Abstract
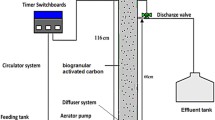
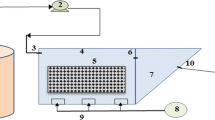
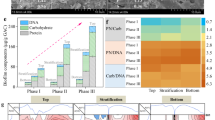
Treatment of oil sands process-affected water (OSPW) using biodegradation has the potential to be an environmentally sound approach for tailings water reclamation. This process is both economical and efficient, however, the recalcitrance of some OSPW constituents, such as naphthenic acids (NAs), require the pre-treatment of raw OSPW to improve its biodegradability. This study evaluated the treatment of OSPW using ozonation followed by fluidized bed biofilm reactor (FBBR) using granular activated carbon (GAC). Different organic and hydraulic loading rates were applied to investigate the performance of the bioreactor over 120 days. It was shown that ozonation improved the adsorption capacity of GAC for OSPW and improved biodegradation by reducing NAs cyclicity. Bioreactor treatment efficiencies were dependent on the organic loading rate (OLR), and to a lesser degree, the hydraulic loading rate (HLR). The combined ozonation, GAC adsorption, and biodegradation process removed 62 % of chemical oxygen demand (COD), 88 % of acid-extractable fraction (AEF) and 99.9 % of NAs under optimized operational conditions. Compared with a planktonic bacterial community in raw and ozonated OSPW, more diverse microbial communities were found in biofilms colonized on the surface of GAC after 120 days, with various carbon degraders found in the bioreactor including Burkholderia multivorans, Polaromonas jejuensis and Roseomonas sp.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aktas O, Cecen F (2007) Bioregeneration of activated carbon: a review. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 59:257–272
Alawi M, Lipski A, Sanders T, Maria PE, Spieck E (2007) Cultivation of a novel cold-adapted nitrite oxidizing betaproteobacterium from the Siberian Arctic. ISME J 1:256–264
Alegado RA, Ferriera S, Nusbaum C, Young SK, Zeng QA, Imamovic A, Fairclough SR, King N (2011) Complete genome sequence of Algoriphagus sp PR1, bacterial prey of a colony-forming choanoflagellate. J Bacteriol 193:1485–1486
Alvares ABC, Diaper C, Parsons SA (2001) Partial oxidation by ozone to remove recalcitrance from wastewaters—a review. Environ Technol 22:409–427
Alvarez-Vazquez H, Jefferson B, Judd SJ (2004) Membrane bioreactors vs conventional biological treatment of landfill leachate: a brief review. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 79:1043–1049
Amat AM, Arques A, Beneyto H, García A, Miranda MA, Seguí S (2003) Ozonisation coupled with biological degradation for treatment of phenolic pollutants: a mechanistically based study. Chemosphere 53:79–86
American Public Health Association, APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Water Works Association and Water Environment Federation, Washington
Anderson JC, Wiseman SB, Wang N, Moustafa A, Perez-Estrada L, El-Din MG, Martin JW, Liber K, Giesy JP (2012) Effectiveness of ozonation treatment in eliminating toxicity of oil sands process-affected water to Chironomus dilutus. Environ Sci Technol 46:486–493
Appia-Ayme C, Little PJ, Matsumoto Y, Leech AP, Berks BC (2001) Cytochrome complex essential for photosynthetic oxidation of both thiosulfate and sulfide in Rhodovulum sulfidophilum. J Bacteriol 183:6107–6118
Barrow MP, Witt M, Headley JV, Peru KM (2010) Athabasca oil sands process water: characterization by atmospheric pressure photoionization and electrospray ionization fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 82:3727–3735
Betancur MJ, Martinez F, Ocampo C, Moreno JA, Buitron G, Moreno-Andrade I (2009) Acclimatization model of an aerobic bioreactor for the treatment of toxic wastewater. Simul Model Pract Th 17:680–691
Buitron G, Schoeb ME, Moreno-Andrade L, Moreno JA (2005) Evaluation of two control strategies for a sequencing batch reactor degrading high concentration peaks of 4-chlorophenol. Water Res 39:1015–1024
Carlson G, Silverstein J (1997) Effect of ozonation on sorption of natural organic matter by biofilm. Water Res 31:2467–2478
Choi J, Hwang G, El-Din MG, Liu Y (2014) Effect of reactor configuration and microbial characteristics on biofilm reactors for oil sands process-affected water treatment. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 89:74–81
Di Iaconi C (2012) Biological treatment and ozone oxidation: integration or coupling? Bioresour Technol 106:63–68
El-Naas MH, Al-Muhtaseb SA, Makhlouf S (2009) Biodegradation of phenol by Pseudomonas putida immobilized in polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) gel. J Hazard Mater 164:720–725
Estrada-Arriaga EB, Ramirez-Camperos E, Moeller-Chavez GE, Garcia-Sanchez L (2012) Anaerobic/aerobic treatment of a petrochemical wastewater from two aromatic transformation processes by fluidized bed reactors. Water Sci Technol 66:2754–2763
Finneran KT, Johnsen CV, Lovley DR (2003) Rhodoferax ferrireducens sp nov., a psychrotolerant, facultatively anaerobic bacterium that oxidizes acetate with the reduction of Fe(III). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:669–673
Gamal El-Din M, Fu HJ, Wang N, Chelme-Ayala P, Perez-Estrada L, Drzewicz P, Martin JW, Zubot W, Smith DW (2011) Naphthenic acids speciation and removal during petroleum-coke adsorption and ozonation of oil sands process-affected water. Sci Total Environ 409:5119–5125
Garcia-Garcia E, Ge JQ, Oladiran A, Montgomery B, El-Din MG, Perez-Estrada LC, Stafford JL, Martin JW, Belosevic M (2011) Ozone treatment ameliorates oil sands process water toxicity to the mammalian immune system. Water Res 45:5849–5857
Golby S, Ceri H, Gieg LM, Chatterjee I, Marques LLR, Turner RJ (2012) Evaluation of microbial biofilm communities from an Alberta oil sands tailings pond. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 79:240–250
Gonzalez G, Herrera G, Garcia MT, Pena M (2001) Biodegradation of phenolic industrial wastewater in a fluidized bed bioreactor with immobilized cells of Pseudomonas putida. Bioresour Technol 80:137–142
Grewer DM, Young RF, Whittal RM, Fedorak PM (2010) Naphthenic acids and other acid-extractables in water samples from Alberta: what is being measured? Sci Total Environ 408:5997–6010
Griffiths M, Taylor A, Woynillowicz D (2006) Troubled waters, troubling trends: technology and policy options to reduce water use in oil and oil sands development in Alberta. The Pembina Institute, Drayton Valley
He YH, Wiseman SB, Wang N, Perez-Estrada LA, El-Din MG, Martin JW, Giesy JP (2012) Transcriptional responses of the brain-gonad-liver axis of fathead minnows exposed to untreated and ozone-treated oil sands process-affected water. Environ Sci Technol 46:9701–9708
Herzberg M, Dosoretz CG, Kuhn J, Klein S, Green M (2006) Visualization of active biomass distribution in a BGAC fluidized bed reactor using GFP tagged Pseudomonas putida F1. Water Res 40:2704–2712
Hoigne J, Bader H (1983) Rate constants of reactions of ozone with organic and inorganic compounds in water—I. Non-dissociating organic compounds. Water Res 17:173–183
Hwang G, Dong T, Islam MS, Sheng ZY, Perez-Estrada LA, Liu Y, El-Din MG (2013) The impacts of ozonation on oil sands process-affected water biodegradability and biofilm formation characteristics in bioreactors. Biores Technol 130:269–277
Jagadevan S, Graham NJ, Thompson IP (2013) Treatment of waste metalworking fluid by a hybrid ozone-biological process. J Hazard Mater 244:394–402
Jeon HJ, Kim MN (2013) Isolation of a thermophilic bacterium capable of low-molecular-weight polyethylene degradation. Biodegradation 24:89–98
Jiang X, Ma M, Li J, Lu A, Zhong Z (2008) Bacterial diversity of active sludge in wastewater treatment plant. Front Earth Sci 15:163–168
Jivraj MN, MacKinnon M, Fung B (1995) Naphthenic acids extraction and quantitative analyses with FT-IR spectroscopy. Syncrude Analytical Methods Manual. Syncrude Canada Ltd. Research Department, Edmonton
Kim ES, Liu Y, El-Din MG (2011) The effects of pretreatment on nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membrane filtration for desalination of oil sands process-affected water. Sep Purif Technol 81:418–428
Kleinsteuber S, Muller FD, Chatzinotas A, Wendt-Potthoff K, Harms H (2008) Diversity and in situ quantification of Acidobacteria subdivision 1 in an acidic mining lake. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 63:107–117
Liu Y, Tay JH (2002) The essential role of hydrodynamic shear force in the formation of biofilm and granular sludge. Water Res 36:1653–1665
Loupasaki E, Diamadopoulos E (2013) Attached growth systems for wastewater treatment in small and rural communities: a review. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 88:190–204
Lu H, Sato Y, Fujimura R, Nishizawa T, Kamijo T, Ohta H (2011) Limnobacter litoralis sp. nov., a thiosulfate-oxidizing, heterotrophic bacterium isolated from a volcanic deposit, and emended description of the genus Limnobacter. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:404–407
Madhaiyan M, Poonguzhali S, Ryu J, Sa T (2006) Regulation of ethylene levels in canola (Brassica campestris) by 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase-containing Methylobacterium fujisawaense. Planta 224:268–278
Martin JW, Barri T, Han XM, Fedorak PM, El-Din MG, Perez-Estrada L, Scott AC, Jiang JT (2010) Ozonation of oil sands process-affected water accelerates microbial bioremediation. Environ Sci Technol 44:8350–8356
Mattes TE, Alexander AK, Richardson PM, Munk AC, Han CS, Stothard P, Coleman NV (2008) The genome of Polaromonas sp. strain JS666: insights into the evolution of a hydrocarbon- and xenobiotic-degrading bacterium, and features of relevance to biotechnology. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:6405–6416
Moreno-Andrade I, Buitrón G (2004) Evolution of the microbial activity during the acclimation and deacclimation (starvation) of activated sludge to 4-chlorophenol. In: 4th IWA World Water Congress, Marrakech
Moreno-Castilla C (2004) Adsorption of organic molecules from aqueous solutions on carbon materials. Carbon 42:83–94
Nedashkovskaya OI, Kim SB, Lee DH, Lysenko AM, Shevchenko LS, Frolova GM, Mikhailov VV, Lee KH, Bae KS (2005) Roseivirga ehrenbergii gen. nov., sp nov, a novel marine bacterium of the phylum ‘Bacteroidetes’, isolated from the green alga Ulva fenestrata. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:231–234
Nishiyama E, Ohtsubo Y, Nagata Y, Tsuda M (2010) Identification of Burkholderia multivorans ATCC 17616 genes induced in soil environment by in vivo expression technology. Environ Microbiol 12:2539–2558
Pérez-Estrada LA, Han X, Drzewicz P, El-Din MG, Fedorak PM, Martin JW (2011) Structure-reactivity of naphthenic acids in the ozonation process. Environ Sci Technol 45:7431–7437
Pikuta E, Lysenko A, Suzina N, Osipov G, Kuznetsov B, Tourova T, Akimenko V, Laurinavichius K (2000) Desulfotomaculum alkaliphilum sp nov., a new alkaliphilic, moderately thermophilic, sulfate-reducing bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:25–33
Pourrezaei P, Drzewicz P, Wang Y, El-Din MG, Perez-Estrada LA, Martin JW, Anderson J, Wiseman S, Liber K, Giesy JP (2011) The impact of metallic coagulants on the removal of organic compounds from oil sands process-affected water. Environ Sci Technol 45:8452–8459
Ried A, Mielcke J, Wieland A, Schaefer S, Sievers M (2007) An overview of the integration of ozone systems in biological treatment steps. Water Sci Technol 55:253–258
Ro KS, Neethling JB (1991) Biofilm density for biological fluidized-beds. Res J Water Pollut C 63:815–818
Ryhiner G, Petrozzi S, Dunn IJ (1988) Operation of a 3-phase biofilm fluidized sand bed reactor for aerobic waste-water treatment. Biotechnol Bioeng 32:677–688
Scott AC, MacKinnon MD, Fedorak PM (2005) Naphthenic acids in athabasca oil sands tailings waters are less biodegradable than commercial naphthenic acids. Environ Sci Technol 39:8388–8394
Scott AC, Zubot W, MacKinnon MD, Smith DW, Fedorak PM (2008) Ozonation of oil sands process water removes naphthenic acids and toxicity. Chemosphere 71:156–160
Shetty KV, Yarangali SB, Srinikethan G (2013) Biodegradation of phenol using immobilized nocardia hydrocarbonoxydans in a pulsed plate bioreactor: effect of packed stages, cell carrier loading, and cell acclimatization on startup and steady-state behavior. Bioremed J 17:252–263
Siddique T, Penner T, Semple K, Foght JM (2011) Anaerobic biodegradation of longer-chain n-alkanes coupled to methane production in oil sands tailings. Environ Sci Technol 45:5892–5899
Stewart FJ, Cavanaugh CM (2006) Bacterial endosymbioses in Solemya (Mollusca: Bivalvia)—model systems for studies of symbiont-host adaptation. Anton Leeuw Int J G Mol Microbiol 90:343–360
Sutton PM, Hurvid J, Hoeksema M (1999) Biological fluidized-bed treatment of wastewater from byproduct coking operations: full-scale case history. Water Environ Res 71:5–9
Wang N, Chelme-Ayala P, Perez-Estrada L, Garcia-Garcia E, Pun J, Martin JW, Belosevic M, El-Din MG (2013) Impact of ozonation on naphthenic acids speciation and toxicity of oil sands process-affected water to Vibrio fischeri and mammalian immune system. Environ Sci Technol 47:6518–6526
Weon HY, Yoo SH, Hong SB, Kwon SW, Stackebrandt E, Go SJ, Koo BS (2008) Polaromonas jejuensis sp nov., isolated from soil in Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:1525–1528
Yapsakli K, Cecen F (2010) Effect of type of granular activated carbon on DOC biodegradation in biological activated carbon filters. Process Biochem 45:355–362
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support provided by research grants from the Helmholtz-Alberta Initiative (MGED and YL) and funding through an NSERC Industrial Research Chair Program in Oil Sands Tailings Water Treatment (MGED), through the support by: Syncrude Canada Ltd., Suncor Energy Inc., Shell Canada, Canadian Natural Resources Ltd., Total E&P Canada Ltd., EPCOR Water Services, IOWC Technologies Inc., Alberta Innovates—Energy and Environment Solution, and Alberta Environment and Sustainable Resource Development.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Islam, M.S., Dong, T., McPhedran, K.N. et al. Impact of ozonation pre-treatment of oil sands process-affected water on the operational performance of a GAC-fluidized bed biofilm reactor. Biodegradation 25, 811–823 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-014-9701-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-014-9701-6