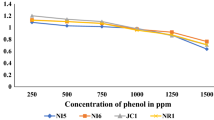
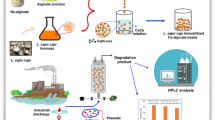
Abstract
The effluents from pulp and paper manufacturing industries contain high concentrations of phenol, which when discharged directly into surface water streams, increases the biological oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD). In this study, two dominant bacteria SP-4 and SP-8 were isolated from the effluent emanating with a pulp and paper industry. The selected phenol-degrading isolates were identified as Staphylococcus sp. and Staphylococcus sciuri respectively by using nucleotide sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis of 16 S rRNA regions of the genome. The two isolates used for the biodegradation process effectively degraded phenol concentration of pulp and paper industry effluent upto 1600 and 1800 mg/L resepctively. The individual isolates and consortium were immobilized using activated carbon, wood dust, and coal ash. Additionally, the effluent was treated using a bio-filter tower packed column immobilized with bacterial cells at a constant flow rate of 5 mL/min. The present study showed that the developed immobilized microbial consortium can effectively degrade 99% of the phenol present in pulp and paper industry effluents, resulting in a significant reduction in BOD and COD of the system. This study can be well implemented on real-scale systems as the bio-filter towers packed with immobilized bacterial consortium can effectively treat phenol concentrations up to 1800 mg/L. The study can be implemented for bioremediation processes in phenolic wastewater-contaminated sites.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data has been included in the manuscript by the authors, however, any raw data if required, will be made available on request.
References
Abd-El-Haleem D, Moawad H, Zaki EA, Zaki S (2002) Molecular characterization of phenol-degrading bacteria isolated from different Egyptian ecosystems. Microb Ecol 43:217–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-002-2003-2
Al-Khalid T, El-Naas MH (2012) Aerobic biodegradation of phenols: a comprehensive review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 42:1631–1690. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2011.569872
Annadurai G, Juang RS, Lee DJ (2002) Microbiological degradation of phenol using mixed liquors of Pseudomonas putida and activated sludge. Waste Manag 22:703–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-053X(02)00050-8
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 21st Edition. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington DC
Asimakoula S, Marinakos O, Tsagogiannis E, Koukkou AI (2023) Phenol degradation by pseudarthrobacter phenanthrenivorans Sphe3. Microorganisms. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020524
Chakraborty S, Bhattacharya T, Patel TN, Tiwari KK (2010) Biodegradation of phenol by native microorganisms isolated from coke processing wastewater. J Environ Biol 31:293–296
Chopra S, Kumar D (2020a) Biodegradation and kinetic analysis of acetaminophen with co-culture of bacterial strains isolated from sewage wastewater. Curr Microbiol 77:3147–3157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02137-6
Chopra S, Kumar D (2020b) Characterization, optimization and kinetics study of acetaminophen degradation by Bacillus drentensis strain S1 and waste water degradation analysis. Bioresour Bioprocess. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-020-0297-x
Chris Felshia S, Aswin Karthick N, Thilagam R et al (2017) Efficacy of free and encapsulated Bacillus lichenformis strain SL10 on degradation of phenol: a comparative study of degradation kinetics. J Environ Manage 197:373–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.04.005
Dhungana TP, Yadav PN (1970) Determination of chromium in tannery effluent and study of adsorption of Cr (VI) on saw dust and charcoal from sugarcane bagasses. J Nepal Chem Soc 23:93–101. https://doi.org/10.3126/jncs.v23i0.2102
Donaldson TL, Strandberg GW, Hewitt JD et al (1987) Biooxidation of coal gasification wastewaters using fluidized-bed bioreactors. Environ Prog 6:205–211. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.670060405
Dubey SK, Hussain A (2013) Phenol biodegradation: a review. Int J Environ Eng 1(2):978–981
Ezeonuegbu BA, Abdullahi MD, Whong CMZ (2022) Characterization and phylogeny of fungi isolated from industrial wastewater using multiple genes. Sci Rep 12 2094
Gu Q, Wu Q, Zhang J et al (2016) Community analysis and recovery of phenol-degrading bacteria from drinking water biofilters. Front Microbiol 7:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00495
Gu Q, Wu Q, Zhang J et al (2018) Isolation and transcriptome analysis of phenol-degrading bacterium from carbon-sand filters in a full-scale drinking water treatment plant. Front Microbiol 9:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02162
Health Protection Agency (HPA) (2007) HPA compendium of chemical hazards: phenol toxicological overview. Bull S. CHAPD HQ, HPA London. 2:1–12
Koch B, Ostermann M, Höke H, Hempel DC (1991) Sand and activated carbon as biofilm carriers for microbial degradation of phenols and nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds. Water Res 25:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(91)90091-4
Kumar S, Mishra VK, Kumar U et al (2013) Biodegradation of phenol by bacterial strains and their catalytic ability. Int J Agric Environ Biotechnol 6:39–44
Lika K, Papadakis IA (2009) Modeling the biodegradation of phenolic compounds by microalgae. J Sea Res 62:135–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seares.2009.02.005
Mahgoub SA, Qattan SYA, Salem SS et al (2023) Characterization and biodegradation of phenol by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella variicola strains isolated from sewage sludge and their effect on soybean seeds germination. Molecules 28:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031203
Maegala NM, Fridelina S, Abdul LI (2011) Bioremediation of cyanide by optimized resting cells of rhodococcus strains isolated from peninsular malaysia. Int J Biosci Biochem Bioinfo 1(2): 98–101
Misson M, Razali F (2012) Immobilization of phenol degrader Pseudomonas Sp in repeated batch culture using Bioceramic and Sponge as support materials. J Teknol. https://doi.org/10.11113/jt.v46.304
Nair CI, Jayachandran K, Shashidhar S (2008) Biodegradation of phenol. Afr J Biotechnol 7:4951–4958. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-5225-8903-7.ch045
Nuhoglu A, Yalcin B (2005) Modelling of phenol removal in a batch reactor. Process Biochem 40:1233–1239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2004.04.003
Olujimi OO, Fatoki OS, Odendaal JP, Okonkwo JO (2010) Endocrine disrupting chemicals (phenol and phthalates) in the South African environment: a need for more monitoring. Water SA 36:671–682. https://doi.org/10.4314/wsa.v36i5.62001
Ozaki H, Liu Z, Terashima Y (1991) Utilization of microorganisms immobilized with magnetic particles for sewage and wastewater treatment. Water Sci Technol 23:1125–1136. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.1991.0564
Pai SL, Hsu YL, Chong NM et al (1995) Continuous degradation of phenol by Rhodococcus sp. immobilized on granular activated carbon and in calcium alginate. Bioresour Technol 51:37–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/0960-8524(94)00078-F
Pishgar R (2011) Anaerobic biodegradation of phenol: comparative study of Free and immobilized growth. Iran J Energy Environ. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.ijee.2011.02.04.2361
Prieto MB, Hidalgo A, Rodríguez-Fernández C et al (2002) Biodegradation of phenol in synthetic and industrial wastewater by Rhodococcus erythropolis UPV-1 immobilized in an air-stirred reactor with clarifier. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58:853–859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-002-0963-2
Priyadarshini A, Mishra S, Sahoo NK et al (2023) Biodegradation of phenol using the indigenous Rhodococcus pyridinivorans Strain PDB9T NS-1 immobilized in calcium alginate beads. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04508-8
Rigo M, Alegre RM (2004) Isolation and selection of phenol-degrading microorganisms from industrial wastewaters and kinetics of the biodegradation. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 49:41–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931644
Sachan P, Madan S, Hussain A (2019a) Isolation and screening of phenol-degrading bacteria from pulp and paper mill effluent. Appl Water Sci 9:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-0994-9
Sachan P, Madan S, Hussain A, Singh U (2019b) Lab scale study on characterization and identification of phenol degrading bacteria isolated from pulp and paper mill effluent. Biochem Cell Arch 19:4635–4641. https://doi.org/10.35124/bca.2019.19.2.4635
Saleh S, Soheyla SM, Gholam RM, Farshad D (2022) Phenol biodegradation by immobilized Rhodococcus qingshengii isolated from coking effluent on Na-alginate and magnetic chitosan-alginate nanocomposite, J Environ Manage 307:114586
Satish K, Neeraj, Viraj KM, Santosh KK (2018) Biodegradation of phenol by free and immobilized Candida tropicalis NPD1401. Afr J Biotechnol 17:57–64. https://doi.org/10.5897/ajb2017.15906
Saxena C, Madan S (2014) Evaluation of adsorbents efficacy for the removal of pollutants from sugar mill effluent. ARPN J Agric Biol Sci 7:325–329
Shanmugam V, Senthil N, Raguchander T et al (2002) Interaction of Pseudomonas fluorescens with Rhizobium for their effect on the management of peanut root rot. Phytoparasitica 30:169–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02979699
Sivasubramanian S, Namasivayam SKR (2013) Evaluation of phenol degradation by effective microorganism (EM) technology with EM-1. Afr J Microbiol Res 7:4117–4122. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR12.1077
Straube G, Hensel J, Niedan C, Straube E (1990) Kinetic studies of phenol degradation by Rhodococcus sp. P1. I. Batch cultivation. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 57(1):29–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00400332
Whiteley AS, Bailey MJ (2000) Bacterial community structure and physiological state within an industrial phenol bioremediation system. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2400–2407. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.66.6.2400-2407.2000
Yang CF, Lee CM (2007) Enrichment, isolation, and characterization of phenol-degrading Pseudomonas resinovorans strain P-1 and Brevibacillus sp. strain P-6. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 59:206–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2006.09.010
Zhang J, Zhou X, Zhou Q et al (2022) A study of highly efficient phenol biodegradation by a versatile Bacillus cereus ZWB3 on aerobic condition. Water Sci Technol 86:355–366. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2022.209
Acknowledgements
The authors thank everyone who helped with the work, whether directly or indirectly.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. PS and US: Material preparation, data collection and analysis, writing original draft preparation, AH and SM: Conceptualization, Curation, Resources, methodology and Analysis, MP: Result Analysis, Writing review and manuscript revision formatting. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The submitted work is an original composition that should not have been previously published in any way, shape, or form (in whole or in part), nor should it be an expansion of another piece of writing.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sachan, P., Hussain, A., Madan, S. et al. Phenol biodegradation using bio-filter tower packed column with immobilized bacterial consortium: a batch test study. Biodegradation (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-024-10074-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-024-10074-5