Abstract
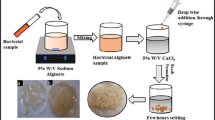
An aerobic microorganism with an ability to utilize phenol as carbon and energy source was isolated from a hydrocarbon contamination site by employing selective enrichment culture technique. The isolate was identified as Arthrobacter citreus based on morphological, physiological and biochemical tests. This mesophilic organism showed optimal growth at 25°C and at pH of 7.0. The phenol utilization studies with Arthrobacter citreus showed that the complete assimilation occurred in 24 hours. The organism metabolized phenol up to 22 mM concentrations whereas higher levels were inhibitory. Thin layer chromatography, UV spectral and enzyme analysis were suggestive of catechol, as a key intermediate of phenol metabolism. The enzyme activities of phenol hydroxylase and catechol 2,3-dioxygenase in cell free extracts of Arthrobacter citreus were indicative of operation of a meta-cleavage pathway for phenol degradation. The organism had additional ability to degrade catechol, cresols and naphthol. The degradation rates of phenol by alginate and agar immobilized cells in batch fermentations showed continuous phenol metabolism for a period of eight days.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DA Abramowicz (1990) ArticleTitleAerobic and anaerobic biodegradation of PCBs A Review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 10 241–251 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXhtFyisbk%3D
M Alexander (1999) Biodegradation and Bioremediation. 2 Academic Press San Diego, CA
InstitutionalAuthorNameAmerican Public Health Association (1992) American Water Works Association and Water Environment Federation Phenols. 5530 D. Direct photometric method AD Eaton LS Clesceri AE Greenburg (Eds) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Environment Federation Washington, D.C. 5–39
RM Atlas CE Cerniglia (1995) ArticleTitleBioremediation of petroleum pollutants Bioscience 45 332–338
RM Atlas D Pramer (1990) ArticleTitleASM News Focus on bioremediation 56 7
RM Atlas R Unterman (1999) Bioremediation AC Demain JE Davies (Eds) Manual of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology EditionNumber2 ASM Press Washington, D.C. 666–681
KH Baker DS Herson (1994) Bioremediation Mc Graw Hill Newyork
I Bartels HJ Knackmuss W Reineke (1984) ArticleTitleSuicide inactivation of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida mt-2 by 3-halocatechols Appl. Environl. Microbiol. 47 500–505 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2cXitVGmtr4%3D
H Battmann HJ Rehm (1984) ArticleTitleDegradation of phenol by polymer entrapped microorganisms Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 20 285–290
RB Bayly S Dagley DT Gibson (1966) ArticleTitleMetabolism of cresols by species of Pseudomonads Biochem J. 101 293–301 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF28XkvFarsbY%3D
J Belfanz HJ Rehm (1991) ArticleTitleBiodegradation of 4-chlorophenol by adsorptive immobilized Alcaligenes sp. A 7–2 in soil Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 35 662–668
H Bettemann HJ Rehm (1984) ArticleTitleDegradation of phenol by polymer entrapped microorganisms Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 20 285–290
A Bisping HJ Rehm (1988) ArticleTitleMulti step reaction with immobilized microorganisms Biotechnol Appl. Biochem. 10 87–98 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXktVGitLY%3D
MM Bradford (1976) ArticleTitleA rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding Anal. Biochem. 72 248–254 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE28XksVehtrY%3D
JA Buswell (1975) ArticleTitleMetabolism of phenol and cresols by Bacillus stearothermophilus J. Bacteriol. 124 1077–1083 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE28Xos1Gqsw%3D%3D
MD Cameron S Timofeevski SD Aust (2000) ArticleTitleEnzymology of Phanerochaete chrysosporium with respect to the degradation of recalcitrant compounds and xenobiotics Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 54 751–758 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002530000459 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXkvVSquw%3D%3D
NG Carr BA Whitton (1982) The biology of cyanobacteria Blackwell Scientific Publications Oxford
CE Cerniglia DT Gibson (1979) ArticleTitleAlgal oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons: formation of 1-napthol from naphthalene by Agmenellum quadruplicatum. strain PR-6 Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 88 55–58 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0006-291X(79)91695-4
PSJ Cheetham (1980) Developments in immobilized cell and their applications W Wiseman (Eds) Topics in enzyme and fermentation technology NumberInSeriesVol 4 Ellis Horwood Chichester 189–238
M Clauben S Schmidt (1998) ArticleTitleBiodegradation of phenol and p-cresol by the hypomycete Scedosporium apiospermum Res. Microbiol. 149 399–406
S Dagley (1971) ArticleTitleCatabolism of aromatic compounds by microorganisms Adv. Micro. Physiol 6 1–46 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE38Xps1Kktw%3D%3D
BE Ellis (1977) ArticleTitleDegradation of phenolic compounds by fresh-water algae Plant Sci. Lett. 8 213–216 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2sXhvVGlt70%3D
LD Eltis JT Bolin (1996) ArticleTitleEvolutionary relationships among extradiol dioxygenases Journal of Bacteriology 178 5930–5937 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XmtFOks7g%3D
A Farell B Quilty (1999) ArticleTitleDegradation of mono-chlorophenols by a mixed microbial community via a meta-cleavage pathway Biodeg. 10 353–362
K Furukawa F Matsumura K Tonomura (1978) ArticleTitleAlcaligenes and Aceinetobacter capable of degrading polychlorinated biphenyls Agric. Biol. Chem. 42 543–548 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1cXhs1Kms7Y%3D
SH Ganji BG Pujar (1992) ArticleTitleBacterial degradation of Benzalphthalide World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 8 324 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01201890 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XlsVKrurw%3D
SH Ganji CS Karigar BG Pujar (1993) ArticleTitleMetabolism of benzalphthalide by Pseudomonas species World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 9 597–598 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00386303 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXitFahsLk%3D
DT Gibson (1982) ArticleTitleMicrobial degradation of hydrocarbons Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 5 237–250 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL38XmtV2ltrw%3D
MM Haggblom (1992) ArticleTitleMicrobial breakdown of halogenated aromatic pesticides and related compounds FEMS Microbiol.Rev. 103 29–72 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XmtVymsb4%3D
S Harayama EL Neidle M Kok (1992) ArticleTitleFunctional and evolutionary relationships among diverse oxygenases Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 46 565–601 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXhvVartQ%3D%3D
S Harayama KN Timmis (1989) Catabolism of aromatic hydrocarbons by Pseudomonas DA Hopwood KF Chater (Eds) Genetics of bacterial diversity Academic Press London 151–174
DJ Hopper DG Taylor (1975) ArticleTitlePathways of degradation of m-cresol and p-cresol by Pseudomonas putida J. Bacteriol. 122 1–6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2MXktVCltL8%3D
SR Kaschabek W Reineke (1992) ArticleTitleMaleylacetate reductase of Pseudomonas sp. strain B13 Dechlorination of chloromaleylacetates, metabolites in the degradation of chloroaromatic compounds. Arch. Microbiol. 158 412–417 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXhs1eqs7Y%3D
Keddie RM, Collins MD, Jones D (1986) Genus Arthrobacter. In: Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Vol 2 (pp 1288–1300). Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
LH Keith WA Telliand (1979) ArticleTitlePriority pollutants Environ. Sci.Technol. 13 416–423
G Knoll J Winter (1987) ArticleTitleAnaerobic degradation of phenol in sewage sludge: Benzoate formation from phenol and carbon dioxide in the presence of hydrogen Appl. Micrbiol. Biotechnol. 25 618–620
GS Kochar RS Kahlon (1995) ArticleTitleDegradation of 2,4-dichloro phenoxy acetic acid by immobilized cells of Pseudomonas putida J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 41 367–370 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXps1GrtbY%3D
A Krastanov (2000) ArticleTitleRemoval of phenols from mixtures by coimmobilized laccase / tyrosinease and polyclar adsorption J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24 383–388 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXmtFyhsb0%3D
T Kurtitz CP Wolk (1995) ArticleTitleUse of filamentous cyanobacteria for biodegradation of organic pollutants Appl Environ. Microbiol. 61 234–238
ST Lee SK Rhee GM Lee (1994) ArticleTitleBiodegradation of pyridine by freely suspended and immobilized Pimelobacter sp Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 41 652–657 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXitleksro%3D
KC Loh SJ Wang (1998) ArticleTitleEnhancement of biodegradation of phenol and a non-growth substrate 4-chloro phenol by medium agumentation with conventional carbon sources Biodeg. 8 329–338
S Manohar TB Karegoudar (1998) ArticleTitleDegradation of naphthalene by cells of Pseudomonas sp. Strain NGK 1 immobilized in alginate, agar and polyacrylamide Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 49 785–792 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002530051247 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXkvVKmur8%3D
R Margesin P Bergauer S Gander (2004) ArticleTitleDegradation of phenol and toxicity of phenolic compounds: a comparison of cold-tolerant Arthrobacter sp. and mesophilic Pseudomonas putida Extremophiles 8 201–7 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00792-004-0378-3 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXkslKgtbg%3D
B Menke HJ Rehm (1992) ArticleTitleDegradation of mixtures of monochlorophenols and phenols as substates for free and immobilized cells of Alcaligenes sp. A 7–2 in soil Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 37 655–661 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00240744 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XmtVylu7k%3D
V Mishra R Lal Srinivasan (2001) ArticleTitleEnzymes and operons mediating xenobiotic degradation in bacteria Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 27 133–166 Occurrence Handle10.1080/20014091096729 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXlvVKitLY%3D
K Murugesan (2003) ArticleTitleBioremediation of paper and pulp mill effluents Indian J Exp. Biol 441 1239–1248
ML Naro CE Cerniglia C Baalen Particlevan DT Gibson (1992) ArticleTitleMetabolism of phenanthrene by the marine cyanobacterium Agmenellum quadruplicatum PR-6 Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58 1351–1359
InstitutionalAuthorNameOECD (2001) OECD Envronmental Outlook OECD Paris
KT O’Reilly RL Crawford (1989) ArticleTitleDegradation of pentachlorophenol by polyurethane-immobilized Flavobacterium cells Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55 2115–2118
FX Prenafeta Boldu H Ballerstedt J Gerritse JTC Grotenhuis (2004) ArticleTitleBioremediation of BTEX hydrocarbons: Effect of soil inoculation with the toluene-growing fungus Cladophialophora sp. strain T1 Biodeg. 15 59–65 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXhtVSjsLrI
FX Prenafeta Boldu A Kuhn D Luykx H Anke JW Groenestijn Particlevan JAM Bont Particlede (2001) ArticleTitleIsolation and characterization of fungi growing on volatile aromatic hydrocarbons as their sole carbon and energy source Mycol. Res. 105 477–484 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXkt1GhtLc%3D
L Que SuffixJr RYN Ho (1996) ArticleTitleDioxygen activation by enzymes with mononuclear non-heme iron active sites Chem. Rev. 96 2607–2624 Occurrence Handle10.1021/cr960039f Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xmt1GmsrY%3D
GVB Reddy MH Gold (2000) ArticleTitleDegradation of pentachlorophenol by Phanerochaete chrysosporium: intermediates and reactions involved Microbiol. 146 405–413 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXhsVylt7g%3D
SR Sahasrabudhe AJ Modi VV Modi (1988) ArticleTitleDehalogenation of 3 chlorobenzoate by immobilized Pseudomonas B-13 cells Biotechnol. Bioeng. 31 889–893 Occurrence Handle10.1002/bit.260310818 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXit1Khur4%3D
JM Sala-Trepat WC Evans (1971) ArticleTitleMeta cleavage of catechol by Azotobacter species: 4-oxalocrotonate pathway Eur. J. Biochem. 20 400–413 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01406.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3MXks1Sitr4%3D
S Shashirekha L Uma G Subramanian (1997) ArticleTitlePhenol degradation by the marine cynobacterium Phormidium valderianum BDU 30501 J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 19 130–133 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXnt1Gisbg%3D
E Shimoni T Baasov U Ravid Y Shoham (2003) ArticleTitleBiotransformations of propenyl benzenes by an Arthrobacter sp. and its t-anethole blocked mutants J Biotechnol. 105 61–70 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-1656(03)00141-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXnsVKmtb8%3D
G Subramanian S Sekar S Sampoornam (1994) ArticleTitleBioremediation and utilization of organophosphorous pesticides by cyanobacteria Int Bioterio. Biodeg. 33 129–143
L Uma G Subramanian (1990) Effective use of cyanobacteria in effluent treatment. Proc. National Symp. cyanobacerial nitrogen fixation IARI New Delhi 437–444
JR Meer Particlevan der WM Vos Particlede S Harayama AJB Zehnder (1992) ArticleTitleMolecular mechanisms of genetic adaptation to xenobiotic compounds Microbiol. Rev. 56 677–694
F Westmeier HJ Rehm (1985) ArticleTitleBiodegradation of 4-chlorophenol by entrapped Alcaligenes sp. A 7–2 Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 22 301–305 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00582412 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXls1Gmtro%3D
F Westmeier HJ Rehm (1987) ArticleTitleBiodegradation of 4-chlorophenol in municipal waste water by absorptive immobilized Alcaligenes sp. A 7–2 Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 26 78–83 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00282152 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXitF2jsLw%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karigar, C., Mahesh, A., Nagenahalli, M. et al. Phenol Degradation by Immobilized Cells of Arthrobacter citreus. Biodegradation 17, 47–55 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-005-3048-y
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-005-3048-y