Abstract
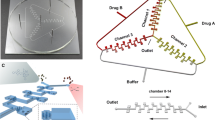
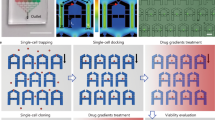
We present the development of a three-dimensional (3-D) combinatorial cell culture array device featured with integrated three-input, eight-output combinatorial mixer and cell culture chambers. The device is designed for cell-based screening of multiple compounds simultaneously on a microfluidic platform. The final assembled device is composed of a porous membrane integrated in between a Parylene 3-D microfluidic chip and a PDMS microfluidic chip. The membrane turned the cell culture chambers into two-level configuration to facilitate cell loading and to maintain cells in a diffusion dominated space during device operation. Experimentally, we first characterized the combined compound concentration profile at each chamber using a fluorescence method. We then successfully demonstrated the functionality of the quantitative cell-based assay by culturing B35 rat neuronal cells on this device and screening the ability of three compounds (1,5-dihydroxyisoquinoline, deferoxamine, and 3-aminobenzoic acid) to attenuate cell death caused by cytotoxic hydrogen peroxide. In another experiment, we assayed for the combinatorial effects of three chemotherapeutic compound exposures (vinorelbine, paclitaxel, and γ-linolenic acid) on human breast cancer cells, MDA-MB-231. The same technology will enable the construction of inexpensive lab-on-a-chip devices with high-input combinatorial mixer for performing high-throughput cell-based assay and highly parallel and combinatorial chemical or biochemical reactions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Barbulovic-Nad, H. Yang, P.S. Park, A.R. Wheeler, Digital microfluidics for cell-based assays. Lab Chip 8, 519–526 (2008)
D.J. Beebe, G.A. Mensing, G.M. Walker, Physics and applications of microfluidics in biology. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 4, 261–286 (2002)
J. Bowes, J. Piper, C. Thiemermann, Inhibitors of the activity of poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase reduce the cell death caused by hydrogen peroxide in human cardiac myoblasts. Br. J. Pharmacol. 124, 1760–1766 (1998)
A.Y. Chang, G.C. Garrow, Pilot study of vinorelbine (Navelbine) and paclitaxel (Taxol) in patients with refractory breast cancer and lung cancer. Semin. Oncol. 22, 66–70 (1995)
J.E. Dancey, H.X. Chen, Strategies for optimizing combinations of molecularly targeted anticancer agents. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 5, 649–659 (2006)
A. Dove, Drug screening—beyond the bottleneck. Nat. Biotechnol. 17, 859–863 (1999)
J. El-Ali, P.K. Sorger, K.F. Jensen, Cells on chips. Nature 442, 403–411 (2006)
R.K. Gregory, I.E. Smith, Vinorelbine—a clinical review. Br. J. Cancer 82, 1907–1913 (2000)
B.-H. Jo, L.M. Van Lerberghe, K.M. Motsegood, D.J. Beebe, Three-dimensional micro-channel fabrication in polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) elastomer. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 9, 76–81 (2000)
Y. Kikutani, T. Horiuchi, K. Uchiyama, H. Hisamoto, M. Tokeshi, T. Kitamori, Glass microchip with three-dimensional microchannel network for 2 × 2 parallel synthesis. Lab Chip 2, 188–192 (2002)
L. Kim, Y.-C. Toh, J. Voldman, H. Yu, A practical guide to microfluidic perfusion culture of adherent mammalian cells. Lab Chip 7, 681–694 (2007)
K.R. King, S. Wang, D. Irimia, A. Jayaraman, M. Toner, M.L. Yarmush, A high-throughput microfluidic real-time gene expression living cell array. Lab Chip 7, 77–85 (2007)
P.J. Lee, P.J. Hung, V.M. Rao, L.P. Lee, Nanoliter scale microbioreactor array for quantitative cell biology. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 94, 5–14 (2006)
M.C. Liu, D. Ho, Y.-C. Tai, Monolithic fabrication of three-dimensional microfluidic networks for constructing cell culture array with an integrated combinatorial mixer. Sens. Actuators, B 129, 826–833 (2008)
H. Lu, L.Y. Koo, W.M. Wang, D.A. Lauffenburger, L.G. Griffith, K.F. Jensen, Microfluidic shear devices for quantitative analysis of cell adhesion. Anal. Chem. 76, 5257–5264 (2004)
B. Ma, G. Zhang, J. Qin, B. Lin, Characterization of drug metabolites and cytotoxicity assay simultaneously using an integrated microfluidic device. Lab Chip 9, 232–238 (2009)
J.A. Menéndez, M. del Mar Barbacid, S. Montero, E. Sevilla, E. Escrich, M. Solanas, H. Cortés-Funes, R. Colomer, Effects of gamma-linolenic acid and oleic acid on paclitaxel cytotoxicity in human breast cancer cells. Eur. J. Cancer 37, 402–413 (2001)
J.A. Menéndez, S. Ropero, M. del Mar Barbacid, S. Montero, M. Solanas, E. Escrich, H. Cortés-Funes, R. Colomer, Synergistic interaction between vinorelbine and gamma-linolenic acid in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 72, 203–219 (2002)
S.J. Morrison, N.M. Shah, D.J. Anderson, Regulatory mechanisms in stem cell biology. Cell 88, 287–298 (1997)
C. Neils, Z. Tyree, B. Finlayson, A. Folch, Combinatorial mixing of microfluidic streams. Lab Chip 4, 342–350 (2004)
R.J. Pomerantz, D.L. Horn, Twenty years of therapy for HIV-1 infection. Nat. Med. 9, 867–873 (2003)
A. Prokop, Z. Prokop, D. Schaffer, E. Kozlov, J. Wikswo, D. Cliffel, F. Baudenbacher, NanoLiterBioReactor: long-term mammalian cell culture at nanofabricated scale. Biomed. Microdevices 6, 325–339 (2004)
E.K. Rowinsky, R.C. Donehower, Paclitaxel (Taxol). N Engl J. Med. 332, 1004–1014 (1995)
C.L. Sawyers, Cancer: mixing cocktails. Nature 449, 993–996 (2007)
R.A. Wagner, R. Tabibiazar, A. Liao, T. Quertermous, Genome-wide expression dynamics during mouse embryonic development reveal similarities to Drosophila development. Dev. Biol. 288, 595–611 (2005)
J.A. Walisser, R.L. Thies, Poly(ADP-Ribose) polymerase inhibition in oxidant-stressed endothelial cells prevents oncosis and permits caspase activation and apoptosis. Exp. Cell Res. 251, 401–413 (1999)
Z. Wang, M.-C. Kim, M. Marquez, T. Thorsen, High-density microfluidic arrays for cell cytotoxicity analysis. Lab Chip 7, 740–745 (2007)
D.S. Warner, H. Sheng, I. Batinić-Haberle, Oxidants, antioxidants and the ischemic brain. J. Exp. Biol. 207, 3221–3231 (2004)
J. Xie, Y. Miao, J. Shih, Y.-C. Tai, T.D. Lee, Microfluidic platform for liquid chromatography—tandem mass spectrometry analyses of complex peptide mixtures. Anal. Chem. 77, 6947–6953 (2005)
S. Zheng, M. Liu, Y.-C. Tai, Micro coulter counters with platinum black electroplated electrodes for human blood cell sensing. Biomed. Microdevices 10, 221–231 (2008)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NSF Center for Embedded Network Sensing (CCR-0120778). The authors would like to thank Trevor Roper and members of the Caltech Micromachining Laboratory for fabrication assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M.C., Tai, YC. A 3-D microfluidic combinatorial cell array. Biomed Microdevices 13, 191–201 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-010-9484-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-010-9484-4