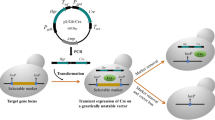
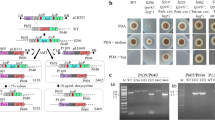
Abstract
Objective
A convenient strategy was developed to recycle selectable markers using Cre/loxP system for constructing Komagataella phaffii strains co-expressing multiple proteins.
Results
A plasmid in this strategy was generated from pPICZαA with integration of lox71-Sh ble-lox66. Firstly, the plasmid was inserted with one target protein gene and then transformed into K. phaffii KM71. Secondly, the auxiliary plasmid pPICZαA/cre/his4 containing CRE recombinase gene was further chromosomally inserted to Sh ble gene therein. Finally, methanol induction was conducted to produce CRE for Cre/loxP-mediated recombination, and consequently, the sequence between lox71 and lox66 was deleted, leading to recycling of ZeoR and His− markers. Then the resulted strain expressing the one target protein was used as the host to which another target protein gene could be inserted by the same procedures.
Conclusions
With easy manipulation, the method was effective in recycling of the selectable markers, and consequently two protein genes were sequential integrated chromosomally and successfully co-expressed in the yeast.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai H, Zhang T, Zhao M, Mao J, Cai C, Feng F (2017) Co-expression of lipase isozymes for enhanced expression in Pichia pastoris. Lett Appl Microbiol 65:335–342
Carter Z, Delneri D (2010) New generation of loxP-mutated deletion cassettes for the genetic manipulation of yeast natural isolates. Yeast 27:765–775
Fang J, Ma Z, Liu D, Wang Z, Cheng S, Zheng S, Wu H, Xia P, Chen X, Yang R, Hao L, Zhang Y (2023) Co-expression of recombinant human collagen α1(III) chain with viral prolyl 4-hydroxylase in Pichia pastoris GS115. Protein Expr Purif 201:106184
Hamilton DL, Abremski K (1984) Site-specific recombination by the bacteriophage P1 lox-Cre system. Cre-mediated synapsis of two lox sites. J Mol Biol 178:481–486
Han M, Wang W, Gong X, Zhou J, Xu C, Li Y (2021) Increased expression of recombinant chitosanase by co-expression of Hac1p in the yeast Pichia pastoris. Protein Pept Lett 28:1434–1441
Han M, Wang W, Gong X, Zhu G, Liu X, Yu Z, Zhou J, Ma C, Ma X (2022) A modified method of gene disruption in Komagataella phaffii with Cre/loxP system. J Biotechnol 347:40–48
He Z, Zhang L, Mao Y, Gu J, Pan Q, Zhou S, Gao B, Wei D (2014) Cloning of a novel thermostable glucoamylase from thermophilic fungus Rhizomucor pusillus and high-level co-expression with α-amylase in Pichia pastoris. BMC Biotechnol 14:114
Higgins DR, Cregg JM (1998) Pichia protocols. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Karbalaei M, Rezaee SA, Farsiani H (2020) Pichia pastoris: a highly successful expression system for optimal synthesis of heterologous proteins. J Cell Physiol 235:5867–5881
Li J, Cai J, Ma M, Li L et al (2021) Preparation of a Bombyx mori acetylcholinesterase enzyme reagent through chaperone protein disulfide isomerase co-expression strategy in Pichia pastoris for detection of pesticides. Enzyme Microb Technol 44:109741
Liu J, Han Q, Cheng Q, Chen Y, Wang R, Li X, Liu Y, Yan D (2020) Efficient expression of human lysozyme through the increased gene dosage and co-expression of transcription factor Hac1p in Pichia pastoris. Curr Microbiol 77:846–854
McLellan MA, Rosenthal NA, Pinto A (2017) Cre-loxP-mediated recombination: general principles and experimental considerations. Curr Protoc Mouse Biol 7:1–12
Näätsaari L, Mistlberger B, Ruth C, Hajek T, Hartner FS, Glieder A (2012) Deletion of the Pichia pastoris KU70 homologue facilitates platform strain generation for gene expression and synthetic biology. PLoS ONE 7(6):e39720
Nett JH, Gerngross TU (2003) Cloning and disruption of the PpURA5 gene and construction of a set of integration vectors for the stable genetic modification of Pichia pastoris. Yeast 20:1279–1290
Sauer B (1987) Functional expression of the cre-lox site-specific recombination system in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Bio 7:2087–2096
Wu D, Zhu H, Chu J, Wu J (2019) N-Acetyltransferase co-expression increases α-glucosidase expression level in Pichia pastoris. J Biotechnol 289:26–30
Zhang Z, Lutz B (2002) Cre recombinase-mediated inversion using lox66 and lox71: method to introduce conditional point mutations into the CREB-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res 30:e90
Zhang Z, Zhang X, Hao H, Gong X, Gu X (2020) Co-expression of Pseudomonas alcaligenes lipase and its specific foldase in Pichia pastoris by a dual expression cassette strategy. Protein Expr Purif 175:105721
Zhao C, Song G, Silver K, Tang T, Wang C, Qiu L (2018) Heterologous co-expression of CYP6B7 and NADPH-dependent cytochrome P450 reductase from Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Pichia pastoris. J Econ Entomol 111:1868–1874
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32260012) and by Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Foundation (Grant No. [2020]1Y148).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the experimental design, hands on work, discussions, and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals.
Consent to participations
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Han, M., Zhu, G. et al. Recycling selectable markers via Cre/loxP system for constructing Komagataella phaffii strains co-expressing multiple proteins. Biotechnol Lett 46, 399–407 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-024-03466-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-024-03466-3