Abstract
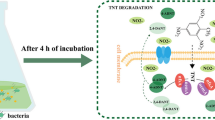
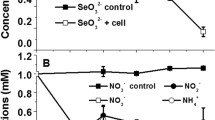
2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene (TNT) is the most widely used nitroaromatic compound and is highly resistant to degradation. Most aerobic microorganisms reduce TNT to amino derivatives via formation of nitroso- and hydroxylamine intermediates. Although pathways of TNT degradation are well studied, proteomic analysis of TNT-degrading bacteria was done only for some individual Gram-negative strains. Here, we isolated a Gram-positive strain from TNT-contaminated soil, identified it as Bacillus pumilus using 16S rRNA sequencing, analyzed its growth, the level of TNT transformation, ROS production, and revealed for the first time the bacillary proteome changes at toxic concentration of TNT. The transformation of TNT at all studied concentrations (20–200 mg/L) followed the path of nitro groups reduction with the formation of 4-amino-2,6-dinitrotoluene. Hydrogen peroxide production was detected during TNT transformation. Comparative proteomic analysis of B. pumilus showed that TNT (200 mg/L) inhibited expression of 46 and induced expression of 24 proteins. Among TNT upregulated proteins are those which are responsible for the reductive pathway of xenobiotic transformation, removal of oxidative stress, DNA repair, degradation of RNA and cellular proteins. The production of ribosomal proteins, some important metabolic proteins and proteins involved in cell division are downregulated by this xenobiotic.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alothman ZA, Bahkali AH, Elgorban AM, Al-Otaibi MS, Ghfar AA, Gabr SA, et al. (2020) Bioremediation of explosive TNT by Trichoderma viride. Molecules 25(6):1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061393
Cabrera MÁ, Márquez SL, Quezada CP, Osorio MI, Castro-Nallar E, González-Nilo FD, Pérez-Donoso JM (2020) Biotransformation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene by Pseudomonas sp. TNT3 isolated from Deception island, Antarctica. Environ Pollut 262:113922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.113922
Cherepnev GV, Velizhinskaya TA, Yakovleva GYu, Denivarova NA, Kurinenko BM (2007) Assessing the toxic effect of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene on cells of Escherichia coli K12 by flow cytofluorometry. Microbiology 76(3): 331–335. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261707030101
Cho Y-S, Lee B-U, Kahng H-Y, Oh K-H (2009) Comparative analysis of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT)-induced cellular responses and proteomes in Pseudomonas sp. HK-6 in two types of media. J Microbiol 47(2):220–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-008-0108-0
Esteve-Nuñez A, Caballero A, Ramos JL (2001) Biological degradation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65(3):333–352. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.65.3.335-352.2001
Heyno E, Innocenti G, Lemaire SD, Issakidis-Bourguet E, Krieger-Liszkay A (2014) Putative role of the malate valve enzyme NADP-malate dehydrogenase in H2O2 signaling in Arabidopsis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 369(1640):20130228. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2013.0228
Ho E-M, Chang H-W, Kim S-I, Kahng H-Y, Oh K-H (2004) Analysis of TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene)-inducible cellular responses and stress shock proteome in Stenotrophomonas sp. OK-5. Curr Microbiol 49(5):346–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-004-4322-7
Khan MI, Lee J, Yoo K, Kim S, Park J (2015) Improved TNT detoxification by starch addition in a nitrogen-fixing Methylophilus-dominant aerobic microbial consortium. J Hazard Mater 300:873–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.08.032
Khilyas IV, Ziganshin AM, Pannier AJ, Gerlach R (2013) Effect of ferrihydrite on 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene biotransformation by an aerobic yeast. Biodeg 24(5):631–644. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-012-9611-4
Khilyas IV, Lochnit G, Ilinskaya ON (2017) Proteomic analysis of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene degrading yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Front Microbiol 8:A.2600. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02600
Konovalova OA, Yakovleva GY, Steryakov OV, Trushin MV (2013) Scanning probe microscopy in the study of morphometric changes and physical parameters of Escherichia coli bacteria under the action of 2,4,6 - trinitrotoluene. World Appl Sci J 23(4):507–509. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.wasj.2013.23.04.13077
Kurinenko BM, Yakovleva GY, Denivarova NA, Abreimova YV (2003) Specific toxic effects of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene on Bacillus subtilis SK1. Appl Biochem Microbiol 39(3):275–8
Kurinenko BM, Denivarova NA, Davydov RE, Yakovleva GYu (2007) Features of the toxic action of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene on Escherichia coli K12. Appl Biochem Microbiol 43(1):52–56. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683807010097
Liao H-Y, Chien C-C, Tang P, Chen C-C, Chen C-Y, Chen S-C (2018) The integrated analysis of transcriptome and proteome for exploring the biodegradation mechanism of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene by Citrobacter sp. J Hazard Mater 349:79–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.01.039
Lin H, Chena Z, Megharajc M, Naidu R (2013) Biodegradation of TNT using Bacillus mycoides immobilized in PVA-sodium alginate-kaolin. Appl Clay Sci 83:336–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2013.08.004
Mercimek HA, Dincer S, Guzeldag G, Ozsavli A, Matyar F (2013) Aerobic biodegradation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) by Bacillus cereus isolated from contaminated soil. Microb Ecol. 66(3):512–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-013-0248-6
Miczak A, Kaberdin VR, Wei CL, Lin-Chao S. (1996) Proteins associated with RNase E in a multicomponent ribonucleolytic complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(9):3865–3869. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.9.3865
Naumenko EA, Sibgatullina GV, Mukhitov AR, Rodionov AA, Ilinskaya ON, Naumova RP (2013) 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene as a trigger of oxidative stress in Fagopyrum tataricum callus cells. Rus J Plant Physiol 60(3):404–410. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443713030102
Naumenko EA, Ahlemeyer B, Baumgart-Vogt E (2017) Species-specific differences in peroxisome proliferation, catalase, and SOD2 upregulation as well as toxicity in human, mouse, and rat hepatoma cells induced by the explosive and environmental pollutant 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. Environ Toxicol 32(3):989–1006. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22299
Serrano-González MY, Chandra R, Castillo-Zacarias C, Robledo-Padilla F, Rostro-Alanis M, Parra-Saldivar R (2018) Biotransformation and degradation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene by microbial metabolism and their interaction. Defence Technol 14(2):151–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dt.2018.01.004
Smets BF, Yin H, Esteve-Nuñez A (2007) TNT biotransformation: when chemistry confronts mineralization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76(2):267–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1008-7
Solyanikova P, Robota IV, Mazur DM, Lebedev AT, Golovleva LA (2014) Application of Bacillus sp. strain VT-8 for decontamination of TNT-polluted sites. Microbiology 83(5):577–584. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261714050257
Whitacre DM (2012) Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology. Springer, New York. http://www.springer.com/gp/book/9781461414629.
Wijker RS, Bolotin J, Nishino SF, Spain JC, Hofstetter TB (2013) Using compound-specific isotope analysis to assess biodegradation of nitroaromatic explosives in the subsurface. Environ Sci Technol 47(13):6872–6883. https://doi.org/10.1021/es3051845
Williford CW Jr, Mark Bricka R (1999) Extraction of TNT from aggregate soil fractions. J Hazard Mater 66(1–2):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(98)00214-3
Wu CF, Xu XM, Zhu Q, Deng MC, Feng L, Peng J, et al. (2014)An effective method for the detoxification of cyanide-rich wastewater by Bacillus sp. CN-22. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(8):3801–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5433-5
Xu M, Liu D, Sun P, Li Y, Wu M, Liu W, et al. (2021) Degradation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT): involvement of protocatechuate 3,4-dioxygenase (P34O) in Buttiauxella sp. S19-1. Toxics 9(10):231. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9100231
Yang X, Lai JL, Li J, Zhang Y, Luo XG, Li ZG (2021) Biodegradation and physiological response mechanism of a bacterial strain to 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene contamination. Chemosphere 270:129280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129280
Yin H, Wood TK, Smets BF (2005) Reductive transformation of TNT by Escherichia coli: pathway description. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67(3):397–404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1736-x
Ziganshin AM, Gerlach R (2014) Pathways of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene transformation by aerobic yeasts. In: Singh SN (ed) Biological remediation of explosive residues, environmental science and engineering. Springer, Cham, pp 301–311
Ziganshin AM, Ziganshina EE, Byrne J, Gerlach R, Struve E, Biktagirov T, et al. (2015) Fe(III) mineral reduction followed by partial dissolution and reactive oxygen species generation during 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene transformation by the aerobic yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. AMB Express 5:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-014-0094-z
Acknowledgements
This work was carried out under the Program of Kazan Federal University Strategic Academic Leadership and supported by Russian Science Foundation Grant No 22-24-00036.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yakovleva, G., Kurdy, W., Gorbunova, A. et al. Bacillus pumilus proteome changes in response to 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene-induced stress. Biodegradation 33, 593–607 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-022-09997-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-022-09997-8