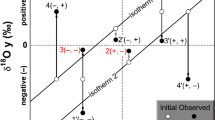
Abstract
This study deals with the chemical characterization of the biogeochemical processes occurring in a shallow aquifer in crystalline rocks. The influence of rock heterogeneity and the related physical processes on the aquifer biogeochemistry have been investigated. A hydrochemical survey (major anion and cation analysis) shows that rock heterogeneity leads to a stronger spatial than temporal variability. Some rapidly recharged and low- mineralized waters are present at the soil/rock interface. However the pumped well intersects a preferential flow path and pumps nitrate-rich water. Sulfur and oxygen isotope data from sulfates in the pumped water clearly show sulfide oxidation with only 20–30% of the oxygen atoms in sulfates formed by sulfide oxidation coming from atmospheric oxygen. This low contribution of molecular oxygen in sulfide oxidation, associated with the drastic decrease in nitrate concentration, involves a marked relationship between the nitrogen and sulfur cycles through denitrification, coupled with sulfide oxidation. Conversely, for rapidly recharged waters, the rock physical heterogeneity allows sulfide oxidation by molecular oxygen indicated by a contribution of atmospheric oxygen of nearly 70% in the newly formed sulfate. As the aquifer biogeochemistry is controlled by the physical characteristics of the rocks, pumping may overcome the natural flux pattern described previously. This anthropogenic disturbance leads to a modification of water pathways (spatial mixing or relative contribution of the fracture/matrix waters to the global fluxes) and, consequently, to a modification of the physical and biogeochemical processes occurring in the aquifer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aquilina L, de Dreuzy JR, Bour O, Davy P (2004) Porosity and fluid velocities in the upper continental crust (2 to 4 km) inferred from the injection tests at the Soultz-sous-Forêts geothermal site. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68:2405–2415
Ayraud V (2006) Détermination du temps de résidence des eaux souterraines: application au transfert d’azote dans les aquifères fracturés hétérogènes. Memoires du CAREN no 14, Rennes
Bennet PC, Hiebert FK, Robert Rogers J (2000) Microbial control of mineral-groundwater equilibria: macroscale to microscale. Hydrolgeol J 8:47–62
Berkowitz B (2002) Characterizing flow and transport in fractured geological media: a review. Adv Water Resour 25:861–884
Beven KJ, Germannn P (1982) Macropores and water flow in soils. Water Resour Res 18:1311–1325
Bonnet E, Bour O, Odling NE, Davy P, Main I, Cowie P, Berkowitz B (2001) Scaling of fracture system in geologic media. Rev Geophys 39:347–383
Bouhnik-Le Coz M, Petitjean P, Serrat E, Gruau G (2001) Validation d’un protocole permettant le dosage simultané des cations majeurs et traces dans les eaux douces naturelles par ICP-MS. Géosciences Rennes, Rennes
Bour O, Davy P, Darcel C, Odling NE (2002) A statistical scaling model for fracture network geometry, with validation on a multiscale mapping of a joint network (Hornelen Basin, Norway). J Geophys Res 107:2113. DOI 2110.2129/2001JB000176
Bu X, Warner MJ (1995) Solubility of chlorofluorocarbon 113 in water and seawater. Deep-Sea Res Pt I 42:1151–1161
Burt TP, Matchett LS, Goulding KWT, Webster CPH, Hancock NE (1999) Denitrification in riparian buffer zones: the role of floodplain hydrology. Hydrol Process 13:1451–1463
Cacas MC, Ledoux E, de Marsily G, Tillie B, Barbeau A, Durand E, Feuga B, Peaudecerf P (1990) Modelling fracture flow with a stochastic discrete fracture network: calibration and validation. Water Resour Res 26:479–489
Chantraine J, Egal E, Thiéblemont D, Le Goff E, Guerrot C, Ballèvre M, Guennoc P (2001) The cadomian active margin (North Armorican Massif, France): a segment of the North Atlantic Panafrican belt. Tectonophysics 331:1–18
Chen JY, Tang CY, Sakura Y, Kondoh A, Yu JJ, Shimada J, Tanaka T (2004) Spatial geochemical and isotopic characteristics associated with groundwater flow in the North China plain. Hydrol Process 18:3133–3146
Clark DI, Fritz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology. Lewis publishers, New York
Clauser C (1992) Permeability of crystalline rocks. Eos Trans Am Geophys Union 73:237–238
Clément J-C, Pinay G, Marmonier P (2002) Seasonal dynamics of denitrification along topohydrosequences in three different riparian wetlands. J Environ Qual 31:1025–1037
Clément J-C, Aquilina L, Bour O, Plaine K, Burt TP, Pinay G (2003) Hydrogeological flowpaths and NO −3 removal rates within a riparian flooplain along fourth-order stream in Brittany (France). Hydrol Process 17:1177–1195
Cook PG, Love AJ, Robinson NI, Simmons CT (2005) Groundwater ages in fractured rock aquifers. J Hydrol 308:284–301
de Dreuzy JR, Darcel C, Davy P, Bour O (2004) Influence of spatial correlation of fracture centers on the permeability of two-dimensional fracture networks following a power law length distribution. Water Resour Res. W01502: DOI 10.1029/2003WR002260
Durand V (2005) Recherche multidisciplinaire pour caractériser deux aquifères fracturés : les eaux minérales de Plancoët en contexte métamorphique, et de Quézac en milieu carbonaté. Sciences de la Terre. Université de Pierre et Marie Curie – Paris VI
Feast NA, Hiscock KM, Dennis PF, Bottrell SH (1997) Controls on stable isotope profiles in the Chalk aquifer of north-east Norfolk, UK, with special reference to dissolved sulphate. Appl Geochem 12:803–812
Frind EO, Duynisveld WHM, Strebel O, Böttcher J (1990) Modeling of multicomponent transport with microbial transformation in groundwater: the Furhberg case. Water Resour Res 26:1707–1719
Geoarmor (2000) Etude hydrogéologique: relation captage/ruisseau de Quincampoix (report no BL/GG-GR/00R1839). SIAEP de la région nord de Rennes
Geoarmor (2002) Etude de l’origine des chlorures présents dans l’eau du forage (report no GG-FD/R2550). SIAEP de la Région Nord de Rennes, Betton
Gouze P, Noiriel C, Bruderer C, Loggia D, Leprovost R (2003) X-ray tomography characterization of fracture surfaces during dissolution. Geophys Res Lett 30:1267. DOI 1029/2002GL016755
Grassi S, Cortecci G (2005) Hydrogeology and geochemistry of the multilayered confined aquifer of the Pisa plain (Tuscany – central Italy). Appl Geochem 20:41–54
Hill AR, Vidon P, Langat J (2004) Denitrification potential in relation to lithology in five headwater riparian zones. J Environ Qual 33:911–919
Höhener P, Werner D, Balsiger C, Pasteris G (2003) Worldwide occurence and fate of chlorofluorocarbons in groundwater. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 33:1–29
Honisch M, Hellmeier C, Weiss K (2002) Response of surface and subsurface water quality to land use changes. Geoderma 105:277–298
Kelly WR (1997) Heterogeneities in ground-water geochemistry in a sand aquifer beneath and irrigated field. J Hydrol 198:15–176
Kendall C, Caldwell EA (1998) Fundamentals of isotope geochemistry. In: Kendall C, McDonnell JJ (eds) Isotope tracers in catchment hydrology. Elservier Science B.V., Amsterdam, pp 51–86
Kölle W, Strebel O, Böttcher J (1985) Formation of sulphate by microbial denitrification in a reducing aquifer. Water Supply 3:35–40
Labasque T (2006) Analyse des CFC dans les eaux souterraines. Géosciences Rennes, Cahiers techniques de Géosciences Rennes, Rennes
Legout C (2006) Etude des mécanismes hydrogéologiques et biogéochimiques de la recharge des nappes libres. Mémoires du CAREN no 16, Rennes
Legout C, Molénat J, Aquilina L, Gascuel Odoux C, Faucheux M, Fauvel Y, Bariac T (in prep) Solute transport in soil and weathered granite with fluctuating water table
Legout C, Molénat J, Lefebvre S, Marmonier P, Aquilina L (2005) Investigation of biogeochemical activities in the soil and unsaturated zone of weathered granite. Biogeochemistry 75:329–350
Little BJ, Wagner PA, Lewandowski Z (1997) Spatial relationships between bacteria and mineral surfaces. In: Banfield JF, Nealson KH (eds) Geomicrobiology: interaction between microbes and minerals. Mineralogical society of America, Washington, pp 5–31
Luo J, Tillman RW, Ball PR (1999) Factors regulating denitrification in a soil under pasture. Soil Biol Biochem 31:913–927
Mariotti A (1986) La dénitrification dans les eaux souterraines, principes et méthodes de son identification: une revue. J Hydrol 88:1–23
Martin C, Aquilina L, Gascuel Odoux C, Molénat J, Faucheux M, Ruiz L (2004) Seasonal and interannual variation of nitrate and chloride in stream water related to spatial and temporal patterns of groundwater concentrations in agricultural catchments. Hydrol Process 18:1237–1254
Molénat J, Gascuel Odoux C (2002) Modelling flow and nitrate transport in groundwater for the prediction of water travel times and of consequences of land use evolution on water chemistry. Hydrol Process 16:479–492
Molénat J, Davy P, Gascuel Odoux C, Durand P (1999) Study of three subsurface hydrologic systems based on spectral and cross-spectral analysis of time series. J Hydrol 222:152–164
Montoroi J-P, Robain H, Schmutz M, Martin C, Molénat J, Ruiz L (2001) Analyse d’un réseau piezométrique par imagerie électrique multi-électrodes (Bassin versant de Kerbernez, Bretagne). 3ème colloque GEOFCAN, Orléans
Moses CO, Nordstrom DK, Herman JS, Mills AL (1987) Aqueous pyrite oxidation by dissolved oxygen and by ferric iron. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 51:1561–1571
Neuman SP (2005) Trends, prospects and challenges in quantifying flow and transport trough fractured rocks. Hydrolgeol J 13:124–147
Parkin T (1987) Soil microsite as a source of denitrification variability. Soil Sci Soc Am J 51:1194–1199
Pauwels H, Kloppmann W, Foucher JC, Martelat A, Fritsche V (1998) Field tracer test for denitrification in a pyrite-bearing schist aquifer. Appl Geochem 13:767–778
Pauwels H, Foucher JC, Kloppmann W (2000) Denitrification and mixing in a schist aquifer: influence on water chemistry and isotopes. Chem Geol 168:307–324
Pauwels H, Lachassagne P, Bordenave P, Foucher JC, Martelat A (2001) Temporal variability of nitrate concentration in a schist aquifer and transfer to surface waters. Appl Geochem 16:583–596
Plummer LN, Busenberg E (2000) Chlorofluorocarbons. In: Cook PG, Herczeg AL (eds) Environmental tracers in subsurface hydrology. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, pp 441–478
Plummer LN, Busenberg E, Böhlke JK, Nelms DL, Michel RL, Schlosser P (2001) Groundwater residence times in Shenandoah National Park, Blue Ridge Mountains, Virginia, USA: a multi-tracer approach. Chem Geol 179:93–111
Postma D, Boesen C, Kristiansen H, Larsen F (1991) Nitrate reduction in an unconfined sandy aquifer: water chemistry, reduction processes, and geochemical modeling. Water Resour Res 27(8):2027–2045
Pruvost J, Connan O, Marty Y, Le Corre P (1999) A sampling device for collection and analysis of volatile halocarbons in coastal and oceanic water. Analyst 124:1389–1394
Rosenberry DO (2003) The significance of ground water in small watershed studies. Ground Water 41:881–882
Sanchez-Peres JM, Tremolieres M (2003) Change in groundwater chemistry as a consequence of suppression of floods: the case of the Rhine flooplain. J Hydrol 270:89–104
Schramm A (2003) In situ analysis of structure and activity of the nitrifying community in biofilms, agregates and sediments. Geomicrobiol J 20:313–333. DOI 310.1080/01290450390241026
Schürmann A, Schroth MH, Saurer M, Bernasconi SM, Zeyer J (2003) Nitrate-consuming processes in a petroleum-contamined aquifer quantified using push-pull tests combined with 15N isotope and acetylene-inhibition methods. J Contam Hydrol 66:59–77
Segall P, Pollard D (1983) Joint formation in granitic rock of the Sierra Nevada. Geol Soc Am Bull 94:563–575
Shapiro SD, Rowe G, Schlosser P, Ludin A, Stute M (1998) Tritium-helium 3 dating under complex conditions in hydraulically stressed areas of a buried-valley aquifer. Water Resour Res 34:1165–1180
Strebel O, Böttcher J, Fritz P (1990) Use of isotope fractionation of sulfate-sulfur and sulfate-oxygen to assess bacterial desulfurication in a sandy aquifer. J Hydrol 121:155–172
Stumm W, Morgan JJ (1996) Aquatic chemistry: chemical equilibria and rates in natural waters. John Wiley and sons, New-York
Stutter MI, Deeks LK, Billett MF (2005) Transport of conservative and reactive tracers through naturally structured upland podzol field lysimeter. J Hydrol 300:1–19
Tarits C, Aquilina L, Ayraud V, Pauwels H, Davy P, Touchard F, Bour O (2006) Oxido-reduction sequence related to flux variations of groundwater from a fractured basement aquifer (Ploemeur area, France). Appl Geochem 21:29
Toran L, Harris RF (1989) Interpretation of sulfur and oxygen isotopes in biological and abiological sulfide oxidation. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 53:2341–2348
Trautmann F, Paris F, Carn A (2000) Carte géologique de la France au 1/50000. Feuille de Rennes no 317. BRGM, Orléans
Tsang C-F, Neretnieks I (1998) Flow channelling in heterogeneous fractured rocks. Rev Geophys 36:257–298
Van Everdingen RO, Krouse HR (1985) Isotope composition of sulphates generated by bacterial and abiological oxidation. Nature 315:395–396
Warner MJ, Weiss RF (1985) Solubilities of chlorofluorocarbons 11 et 12 in water and seawater. Deep-Sea Res 32:1485–1497
Weissmann GS, Zhang Y, LaBolle EM, Fogg GE (2002) Dispersion of groundwater age in an alluvial aquifer system. Water Resour Res 38:16-11–16-13
Whitehead PJ, Johnes PJ, Butterfield D (2002) Steady state and dynamics modelling of nitrogen in the river Kennet: impacts of land use change since the 1930’s. Sci Total Environ 282–283:417–434
Wyns R, Baltassat J-M, Lachassagne P, Legchenko A, Vairon J, Mathieu F (2004) Application of magnetic resonance soundings to groundwater reserve mapping in weathered basement rocks (Brittany, France). Bull Soc géol Fr 175:21–34
Acknowledgements
Thanks to municipality and CGE (particularly to Anthony Rohou) for the site access. Thanks to Yves Quété for sharing his knowledge about investigated site. Thanks to Odile Hénin, Patrice Petitjean and Martine Bouhnik-Le Coz, for analyses. Financial and field support have been provided by the region Bretagne regional Council (PRIR DATEAU) and BRGM (funding of V. Ayraud thesis).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayraud, V., Aquilina, L., Pauwels, H. et al. Physical, biogeochemical and isotopic processes related to heterogeneity of a shallow crystalline rock aquifer. Biogeochemistry 81, 331–347 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-006-9044-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-006-9044-4