Abstract
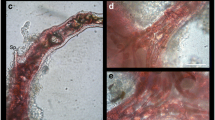
Here we present the first observation of the impact of the invasive Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea on native photophilic sponge species in the Adriatic Sea, with special focus on Sarcotragus spinosulus. Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea is able to completely overgrow the sponge, developing an exceptionally thick canopy with a maximum measured density of 1,887 m of stolons m−2 and 40,561 fronds m−2. Necrosis of the sponge surface was significantly correlated with the algal dry biomass, frond number and stolon length. Dense algal canopy, penetration of the algal stolon and rhizoids into the sponge oscula and covering of the ostiae probably diminishes the seawater circulation through the sponge and consequently results in its smothering and even death. We suggest that chemotropism is the reason why C. racemosa penetrates the sponge oscula and establishes such dense canopy on the sponge.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antolić B, Žuljević A, Despalatović M, Grubelić I, Cvitković I (2008) Impact of the invasive green alga Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea on the epiphytic macroalgal assemblage of Posidonia oceanica seagrass rhizomes in the Adriatic Sea. Nova hedwigia 86(1–2):155–167
Baldacconi R, Corriero G (2009) Effects of the spread of the alga Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea on the sponge assemblage from coralligenous concretions of the Apulian coast (Ionian Sea, Italy). Mar Ecol 30:337–345
Casu D, Ceccherelli G, Palomba D, Curini-Gelletti M, Castelli A (2005) Effetto immediato della rimozione di Caulerpa racemosa sullo zoobenthos dell’infralittorale superficiale roccioso di Porto Torres (Nord Sardegna). In: XV Meeting of the Italian Society of Ecology, pp 1–3
Chisholm JRM, Dauga C, Ageron E, Grimont PAD, Jaubert JM (1996) “Roots” in mixotrophic algae. Nature 381:382
Choi K, Hong J, Lee C, Kim D, Sim C, Im K, Jung J (2004) Cyotoxic furanoses-tertepenes from a marine sponge Psammocinia sp. L Nat Prod 67:1186–1189
Cottalorda JM, Gratiot J, Mannoni PA, De Vaugelas J, Meinesz A (2008) Suivi de l’invasion des algues introduites Caulerpa taxifolia et Caulerpa racemosa en Méditerranée: situation devant les côtes françaises au 31 décembre 2007. E.A. 4228 ECOMERS, Laboratoire Environnement Marin Littoral - Université de Nice-Sophia Antipolis publ.: 42 pp+96 pages d’annexes
Davis AR, Roberts DE, Cummins SP (1997) Rapid invasion of a sponge dominated deep-reef by Caulerpa scalpeliformis (Chlorophyta) in Botany Bay, New South Wales. Austral J Ecol 22:146–150
Iveša Lj, Devescovi M (2006) Seasonal vegetation patterns of the introduced Caulerpa racemosa (Caulerpales, Chlorophyta) in the northern Adriatic Sea (Vrsar, Croatia). Period Biol 108(2):111–116
Klein J (2007) Impact de Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindrea (Caulerpales, Chlorophyta) sur les communautés macrophytiques en Méditerranée nord-occidentale. Thèse de Doctorat, Université Aix-Marseille II, France
Klein J, Verlaque M (2008) The Caulerpa racemosa invasion: a critical review. Mar Pollut Bull 56:205–225
Maier I, Müller DG (1986) Sexual pheromones in algae. Biol Bull 170:145–175
Ould-Ahmed N, Meinesz A (2007) First record of the invasive alga Caulerpa racemosa (Caulerpales, Chlorophyta) on the coast of Algeria. Cryptogam Algol 28:303–305
Pawlik JR, Mac Fall G, Zea S (2002) Does the odor from sponges of the genus Ircinia protect them from fish predators? J Chem Ecol 28:1103–1115
Piazzi L, Balata D (2008) The spread of Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea in the Mediterranean Sea: an example of how biological invasions can influence beta diversity. Mar Environ Res 65:50–61
Piazzi L, Cinelli F (1999) Development and seasonal dynamics of a population of the tropical alga Caulerpa racemosa (Forsskål). J. Agardh in the Mediterranean. Cryptogam Algol 20:295–300
Piazzi L, Ceccherelli G, Cinelli F (2001) Threat to macroalgal diversity: effects of the introduced green alga Caulerpa racemosa in the Mediterranean. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 210:149–159
Piazzi L, Meinesz A, Verlaque M, Akçali B, Antolić B, Argyrou M, Balata D, Ballesteros E, Calvo S, Cinelli F, Cirik S, Cossu A, D’archino F, Djellouli AS, Javel F, Lanfranco E, Mifsud C, Pala D, Panayotidis P, Peirano A, Pergent G, Petrocelli A, Ruitton S, Žuljević A, Ceccherelli G (2005) Invasion of Caulerpa racemosa var cylindracea (Caulerpales, Chlorophyta) in the Mediterranean Sea: an assessment of the spread. Cryptogam Algol 26(2):189–202
Ruitton S, Javel F, Culioli JM, Meinesz A, Pergent G, Verlaque M (2005) First assessment of the Caulerpa racemosa (Caulerpales, Chlorophyta) invasion along the French Mediterranean coast. Mar Pollut Bull 50:1061–1068
Tsoukatou M, Hellio C, Vagias C, Harvala C, Roussis V (2002) Chemical defense and antifouling activity of three mediterranean sponges of the genus Ircinia. Z Naturforsch 57:161–171
Vacelet J (1991) Statut des éponges commerciales en Méditerranée. In: Boudouresque CF, Avon M, Gravez V (eds) Les espèces marines à protéger en Méditerranée. Gis Posidonie publi, France, pp 35–42
Vázquez-Luis M, Sanchez-Jerez P, Bayle-Sempere JT (2008) Changes in amphipod (Crustacea) assemblages associated with shallow-water algal habitats invaded by Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea in the western Mediterranean Sea. Mar Environ Res 65:416–426
Verlaque M, Boudouresque CF, Meinesz A, Gravez V (2000) The Caulerpa racemosa complex (Caulerpales, Ulvophyceae) in the Mediterranean Sea. Bot Mar 43:49–68
Verlaque M, Durand C, Huisman JM, Boudouresque CF, Le Parco Y (2003) On the identity and origin of the Mediterranean invasive Caulerpa racemosa (Caulerpales, Chlorophyta). Eur J Phycol 38:325–339
Wang N, Shin J (2008) Secondary metabolites of marine sponge Sarcotragus sp. J Biotechnol 136:577–578
Žuljević A, Antolić B, Onofri V (2003) First record of Caulerpa racemosa (Caulerpales: Chlorophyta) in the Adriatic Sea. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 83:711–712
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10530_2011_43_MOESM1_ESM.mpg
Online Resource – Video 1 Shallow rocky bottom affected by Caulerpa racemosa. Diver is collecting a sponge (Sarcotragus spinosulus) completely overgrown by the invasive alga at a depth of 7 m. Note that diver detaches the invaded sponge only by hand, which is not possible if the sponge is healthy (MPG 8431 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Žuljević, A., Thibaut, T., Despalatović, M. et al. Invasive alga Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea makes a strong impact on the Mediterranean sponge Sarcotragus spinosulus . Biol Invasions 13, 2303–2308 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-011-0043-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-011-0043-6