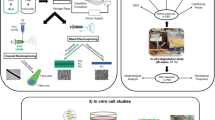
Abstract
Embryonic stem (ES) cell is of great interest cell source in regenerating tissue constructs. We hypothesized that the interaction of cell-extracellular matrices (ECMs) would enable the control of ES cell differentiation pathway. We fabricated the hydrogel microwell array system to regulate uniform-sized embryoid bodies (EBs) and replate into various ECM components (e.g., gelatin, collagen I, fibronectin, laminin, and Matrigel). We demonstrated that collagen I and laminin largely induced ES cell-derived endothelial cell differentiation compared to gelatin. We also characterized ECMs-dependent endothelial cell differentiation by evaluating the endothelial gene expression, showing that Flk1 endothelial gene was highly expressed on collagen I. We also demonstrated the effect of the integrin on uniform-sized EBs-derived endothelial cell differentiation, showing that integrin α1 was largely expressed on laminin. Therefore, the cell-ECM interaction could be potentially powerful for controlling the uniform-sized EBs-derived endothelial cell differentiation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.L. Bauwens, R. Peerani, S. Niebruegge, K.A. Woodhouse, E. Kumacheva, M. Husain, P.W. Zandstra, Control of human embryonic stem cell colony and aggregate size heterogeneity influences differentiation trajectories. Stem Cells 26(9), 2300–2310 (2008)
Y.Y. Choi, B.G. Chung, D.H. Lee, A. Khademhosseini, J.H. Kim, S.H. Lee, Controlled-size embryoid body formation in concave microwell arrays. Biomaterials 31(15), 4296–4303 (2010)
J.E. Ferguson, R.W. Kelley, C. Patterson, Mechanisms of endothelial differentiation in embryonic vasculogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. 25(11), 2246–2254 (2005)
S.E. Francis, K.L. Goh, K. Hodivala-Dilke, B.L. Bader, M. Stark, D. Davidson, R.O. Hynes, Central roles of alpha(5)beta(1) integrin and fibronectin in vascular development in mouse embryos and embryoid bodies. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. 22(6), 927–933 (2002)
R. Friel, S. van der Sar, P.J. Mee, Embryonic stem cells: understanding their history, cell biology and signalling. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 57(13), 1894–1903 (2005)
R. Hallmann, N. Horn, M. Selg, O. Wendler, F. Pausch, L.M. Sorokin, Expression and function of laminins in the embryonic and mature vasculature. Physiol. Rev. 85(3), 979–1000 (2005)
Y. Hayashi, M.K. Furue, T. Okamoto, K. Ohnuma, Y. Myoishi, Y. Fukuhara, T. Abe, J.D. Sato, R. Hata, M. Asashima, Integrins regulate mouse embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Stem Cells 25(12), 3005–3015 (2007)
N.F. Huang, B. Patlolla, O. Abilez, H. Sharma, J. Rajadas, R.E. Beygui, C.K. Zarins, J.P. Cooke, A matrix micropatterning platform for cell localization and stem cell fate determination. Acta Biomater. 6(12), 4614–4621 (2010)
Y.S. Hwang, B.G. Chung, D. Ortmann, N. Hattori, H.C. Moeller, A. Khademhosseini, Microwell-mediated control of embryoid body size regulates embryonic stem cell fate via differential expression of WNT5a and WNT11. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106(40), 16978–16983 (2009)
J. Ivaska, J. Heino, Adhesion receptors and cell invasion: mechanisms of integrin- guided degradation of extracellular matrix. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 57(1), 16–24 (2000)
R.K. Jain, Molecular regulation of vessel maturation. Nat. Med. 9(6), 685–693 (2003)
L. Jakobsson, A. Domogatskaya, K. Tryggvason, D. Edgar, L. Claesson-Welsh, Laminin deposition is dispensable for vasculogenesis but regulates blood vessel diameter independent of flow. FASEB J. 22(5), 1530–1539 (2008)
M.J. Jang, Y. Nam, Aqueous micro-contact printing of cell-adhesive biomolecules for patterning neuronal cell cultures. BioChip J. 6(2), 107–113 (2012)
N.M. Kane, Q. Xiao, A.H. Baker, Z. Luo, Q. Xu, C. Emanueli, Pluripotent stem cell differentiation into vascular cells: a novel technology with promises for vascular re(generation). Pharmacol. Ther. 129(1), 29–49 (2011)
G.D. Kim, G.J. Kim, J.H. Seok, H.M. Chung, K.M. Chee, G.S. Rhee, Differentiation of endothelial cells derived from mouse embryoid bodies: a possible in vitro vasculogenesis model. Toxicol. Lett. 180(3), 166–173 (2008)
S.H. Kim, G.H. Lee, J.Y. Park, Microwell fabrication methods and applications for cellular studies. Biomed. Eng. Lett 3(3), 131–137 (2013)
D. Malan, D. Wenzel, A. Schmidt, C. Geisen, A. Raible, B. Bolck, B.K. Fleischmann, W. Bloch, Endothelial beta1 integrins regulate sprouting and network formation during vascular development. Development 137(6), 993–1002 (2010)
H.C. Moeller, M.K. Mian, S. Shrivastava, B.G. Chung, A. Khademhosseini, A microwell array system for stem cell culture. Biomaterials 29(6), 752–763 (2008)
J.C. Mohr, J.J. de Pablo, S.P. Palecek, 3-D microwell culture of human embryonic stem cells. Biomaterials 27(36), 6032–6042 (2006)
H. Niwa, Mouse ES cell culture system as a model of development. Dev. Growth Differ. 52(3), 275–283 (2010)
J. Park, C.H. Cho, N. Parashurama, Y. Li, F. Berthiaume, M. Toner, A.W. Tilles, M.L. Yarmush, Microfabrication-based modulation of embryonic stem cell differentiation. Lab Chip 7(8), 1018–1028 (2007)
P. Pimton, S. Sarkar, N. Sheth, A. Perets, C. Marcinkiewicz, P. Lazarovici, P.I. Lelkes, Fibronectin-mediated upregulation of α5β1 integrin and cell adhesion during differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Cell Adhes. Migr. 5(1), 73–82 (2011)
J.M. Rhodes, M. Simons, The extracellular matrix and blood vessel formation: not just a scaffold. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 11(2), 176–205 (2007)
T.J. Rowland, L.M. Miller, A.J. Blaschke, E.L. Doss, A.J. Bonham, S.T. Hikita, L.V. Johnson, D.O. Clegg, Roles of integrins in human induced pluripotent stem cell growth on matrigel and vitronectin. Stem Cells Dev. 19(8), 1231–1240 (2010)
Y. Sakai, Y. Yoshiura, K. Nakazawa, Embryoid body culture of mouse embryonic stem cells using microwell and micropatterned chips. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 111(1), 85–91 (2011)
A. van der Flier, K. Badu-Nkansah, C.A. Whittaker, D. Crowley, R.T. Bronson, A. Lacy-Hulbert, R.O. Hynes, Endothelial alpha 5 and alpha v integrins cooperate in remodeling of the vasculature during development. Development 137(14), 2439–2349 (2010)
E.S. Wijelath, S. Rahman, J. Murray, Y. Patel, G. Savidge, M. Sobel, Fibronectin promotes VEGF-induced CD34 cell differentiation into endothelial cells. J. Vasc. Surg. 39(3), 655–660 (2004)
J. Yamashita, H. Itoh, M. Hirashima, M. Ogawa, S. Nishikawa, T. Yurugi, M. Naito, K. Nakao, S. Nishikawa, Flk1-positive cells derived from embryonic stem cells serve as vascular progenitors. Nature 408(6808), 92–96 (2000)
M.H. Zaman, Understanding the molecular basis for differential binding of integrins to collagen and gelatin. Biophys. J. 92(2), L17–L19 (2007)
Acknowledgments
This paper was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (Grant Number 20110016331, 2012R1A1A2005822). This work was also supported by Sogang University Research Grant (201310012.01, SRF-201314004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Je., Lee, J.M. & Chung, B.G. Microwell arrays for uniform-sized embryoid body-mediated endothelial cell differentiation. Biomed Microdevices 16, 559–566 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-014-9858-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-014-9858-0