Abstract
Objectives
Different sulfur contents of diesel oils were used for biodesulfurization to study the desulfurization capacity of Gordonia sp. SC-10 in oil–water two-phase reaction system.
Results
Gordonia sp. SC-10 showed great properties in desulfurizing diesel oil with different sulfur contents. This bacterium could decrease sulfur contents in different diesel oils from 194.7 ± 3.7 to 30.4 ± 0.5 mg/l and from 3035.3 ± 23.8 to 1792.8 ± 48.9 mg/l, respectively. Furthermore, this bacterium could desulfurize broad range of organosulfur compounds and had strong desulfurization activity against alkylated DBTs. For low-sulfur diesel oil, sulfur could be removed from 10.2 ± 0.1 to 5.0 ± 0.1 mg/l.
Conclusions
The newly isolated bacteria Gordonia sp. SC-10 showed a good performance in desulfurizing diesel oils, and it might be a useful desulfurizing biocatalyst to enable the industrialized application of biodesulfurization process.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar N, Akhtar K, Ghauri MA (2018) Biodesulfurization of thiophenic compounds by a 2-hydroxybiphenyl-resistant Gordonia sp. HS126-4 N carrying dszABC genes. Curr Microbiol 75:597–603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-017-1422-8
Babich IV, Moulijn JA (2003) Science and technology of novel processes for deep desulfurization of oil refinery streams: a review. Fuel 82:607–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-2361(02)00324-1
Bachmann RT, Johnson AC, Edyvean RGJ (2014) Biotechnology in the petroleum industry: an overview. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 86:225–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.09.011
Bhatia S, Sharma DK (2010) Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene, its alkylated derivatives and crude oil by a newly isolated strain Pantoea agglomerans D23W3. Biochem Eng J 50:104–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2010.04.001
Chang JH, Rhee SK, Chang YK, Chang HN (1998) Desulfurization of diesel oils by a newly isolated dibenzothiophene-degrading Nocardia sp. strain CYKS2. Biotechnol Prog 14:851–855. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp9800788
Chen S, Zhao C, Liu Q et al (2018) Thermophilic biodesulfurization and its application in oil desulfurization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:9089–9103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9342-5
de Bont JAM (1998) Solvent-tolerant bacteria in biocatalysis. Trends Biotechnol 1999:493–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7799(98)01234-7
Depauw GA, Froment GF (1997) Molecular analysis of the sulphur components in a light cycle oil of a catalytic cracking unit by gas chromatography with mass spectrometric and atomic emission detection. J Chromatogr A 761:231–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(96)00819-9
Folsom BR, Schieche DR, DiGrazia PM et al (1999) Microbial desulfurization of alkylated dibenzothiophenes from a hydrodesulfurized middle distillate by Rhodococcus erythropolis I-19. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4967–4972
Furuya T, Ishii Y, Noda-ichi K et al (2003) Thermophilic biodesulfurization of hydrodesulfurized light gas oils by Mycobacterium phlei WU-F1. FEMS Microbiol Lett 221:137–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1097(03)00169-1
Gunam IBW, Yaku Y, Hirano M et al (2006) Biodesulfurization of alkylated forms of dibenzothiophene and benzothiophene by Sphingomonas subarctica T7b. J Biosci Bioeng 101:322–327. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.101.322
Ishii Y, Kozaki S, Furuya T et al (2005) Thermophilic biodesulfurization of various heterocyclic sulfur compounds and crude straight-run light gas oil fraction by a newly isolated strain Mycobacterium phlei WU-0103. Curr Microbiol 50:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-004-4403-7
Kawaguchi H, Kobayashi H, Sato K (2012) Metabolic engineering of hydrophobic Rhodococcus opacus for biodesulfurization in oil-water biphasic reaction mixtures. J Biosci Bioeng 113:360–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2011.10.017
Kilbane JJ (2017) Biodesulfurization: how to make it work? Arab J Sci Eng 42:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-016-2269-1
Kirimura K, Furuya T, Nishii Y et al (2001) Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene and its derivatives through the selective cleavage of carbon-sulfur bonds by a moderately thermophilic bacterium Bacillus subtilis WU-S2B. J Biosci Bioeng 91:262–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1389-1723(01)80131-6
Kobayashi M, Onaka T, Ishii Y et al (2000) Desulfurization of alkylated forms of both dibenzothiophene and benzothiophene by a single bacterial strain. FEMS Microbiol Lett 187:123–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1097(00)00187-7
Kobayashi M, Horiuchi K, Yoshikawa O et al (2001) Kinetic analysis of microbial desulfurization of model and light gas oils containing multiple alkyl dibenzothiophenes. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65:298–304. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.65.298
Konishi J, Onaka T, Ishii Y, Suzuki M (2000) Demonstration of the carbon-sulfur bond targeted desulfurization of benzothiophene by thermophilic Paenibacillus sp. strain A11-2 capable of desulfurizing dibenzothiophene. FEMS Microbiol Lett 187:151–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1097(00)00186-5
Lai WC, Song C (1995) Temperature-programmed retention indices for g.c. and g.c.-m.s. analysis of coal- and petroleum-derived liquid fuels. Fuel 74:1436–1451. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-2361(95)00108-H
Li F, Xu P, Ma C et al (2003) Deep desulfurization of hydrodesulfurization-treated diesel oil by a facultative thermophilic bacterium Mycobacterium sp. X7B. FEMS Microbiol Lett 223:301–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1097(03)00397-5
Li F, Xu P, Feng J et al (2005) Microbial desulfurization of gasoline in a Mycobacterium goodii X7B immobilized-cell system. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:276–281. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.1.276-281.2005
Ma X, Sakanishi K, Mochida I (1994) Hydrodesulfurization reactivities of various sulfur compounds in diesel fuel. Ind Eng Chem Res 33:218–222. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie00026a007
Ma X, Sun L, Song C (2002) A new approach to deep desulfurization of gasoline, diesel fuel and jet fuel by selective adsorption for ultra-clean fuels and for fuel cell applications. Catal Today 77:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0920-5861(02)00237-7
Martínez I, El-Said Mohamed M, Santos VE et al (2017) Metabolic and process engineering for biodesulfurization in Gram-negative bacteria. J Biotechnol 262:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.09.004
Mohebali G, Ball AS (2016) Biodesulfurization of diesel fuels - Past, present and future perspectives. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 110:163–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.03.011
Monticello DJ (2000) Biodesulfurization and the upgrading of petroleum distillates. Curr Opin Biotechnol 11:540–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-1669(00)00154-3
Nomura N, Takada M, Okada H et al (2005) Identification and functional analysis of genes required for desulfurization of alkyl dibenzothiophenes of Mycobacterium sp. G3. J Biosci Bioeng 100:398–402. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.100.398
Ohshiro T, Nakura S, Ishii Y et al (2009) Novel reactivity of dibenzothiophene monooxygenase from Bacillus subtilis WU-S2B. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73:2128–2130. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.90284
Okada H, Nomura N, Nakahara T, Maruhashi K (2002) Analyses of substrate specificity of the desulfurizing bacterium Mycobacterium sp. G3. J Biosci Bioeng 93:228–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1389-1723(02)80019-6
Sadare OO, Obazu F, Daramola MO (2017) Biodesulfurization of petroleum distillates—current status, opportunities and future challenges. Environments 4:85. https://doi.org/10.1080/13869795.2016.1176233
Song C (2003) An overview of new approaches to deep desulfurization for ultra-clean gasoline, diesel fuel and jet fuel. Catal Today 86:211–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0920-5861(03)00412-7
Tanaka Y, Matsui T, Konishi J et al (2002) Biodesulfurization of benzothiophene and dibenzothiophene by a newly isolated Rhodococcus strain. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:325–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-002-0985-9
Tao F, Yu B, Xu P, Ma CQ (2006) Biodesulfurization in biphasic systems containing organic solvents. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:4604–4609. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00081-06
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 16CX06008A).
Supporting information
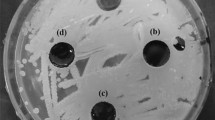
Supplementary Figure 1—Two of the samples after 5 days of cultivation. Each flask contained 50 ml of SF medium supplemented with 5 ml of light cycle oil (LCO) and was cultivated at 160 rpm and 30 °C for 5 days. (a) was the blank sample (uninoculated sample after treatment under the same conditions); (b) was the sample added with Gordonia sp. SC-10. No oil droplet formed in the blank samples. In samples added with Gordonia sp. 10, the bacteria adhered to the oil-water interface and formed an upper emulsion layer, and the average size of oil droplets was about 30.3 μm (measured by optical microscope). No evaporation of water was observed within five days.
Supplementary Table 1—Abbreviations and structural formulas of sulfur components.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Zhao, C., Liu, Q. et al. Biodesulfurization of diesel oil in oil–water two phase reaction system by Gordonia sp. SC-10. Biotechnol Lett 41, 547–554 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-019-02663-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-019-02663-9