Abstract
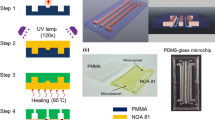
This paper presents two methods for the fabrication of UV epoxy resin masters for the replication of PDMS-based microfluidic chips. In the first method, the epoxy resin master is fabricated from a negative glass template manufactured using conventional lithography and wet etching techniques. However, in the second method, the master is produced simply by exposing a layer of UV epoxy resin coated on a glass substrate. Although the first method enables the replication of multiple PDMS structures from a single master, the latter method avoids the requirement for a wet chemical etching process and enables the epoxy master to be produced in 40 min or less. The experimental results show that the epoxy resin masters enable the mass production of PDMS replicas with highly precise geometrical tolerances. A series of electrokinetic focusing experiments are performed using PDMS microchips replicated from the current epoxy resin masters. The experimental results obtained for the width of the electrokinetically-focused sample stream under different focusing ratios are found to be in good agreement with the theoretical predictions. The sample handling characteristics of the microfluidic chips are also investigated. It is shown that the sample flow can be electrokinetically pre-focused into a narrow stream and then guided to the desired outlet port by applying a simple voltage control model. Finally, it is demonstrated that through an appropriate alignment of the sample flow and the conductivity gradient, the electrokinetic instability phenomenon can be induced at a relatively low electrical field strength of 0.35 kV/cm.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.K. Chaudhury, G.M. Whitesides, Langmuir 7, 1013 (1991)
L.M. Fu, R.J. Yang, G.B. Lee, Y.J. Pan, Electrophoresis 24, 3026 (2003)
L.M. Fu, R.J. Yang, C.H. Lin, Y.J. Pan, G.B. Lee, Anal. Chim. Acta. 507, 163 (2004)
C. Fütterer, N. Minc, V. Bormuth, J.H. Codarbox, P. Laval, J. Rossier, J.L. Viovy, Lab. Chip. 4, 351 (2004)
P. Grodzinski, R.H. Liu, B. Chen, J. Blackwell, Y. Liu, D. Rhine, T. Smekal, D. Ganser, C. Romero, H. Yu, T. Chan, N. Kroutchinina, Biomed. Microd. 3, 275 (2001)
J.W. Hong, T. Fuji, M. Seki, T. Yamamoto, I. Endo, Electrophoresis 22, 328 (2001)
V.V. Kancharla, S. Chen, Biomed. Microdev. 4, 105 (2002)
C.H. Lin, G.B. Lee, Y.H. Lin, C.H. Chang, J. Micromechanics Microengineering 11, 726 (2001)
R.M. McCormick, R.J. Nelson, G.M. A.-Amigo, D.J. Benvegnu, H.H. Hooper, Anal. Chem. 69, 2626 (1997)
N.T. Nguyen, X. Huang, Biomed. Microdev. 8, 133 (2006)
M.H. Oddy, J.G. Santiago, J.C. Mikkelsen, Anal. Chem. 73, 5822 (2001)
Y.J. Pan, R.J. Yang, J. Micromechanics Microengineering 16, 2666 (2006)
Y.J. Pan, J.J. Lin, W.J. Luo, R.J Yang, Biosens. Bioelectron. 21, 1644 (2006)
A.P. Russo, D. Apoga, N. Dowell, W. Shain, A.M.P. Turner, H.G. Craighead, H.C. Hoch, J.N. Turner, Biomed. Microdev. 4, 277 (2002)
V. Saarela, S. Franssila, S. Tuomikoski, S. Marttila, P. Östman, T. Sikanen, T. Kotiaho, R. Kostiainen, Sens. Actuators, B 114, 552 (2006)
T. Stiles, R. Fallon, T. Vestad, J. Oakey, D.W.M. Marr, J. Squier, R Jimenez, Microfluid. Nanofluid. 1, 280 (2005)
Y.C. Tan, V. Cristini, A.P. Lee, Sens. Actuators, B 114, 350 (2006)
G. Tresset, S. Takeuchi, Biomed. Microdev. 6, 213 (2004)
Z. Wu, N.T. Nguyen, Biomed. Microdev. 7, 13 (2005)
C. Yamahata, C. Lotto, E. Al-Assaf, M.A.M. Gijs, Microfluid. Nanofluid. 1, 197 (2005)
R.J. Yang, C.C. Chang, S.B. Huang, G.B. Lee, J. Micromechanics Microengineering 15, 2141 (2005)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided to this study by the National Science Council of Taiwan under Grant No. NSC-95-2221-E-006-253 and by the National Nano Device Laboratory of Taiwan under Grant No. NDL-95S-C-053.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, YJ., Yang, RJ. Fabrication of UV epoxy resin masters for the replication of PDMS-based microchips. Biomed Microdevices 9, 555–563 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-007-9063-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-007-9063-5