-Van Andel JF, Gabreëls FJ, et al (2000) l-Dopa responsive infantile hypokinetic rigid parkinsonism due to tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency. Neurology 55:1926–1928.
Echenne B, Roubertie A, Assmann B, et al (2006) Sepiapterin reductase deficiency: clinical presentation and evaluation of long-term therapy. Pediatr Neurol 35:308–313. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2006.05.006
Eerola J, Tienari PJ, Kaakkola S, Nikkinen P, Launes J (2005) How useful is [123I]beta-CIT SPECT in clinical practice? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:1211–1216. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2004.045237
Ethofer T, Seeger U, Klose U, et al (2004) Proton MR spectroscopy in succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. Neurology 62:1016–1018.
Friedman J, Hyland K, Blau N, MacCollin M (2006) Dopa-responsive hypersomnia and mixed movement disorder due to sepiapterin reductase deficiency. Neurology 67:2032–2035. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000247274.21261.b4
Furukawa Y, Graf WD, Wong H, Shimadzu M, Kish SJ (2001) Dopa-responsive dystonia simulating spastic paraplegia due to tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) gene mutations. Neurology 56:260–263.
Gaspar P, Cases O, Maroteaux L (2003) The developmental role of serotonin: news from mouse molecular genetics. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:1002–1012. doi:10.1038/nrn1256
Gibson KM, Christensen E, Jakobs C, et al (1997) The clinical phenotype of SSADH deficiency: case reports of 23 new patients. Pediatrics 99:567–574. doi:10.1542/peds.99.4.567
Harper A, Bayliss M, Saha R, Scutt A, Nisbet A (2008) Late onset dopa-responsive dystonia with tremor, gait freezing and behavioural disturbance and a normal dopamine transporter scan. Age Ageing 37:719–720. doi:10.1093/ageing/afn216
Hoffmann GF, Assmann B, Bräutigam C, et al (2003) Tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency causes progressive encephalopathy and dopa-nonresponsive dystonia. Ann Neurol 54Supplement 6:S56–65. doi:10.1002/ana.10632
Horn AS (1990) Dopamine uptake: a review of progress in the last decade. Prog Neurobiol 34:387–400. doi:10.1016/0301-0082(90)90033-D
Huang CC, Yen TC, Weng YH, Lu CS (2002) Normal dopamine transporter binding in dopa responsive dystonia. J Neurol 249:1016–1020. doi:10.1007/s00415-002-0776-3
Hwang WJ, Yao WJ, Wey SP, Ting G (2004) Clinical and [99mTc]TRODAT-1/[123I]IBZM SPECT imaging findings in dopa-responsive dystonia. Eur Neurol 51:26–29. doi:10.1159/000074914
Hyland K, Clayton PT (1990) Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase deficiency in twins. J Inherit Metab Dis 13:301–304. doi:10.1007/BF01799380
Hyland K, Surtees RAH, Rodeck C, Clayton PT (1992) Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of a new inborn error of neurotransmitter amine synthesis. Neurology 42:1980–1988.
Jenner PG, Brin MF (1998) Levodopa neurotoxicity: experimental studies versus clinical relevance. Neurology 50 (6 Suppl 6):S39–S43.
Knappskog PM, Flatmark T, Mallet J, Lüdecke B, Bartholomé K (1995) Recessively inherited l-DOPA-responsive dystonia caused by a point mutation (Q381K) in the tyrosine hydroxylase gene. Hum Mol Genet 4:1209–1212. doi:10.1093/hmg/4.7.1209
Kung HF, Kung MP, Wey SP, Lin KJ, Yen TC (2007) Clinical acceptance of a molecular imaging agent: a long march with [99mTc]TRODAT. Nucl Med Biol 34:787–789. doi:10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2007.03.010
Latini A, Scussiato K, Leipnitz G, et al (2007) Evidence for oxidative stress in tissues derived from succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase-deficient mice. J Inherit Metab Dis 30:800–810. doi:10.1007/s10545-007-0599-6
Lee CS, Samii A, Sossi V, et al (2000) In vivo positron emission tomographic evidence for compensatory changes in presynaptic dopaminergic nerve terminals in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 47:493–503.
Lu CS, Chang HC, Kuo PC, et al (2004) The parkinsonian phenotype of spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 in a Taiwanese family. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 10:369–373. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2004.03.009
Martin WR, Palmer MR, Patlak CS, Calne DB (1989) Nigrostriatal function in humans studied with positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol 26:535–542. doi:10.1002/ana.410260407
Martin WR, Wieler M, Stoessl AJ, Schulzer M (2008) Dihydrotetrabenazine positron emission tomography imaging in early, untreated Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 63:388–394. doi:10.1002/ana.21320
Miller DW, Abercrombie ED (1999) Role of high-affinity dopamine uptake and impulse activity in the appearance of extracellular dopamine in striatum after administration of exogenous l-DOPA: studies in intact and 6-hydroxydopamine-treated rats. J Neurochem 72:1516–1522. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.721516.x
Nagata E, Kosakai A, Tanaka K, et al (2007) Dopa-responsive dystonia (Segawa disease)-like disease accompanied by mental retardation: a case report. Mov Disord 22:1202–1203. doi:10.1002/mds.21517
Neville BG, Parascandalo R, Farrugia R, Felice A (2005) Sepiapterin reductase deficiency: a congenital dopa-responsive motor and cognitive disorder. Brain 128Pt 10:2291–2296. doi:10.1093/brain/awh603
Pearl PL, Gibson KM, Acosta MT, et al (2003a) Clinical spectrum of succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. Neurology 60:1413–1417.
Pearl PL, Novotny EJ, Acosta MT, Jakobs C, Gibson KM (2003b) Succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency in children and adults. Ann Neurol 54 (Suppl 6):S73–80. doi:10.1002/ana.10629
Pearl PL, Gibson KM (2004) Clinical aspects of the disorders of GABA metabolism in children. Curr Opin Neurol 17:107–113. doi:10.1097/00019052-200404000-00005
Pearl PL, Vezina LG, Saneto RP, et al (2009) Cerebral MRI abnormalities associated with vigabatrin therapy. Epilepsia 50:184–194. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01728.x
Pons R, Ford B, Chiriboga CA, et al (2004) Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: clinical features, treatment and prognosis. Neurology 62:1058–1065.
Sawle GV, Leenders KL, Brooks DJ, et al (1991) Dopa-responsive dystonia: [18F]dopa positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol 30:24–30. doi:10.1002/ana.410300106
Schiller A, Wevers RA, Steenbergen GC, Blau N, Jung HH (2004) Long-term course of l-dopa-responsive dystonia caused by tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency. Neurology 63:1524–1526.
Snow BJ, Nygaard TG, Takahashi H, Calne DB (1993) Positron emission tomographic studies of dopa-responsive dystonia and early-onset idiopathic parkinsonism. Ann Neurol 34:733–738. doi:10.1002/ana.410340518
Swoboda KJ, Hyland K, Goldstein DS, et al (1999) Clinical and therapeutic observations in aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency. Neurology 53:1205–1211.
Swoboda KJ, Saul JP, McKenna CE, Speller NB, Hyland K (2003) Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: overview of clinical features and outcomes. Ann Neurol 54 (Suppl 6):S49–S55. doi:10.1002/ana.10631
Tennison M (1999) Focal lesion in the splenium of the corpus callosum in epileptic patients: antiepileptic drug toxicity? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:131–132.
Van Laere K, De Ceuninck L, Dom R, et al (2004) Dopamine transporter SPECT using fast kinetic ligands: 123I-FP-beta-CIT versus 99mTc-TRODAT-1. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 31:1119–1127.
Verbeek MM, Willemsen MA, Wevers RA, et al (2008) Two Greek siblings with sepiapterin reductase deficiency. Mol Genet Metab 94:403–409. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2008.04.003
Wüllner U, Reimold M, Abele M, et al (2005) Dopamine transporter positron emission tomography in spinocerebellar ataxias type 1, 2, 3, and 6. Arch Neurol 62:1280–1285. doi:10.1001/archneur.62.8.1280
Yalcinkaya C, Gibson KM, Gunduz E, et al (2000) MRI Findings in succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. Neuropediatrics 31:45–46. doi:10.1055/s-2000-15298
Zafeiriou DI, Willemsen MA, Verbeek MM, Vargiami E, Ververi A, Wevers R (2009) Tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency with severe clinical course. Mol Genet Metab 97:18–20. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2009.02.001
Ziyeh S, Berlis A, Korinthenberg R, et al (2002) Selective involvement of the globus pallidus and dentate nucleus in succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase activity. Pediatr Radiol 32:598–600. doi:10.1007/s00247-002-0717-4
Zhou QY, Qualfe CJ, Palmiter RD (1995) Targeted disruption of the tyrosine hydroxylase gene reveals that catecholamines are required for mouse fetal development. Nature 374:640–643. doi:10.1038/374640a0
Acknowledgements
The symposium was supported in part by R13 NS 60363 from the NIH NINDS and Office of Rare Diseases (ORD), and the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicating editor: Michael Gibson
Competing interests: None declared
Presented at the 2nd Pediatric Neurotransmitter Disease (PND) Association Symposium, “Medical Management of Pediatric Neurotransmitter Disorders: A Multidisciplinary Approach”, 18–19 July, 2008, Hyatt Dulles Hotel, Herndon, VA, USA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, WT., Weng, WC., Peng, SF. et al. Neuroimaging findings in children with paediatric neurotransmitter diseases. J Inherit Metab Dis 32, 361–370 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-009-1106-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-009-1106-z