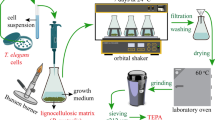
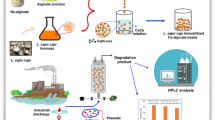
Abstract
Tramates trogii biomass was immobilized in carboxymethyl cellulose-lignin composite beads via cross-linking with Fe(III) ions (i.e., Fe(III)-CMC@Lig(1–4)@FB). The composite beads formulations were used for the adsorption and degradation of bisphenol A (BPA) using the free fungal biomass as a control system. The maximum adsorption capacity of the free fungal biomass and Fe(III)-CMC@Lig-3@FB for BPA was found to be 57.8 and 95.6, mg/g, respectively. The degradation rates of BPA were found to be 87.8 and 89.6% for the free fungal biomass and Fe(III)CMC@Lig-3@FB for 72 h in a batch reactor, respectively. Adsorption of BPA on the free fungal biomass and Fe(III)CMC@Lig-3@FB fungal preparations described by the Langmuir and Temkin isotherm models, and the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The values of Gibbs free energy of adsorption (ΔG°) were − 20.7 and − 25.8 kJ/mol at 298 K for BPA on the free fungal biomass and Fe(III)-CMC@Lig-3@FB beads, respectively. Moreover, the toxicities of the BPA and degradation products were evaluated with three different test organisms: (i) a freshwater micro-crustacean (Daphnia magna), (ii) a freshwater algae (Chlamydomonas reinhardti), and (iii) a Turkish winter wheat seed (Triticum aestivum L.). After treatment with the Fe(III)CMC@Lig-3@FB formulation, the degradation products had not any significant toxic effect compared to pure BPA. This work shows that the prepared composite bioactive system had a high potential for degradation of BPA from an aqueous medium without producing toxic end-products. Thus, it could be a good candidate for environmentally safe biological methods.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adnan LA, Sathishkumar P, Yusoff ARM, Hadibarata T, Ameen F (2017) Rapid bioremediation of Alizarin Red S and Quinizarine Green SS dyes using Trichoderma lixii F21 mediated by biosorption and enzymatic processes. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 40:85–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-016-1677-7
Arica TA, Ayas E, Arica MY (2017) Magnetic MCM-41 silica particles grafted with poly(glycidylmethacrylate) brush: modification and application for removal of direct dyes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 243:164–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.02.011
Arica TA, Balci FM, Balci S, Arica MY (2022) Highly porous poly(o-phenylenediamine) loaded magnetic carboxymethyl cellulose hybrid beads for removal of two model textile dyes. Fibers Polym 23(10):2838–2854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-022-0221-4
Basaka B, Jeon B-H, Kurade MB, Saratale GD, Bhunia B, Chatterjee PK, Dey A (2019) Biodegradation of high concentration phenol using sugarcane bagasse immobilized Candida tropicalis PHB5 in a packed-bed column reactor. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 180:317–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.05.020
Bayramoglu G, Arica MY (2002) Procion Green H-4G immobilized on a new IPN hydrogel membrane composed of poly(2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate)/chitosan preparation and its application to the adsorption of lysozyme. Colloids Surf A 202:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(01)01055-X
Bayramoglu G, Arica MY (2021) Grafting of regenerated cellulose films with fibrous polymer and modified into phosphate and sulfate groups: application for removal of a model azo-dye. Colloids Surf A 614:126173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126173
Bayramoglu G, Metin AU, Altıntas B, Arica MY (2010) Reversible immobilization of glucose oxidase on polyaniline grafted polyacrylonitrile conductive composite membrane. Biores Technol 101:6881–6887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.04.025
Bayramoglu G, Salih B, Akbulut A, Arica MY (2019) Biodegradation of Cibacron Blue 3GA by insolubilized laccase and identification of enzymatic byproduct using MALDI-ToF-MS: toxicity assessment studies by Daphnia magna and Chlorella vulgaris. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 170:453–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.014
Bayramoglu G, Angi SB, Acikgoz-Erkaya I, Arica MY (2022) Preparation of effective green sorbents using O. Princeps alga biomass with different composition of amine groups: comparison to adsorption performances for removal of a model acid dye. J Mol Liq 347:118375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.118375
Bazan-Wozniak A, Cielecka-Piontek J, Nosal-Wiercinska A, Pietrzak R (2022) Adsorption of organic compounds on adsorbents obtained with the use of microwave heating. Materials 15:5664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165664
Beck S, Berry E, Duke S, Milliken A, Patterson H, Prewett DL, Rae TC, Sridhar V, Wendland N, Gregory BW, Johnson CM (2018) Characterization of Trametes versicolor laccase-catalyzed degradation of estrogenic pollutants: substrate limitation and product identification. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 127:146–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.11.020
Benit N, Lourthuraj AA, Barathikannan K, Mostafa AA-F, Alodaini HA, Yassin MT, Hatamle AA (2022) Immobilization of Halomonas halodurans and Bacillus halodurans in packed bed bioreactor for continuous removal of phenolic impurities in waste water. Environ Res 209:112822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.112822
Cao Q, Wu Q, Da L, Shen X, Chuanling S (2021) A well-defined lignin-based filler for tuning the mechanical properties of polymethyl methacrylate. Green Chem 23:2329. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1gc00249j
Chen L, Zhang X, Zhang M, Zhu Y, Zhuo R (2022) Removal of heavy-metal pollutants by white rot fungi: Mechanisms, achievements, and perspectives. J Clean Prod 354:131681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131681
De Paula NM, da Silva K, Brugnari T, Haminiuk CWI, Maciel GM (2022) Biotechnological potential of fungi from a mangrove ecosystem: enzymes, salt tolerance and decolorization of a real textile effluent. Microbiol Res 254:126899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2021.126899
Dong Y, Li L, Hu X, Wu C (2017) Optimization of o-chlorophenol biodegradation by combined mycelial pellets using response surface methodology. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3606-z
Eltoukhy A, Jia Y, Nahurira Y, Abo-Kadoum MA, Khokhar I, Wang J, Yan Y (2020) Biodegradation of endocrine disruptor Bisphenol A by Pseudomonas putida strain YC-AE1 isolated from polluted soil, Guangdong. China BMC Microbiol 20:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-020-1699-9
Erkaya IA, Arica MY, Akbulut A, Bayramoglu G (2014) Biosorption of uranium (VI) by free and entrapped Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 299:1993–2003. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-014-2964-x
Fang Y, Wu M, Zhang Q, Zhou F, Deng C, Yan Y, Shen H-H, Tang Y, Wang Y (2022) Hierarchical covalent organic frameworks-modified diatomite for efficient separation of bisphenol A from water in a convenient column mode. Sep Purif Technol 298:121611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121611
He K, Chen G, Zeng G, Zeng G, Huang Z, Guo Z, Huang T, Peng M, Shi J, Hu L (2017) Applications of white rot fungi in bioremediation with nanoparticles and biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:4853–4862. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8328-z
Heidari H, Sedighi M, Zamir SM, Shojaosadati SA (2017) Bisphenol A degradation by Ralstonia eutropha in the absence and presence of phenol. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 119:37–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.10.052
Hejna M, Kapuscinska D, Aksmann A (2022) Pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment: a review on eco-toxicology and the remediation potential of algae. Int J Environ Res Pub Health 19:7717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19137717
Iliuta I, Iliuta MC (2022) Intensified phenol and p-cresol biodegradation for wastewater treatment in countercurrent packed-bed column bioreactors. Chemosphere 286:131716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131716
Jiang Y, Deng T, Shang Y, Yang K, Wang H (2017) Biodegradation of phenol by entrapped cell of Debaryomyces sp. With nano-Fe3O4 under hypersaline conditions. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 123:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.05.029
Kataria N, Bhushan D, Gupta R, Rajendran S, Teo MYM, Khoo KS (2022) Current progress in treatment technologies for plastic waste (bisphenol A) in aquatic environment: occurrence, toxicity and remediation mechanisms. Environ Pollut 315:120319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120319
Keum YS, Lee HR, Park HW, Kim J-H (2010) Biodegradation of bisphenol A and its halogenated analogues by Cunninghamella elegans ATCC36112. Biodegradation 21:989–997. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9358-8
Khalatbary M, Sayadi MH, Hajiani M, Nowrouzi M (2022) Adsorption studies on the removal of malachite green by γ-Fe2O3/MWCNTs/Cellulose as an eco-friendly nanoadsorbent. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02475-4
Khazaali F, Kargari A, Rokhsaran M (2014) Application of low-pressure reverse osmosis for effective recovery of bisphenol A from aqueous wastes. Desalin Water Treat 52(40–42):7543–7551. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.831795
Kotika MM, Marková E, Homolka L (2016) Biodegradation of phenolic compounds by Basidiomycota and its phenol oxidases: a review. Chemosphere 149:373–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.01.022
Kumar V, Shahi SK, Ferreira LFR, Bilal M, Biswas JK, Bulgariu L (2021) Detection and characterization of refractory organic and inorganic pollutants discharged in biomethanated distillery effluent and their phytotoxicity, cytotoxicity, and genotoxicity assessment using Phaseolus aureus L. and Allium cepa L. Environ Res 201:111551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111551
Leong K-Y, Adnan R, Lim P-E, Ng S-L, Seng C-E (2017) Effect of operational factors on bioregeneration of binary phenol and 4-chlorophenol-loaded granular activated carbon using PVA-immobilized biomass cryogels. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:20959–20971. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9636-7
Levin L, Viale A, Forchiassin A (2003) Degradation of organic pollutants by the white rot basidiomycete Trametes trogii. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 52:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0964-8305(02)00091-4
Liang L, Xi F, Tan W, Meng X, Hu B, Wang X (2021) Review of organic and inorganic pollutants removal by biochar and biochar-based composites. Biochar 3:255–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42773-021-00101-6
Liu Y, Wu Y, Zhang Y, Yang X, Yang E, Xu H, Yang Q, Chagan I, Cui X, Chen W, Yan J (2019) Lignin degradation potential and draft genome sequence of Trametes trogii S0301. Biotechnol Biofuels 12:256. https://doi.org/10.1186/s1308-019-1596-3
Liu Y, Wang Y, Wang Q, Wang B, Liu X, Wu B (2020) Adsorption and removal of bisphenol A in two types of sediments and its relationships with bacterial community. Int Biodeterioration Biodegrad 153:105021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2020.105021
Ma Y, Gao W, Zhang F, Xi Z, Kong W, Niu S, Gao K, Yang H (2022) Community composition and trophic mode diversity of fungi associated with fruiting body of medicinal Sanghuangporus vaninii. BMC Microbiol 22:251. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-022-02663-2
Maryskova M, Ardao I, García-Gonzaleze CA, Martinova L, Rotkova J, Sevcu A (2016) Polyamide 6/chitosan nanofibers as support for the immobilization of Trametes versicolor laccase for the elimination of endocrine disrupting chemicals. Enzyme Microb Technol 89:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2016.03.001
Matejczyk M, Plaza GA, Nalecz-Jawecki G, Ulfig K, Markowska-Szczupak A (2011) Estimation of the environmental risk posed by landfills using chemical, microbiological and ecotoxicological testing of leachates. Chemosphere 82:1017–1023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.10.066
Modaressi K, Taylor KE, Bewtra JK, Biswas N (2005) Laccase catalyzed removal of bisphenol-A from water: protective effect of PEG on enzyme activity. Water Res 39:4309–4316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.08.005
Naghdi M, Taheran M, Brar SK, Kermanshahi-pour A, Verma M, Surampallic RY (2018) Biotransformation of carbamazepine by laccase-mediator system: kinetics, by-products and toxicity assessment. Process Biochem 67:147–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.014
Nasiri A, Rajabi S, Amiri A, Fattahizade M, Hasani O, Lalehzari A, Hashemi M (2022) Adsorption of tetracycline using CuCoFe2O4@Chitosan as a new and green magnetic nanohybrid adsorbent from aqueous solutions: isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic study. Arab J Chem 15:104014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.104014
Noszczynska M, Chodor M, Jałowiecki Ł, Piotrowska-Seget Z (2021) A comprehensive study on bisphenol A degradation by newly isolated strains Acinetobacter sp. K1MN and Pseudomonas sp. BG12. Biodegradation 32:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-020-09919-6
OECD (2004) Acute Immobilization Test, Daphnia sp. OECD Guideline for the testing of chemicals, Guideline 202
OECD (2011) Freshwater Alga and Cyanobacteria, Growth Inhibition Test. OECD Guideline for the testing of chemicals, Guideline 201
Orozco AMF, Contreras EM, Zaritzky NE (2016) Monitoring the biodegradability of bisphenol A and its metabolic intermediates by manometric respirometry tests. Biodegradation 27:209–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-016-9767-4
Panigrahy N, Priyadarshini A, Sahoo MM, Verma AK, Daverey A, Sahoo NK (2022) A comprehensive review on eco-toxicity and biodegradation of phenolics: recent progress and future outlook. Environ Technol Innov 27:102423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2022.102423
Parimal AS, Bhomick C, Baruah M, Upasana CP, Sinha B, Sinha D (2019) Adsorptive removal of Bisphenol A by biomass activated carbon and insights into the adsorption mechanism through density functional theory calculations. Sustain Chem Pharm 13:100159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2019.100159
Pointing SB (2001) Feasibility of bioremediation by white-rot fungi. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57:20–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530100745
Rodríguez-Couto S (2017) Industrial and environmental applications of white rot fungi. Mycosphere 8:456–466. https://doi.org/10.5943/mycosphere/8/7
Senthilkumar S, Perumalsamy M, Janardhana H, Prabhu J (2014) Decolourization potential of white-rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium on synthetic dye bath effluent containing Amido black 10B. J Saudi Chem Soc 18:845–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2011.10.010
Shahabivand S, Mortazavi SS, Mahdavinia GR, Darvishi F (2022) Phenol biodegradation by immobilized Rhodococcus qingshengii isolated from coking effluent on Na-CMC and magnetic chitosan-CMC nanocomposite. J Environ Manag 307:114586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114586
Song L, Yu H, Dong J, Che X, Jiao Y, Liu D (2016) The molecular mechanism of ethylene-mediated root hair development induced by phosphate starvation. PLoS Genet 12:e1006194. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006194
Sulthana R, Taqui SN, Syed UT, Soudagar ME, Mujtaba MA, Mir RA, Shahapurkar K, Khidmatgar A, Mohanavel V, Syed AA, Hossain N (2022) Biosorption of crystal violet by nutraceutical industrial fennel seed spent equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 43:102402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2022.102402
Temkin MI (1941) Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics of processes on nonhomogeneous surfaces and at interaction between adsorbed molecules. Zh Fiz Khim 15:296–332
Terreros-Mecalco J, Guzman-Lopez O, García-Solorio L (2022) Simultaneous aerobic-anaerobic biodegradation of an industrial effluent of polymeric resins with high phenol concentration at different organic loading rates in a non-conventional UASB type reactor. Chem Eng J 430:133180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.133180
Uddin MK, Malek NNA, Jawad AH, Sabar S (2022) Pyrolysis of rubber seed pericarp biomass treated with sulfuric acid for the adsorption of crystal violet and methylene green dyes: an optimized process. Int J Phytoremed. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2022.2086214
USEPA 1996 (2012) Waste and cleanup risk assessment. http://www2.epa.gov/risk/waste-and-cleanup-risk-assessment
Vipotnik Z, Michelin M, Tavares T (2022) Biodegradation of chrysene and benzo[a]pyrene and removal of metals from naturally contaminated soil by isolated Trametes versicolor strain and laccase produced thereof. Environ Technol Innov 28:102737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2022.102737
Wang J, Zhang M (2020) Adsorption characteristics and mechanism of Bisphenol A by magnetic biochar. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031075
Wu J, Yu H-Q (2006) Biosorption of phenol and chlorophenols from aqueous solutions by fungal mycelia. Process Biochem 41:44–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2005.03.065
Wu L, Shi M, Guo R, Dong W (2022) Development of a novel pullulan/polydopamine composite hydrogel adsorbent for dye removal. Colloids Surf A 652:129632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129632
Xia L, Luo X, Zhu Y, Zhang X, Luo L (2019) Effects of CaCl2 freeze-drying and acidic solutions on the reusability of calcium CMC beads; and degradation of phenol by immobilized Acinetobacter sp. PR1. Biochem Eng J 151:107339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2019.107339
Xing L, Sun J, Liu H, Yu H (2012) Combined toxicity of three chlorophenols 2,4-dichlorophenol, 2,4,6-trichlorophenol and diclofenac to Daphnia magna. J Environ Monitor 4:1677–1683. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2em30185g
Xu H, Guo M-Y, Gao Y-H, Bai XH, Zhou X-W (2017) Expression and characteristics of manganese peroxidase from Ganoderma lucidum in Pichia pastoris and its application in the degradation of four dyes and phenol. BMC Biotechnol 17:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-017-0338-5
Young BJ, Rizzo PF, Riera NI, Torre VD, López VA, Molina CD, Fernández FE, Crespo DC, Barrena R, Komilis D, Sánchez A (2016) Development of phytotoxicity indexes and their correlation with ecotoxicological, stability and physicochemical parameters during passive composting of poultry manure. Waste Manage 54:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.05.001
Yuan Y, Jiang B, Chen H, Wu W, Wu S, Jin Y, Xiao H (2021) Recent advances in understanding the efects of lignin structural characteristics on enzymatic hydrolysisl. Biotechnol Biofuels 14:205. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-021-02054-1
Zeng XK, Cai YJ, Liao XR, Zeng XL, Li WX, Zhang DB (2011) Decolorization of synthetic dyes by crude laccase from a newly isolated Trametes trogii strain cultivated on solid agro-industrial residue. J Hazard Mater 187:517–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.01.068
Zhang C, Pan X, Wu X, Dong F, Liu X, Xu J, Wu X, Li M, Zheng Y (2019) Removal of dimethachlon from soils using immobilized cells and enzymes of a novel potential degrader Providencia stuartii JD. J Hazard Mater 378:120606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.04.089
Zhao L, Xiao D, Liu Y, Xu H, Nan H, Li D, Kan Y, Cao X (2020) Biochar as simultaneous shelter, adsorbent, pH buffer, and substrate of Pseudomonas citronellolis to promote biodegradation of high concentrations of phenol in wastewater. Water Res 172:115494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115494
Zhuo R, Fan F (2021) A comprehensive insight into the application of white rot fungi and their lignocellulolytic enzymes in the removal of organic pollutants. Sci Total Environ 778:146132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146132
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GB: Visualization, Validation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. MK: Investigation, Data curation. MYA: Formal analysis, Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bayramoglu, G., Kilic, M. & Arica, M.Y. Tramates trogii biomass in carboxymethylcellulose-lignin composite beads for adsorption and biodegradation of bisphenol A. Biodegradation 34, 263–281 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-023-10024-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-023-10024-7