Abstract
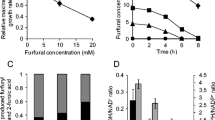
Ethanol is a renewable biofuel, and it can be produced from lignocellulosic biomass. The biomass is usually converted to hydrolysates that consist of sugar and sugar derivatives, such as furfural. Yeast ferments sugar to ethanol, but furfural higher than 3 mM is inhibitory. It can take several days for yeast cells to reduce furfural to non-inhibitory furfuryl alcohol before producing ethanol. Bioreduction of furfural to furfuryl alcohol before fermentation may relieve yeast from furfural toxicity. We observed that Cupriavidus necator JMP134, a strict aerobe, rapidly reduced 17 mM furfural to less than 3 mM within 14 min with cell turbidity of 1.0 at 600 nm at 50°C. The rapid reduction consumed ethanol. The “furfural reductase” (FurX) was purified, and it oxidized ethanol to acetaldehyde and reduced furfural to furfuryl alcohol with NAD+ as the cofactor. The protein was identified with mass spectrometry fingerprinting to be a hypothetical protein belonging to Zn-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase family. The furX-inactivation mutant of C. necator JMP134 lost the ability to rapidly reduce furfural, and Escherichia coli producing recombinant FurX gained the ability. Thus, an alcohol dehydrogenase enabled bacteria to rapidly reduce furfural with ethanol as the reducing power.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida JRM, Bertilsson M, Gorwa-Grauslund MF, Gorsich SW, Liden G (2009) Metabolic effects of furaldehydes and impacts on biotechnological processes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:625–638
Antal MJ, Leesomboon T, Mok WS, Richards GN (1991) Mechanism of formation of 2-furaldehyde from D-xylose. Carbohydr Res 217:71–85
Boopathy R, Bokang H, Daniels L (1993) Biotransformation of furfural and 5-hydroxymethyl furfural by enteric bacteria. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 11:147–150
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Ceccarelli C, Liang ZX, Strickler M, Prehna G, Goldstein BM, Klinman JP, Bahnson BJ (2004) Crystal structure and amide H/D exchange of binary complexes of alcohol dehydrogenase from Bacillus stearothermophilus: insight into thermostability and cofactor binding. Biochemistry 43:5266–5277
Gutierrez T, Ingram LO, Preston JF (2006) Purification and characterization of a furfural reductase (FFR) from Escherichia coli strain LYO1: an enzyme important in the detoxification of furfural during ethanol production. J Biotechnol 121:154–164
Heer D, Sauer U (2008) Identification of furfural as a key toxin in lignocellulosic hydrolysates and evolution of a tolerant yeast strain. Microb Biotech 1:497–506
Klinke HB, Thomsen AB, Ahring BK (2004) Inhibition of ethanol-producing yeast and bacteria by degradation products produced during pre-treatment of biomass. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:10–26
Koopman F, Wierckx N, de Winde JH, Ruijssenaars HJ (2010) Identification and characterization of the furfural and 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural degradation pathways of Cupriavidus basilensis HMF14. PNAS 107:4919–4924
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Levin I, Meiri G, Peretz M, Burstein Y, Frolow F (2004) The ternary complex of Pseudomonas aeruginosa alcohol dehydrogenase with NADH and ethylene glycol. Protein Sci 13:1547–1556
Li Q, Lam LKM, Xun L (2011) Biochemical characterization of ethanol-dependent reduction of furfural by alcohol dehydrogenases. Biodegradation. doi:10.1007/s10532-011-9477-x
Liu ZL, Slininger PJ, Dien BS, Berhow MA, Kurtzman CP, Gorsich SW (2004) Adaptive response of yeasts to furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and new chemical evidence for HMF conversion to 2,5-bis-hydroxymethylfuran. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 31:345–352
Liu ZL, Moon J, Andersh AJ, Slininger PJ, Weber S (2008) Multiple gene mediated NAD(P)H-dependent aldehyde reduction is a mechanism of in situ detoxification of furfural and HMF by ethanologenic yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81:743–753
Liu ZL, Ma M, Song M (2009) Evolutionarily engineered ethanologenic yeast detoxifies lignocellulosic biomass conversion inhibitors by reprogrammed pathways. Mol Genet Genomics 282:233–244
Louie TM, Webster CM, Xun L (2002) Genetic and biochemical characterization of a 2,4,6-trichlorophenol degradation pathway in Ralstonia eutropha JMP134. J Bacteriol 184:3492–3500
Martín C, Marcet M, Almazán O, Jönsson LJ (2007) Adaptation of a recombinant xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain to a sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate with high content of fermentation inhibitors. Biores Technol 98:1767–1773
Miller EN, Jarboe LR, Yomano LP, York SW, Shanmugam KT, Ingram LO (2009) Silencing of NADPH-dependent oxidoreductase genes (yqhD and dkgA) in furfural-resistant ethanologenic Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:4315–4323
Modig T, Lidén G, Taherzadeh MJ (2002) Inhibition effects of furfural on alcohol dehydrogenase, aldehyde dehydrogenase and pyruvate dehydrogenase. Biochem J 363:769–776
Mussatto SI, Roberto IC (2004) Alternatives for detoxification of diluted-acid lignocellulosic hydrolyzates for use in fermentative processes: a review. Bioresour Technol 93:1–10
Pellegrino S, Bruno FS, Petrarulo M (1999) Liquid chromatographic determination of ethyl alcohol in body fluids. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 729:103–110
Petersson A, Almeida JR, Modig T, Karhumaa K, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF, Lidén G (2006) A 5-hydroxymethyl furfural reducing enzyme encoded by the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ADH6 gene conveys HMF tolerance. Yeast 23:455–464
Sambrook J, Fritch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Taherzadeh MJ, Gustafsson L, Niklasson C, Lidén G (1999) Conversion of furfural in aerobic and anaerobic batch fermentation of glucose by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biosci Bioeng 87:169–174
Tang X, Munske GR, Siems WF, Bruce JE (2005) Mass spectrometry identifiable cross-linking strategy for studying protein-protein interactions. Anal Chem 77:311–318
Thomsen MH, Thygesen A, Thomsen AB (2009) Identification and characterization of fermentation inhibitors formed during hydrothermal treatment and following SSF of wheat straw. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83:447–455
Zaldivar J, Martinez A, Ingmar L (1999) Effect of selected aldehydes on the growth and fermentation of ethanologenic Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 65:24–33
Acknowledgments
Q. Li was partially funded by a scholarship from the Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China. L. K. M. Lam was partially funded by College of Science, Washington State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Metthew Lam, L.K. & Xun, L. Cupriavidus necator JMP134 rapidly reduces furfural with a Zn-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase. Biodegradation 22, 1215–1225 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-011-9476-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-011-9476-y