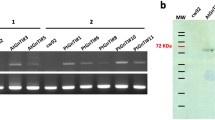
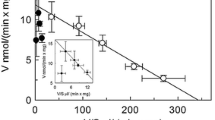
Abstract
Objectives
To investigate the translocation of nucleotide-activated sugars from the cytosol across a membrane into the endoplasmatic reticulum or the Golgi apparatus which is an important step in the synthesis of glycoproteins and glycolipids in eukaryotes.
Results
The heterologous expression of the recombinant and codon-adapted human GDP-l-fucose antiporter gene SLC35C1 (encoding an N-terminal OmpA-signal sequence) led to a functional transporter protein located in the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. The in vitro transport was investigated using inverted membrane vesicles. SLC35C1 is an antiporter specific for GDP-l-fucose and depending on the concomitant reverse transport of GMP. The recombinant transporter FucT1 exhibited an activity for the transport of 3H-GDP-l-fucose with a Vmax of 8 pmol/min mg with a Km of 4 µM. The functional expression of SLC35C1 in GDP-l-fucose overproducing E. coli led to the export of GDP-l-fucose to the culture supernatant.
Conclusions
The export of GDP-l-fucose by E. coli provides the opportunity for the engineering of a periplasmatic fucosylation reaction in recombinant bacterial cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeijon C, Robbins PW, Hirschberg CB (1996) Molecular cloning of the Golgi apparatus uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine transporter from Kluyveromyces lactis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:5963–5968
Berninsone P, Eckhardt M, Gerardy-Schahn R, Hirschberg CB (1997) Functional expression of the murine Golgi CMP-sialic acid transporter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 272:12616–12619
Caffaro CE, Hirschberg CB (2006) Nucleotide sugar transporters of the Golgi apparatus. Acc Chem Res 39:805–812
Chan KF, Shahreel W, Wan C, Teo G, Hayati N, Tay SJ, Tong WH, Yang Y, Rudd PM, Zhan P, Song Z (2016) Inactivation of GDP-fucose transporter gene (Slc35c1) in CHO cells by ZFNs, TALENs and CRISPR-Cas9 for production of fucose-free antibodies. Biotechnol J 11:399–414
Coyne MJ, Reinap B, Lee MM, Comstock LE (2005) Human symbionts use a host-like pathway for surface fucosylation. Science 307:1778–1781
Facey SJ, Kuhn A (2004) Membrane integration of E. coli model membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1694:55–66
Guillen E, Abeijon C, Hirschberg CB (1998) Mammalian Golgi apparatus UDP-N-acetylglucosamine transporter: molecular cloning by phenotypic correction of a yeast mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:7888–7892
Helmus Y, Denecke J, Yakubenia S, Robinson P, Lühn K, Watson DL, McGrogan PJ, Vestweber D, Marquardt T, Wild MK (2006) Leukocyte adhesion deficiency II patients with a dual defect of the GDP-fucose transporter. Blood 107:3959–3966
Hirschberg CB (2001) Golgi nucleotide sugar transport and leukocyte adhesion deficiency II. J Clin Invest 108:3–6
Hirschberg CB, Robbins PW, Abeijon C (1998) Transporters of nucleotide sugars, ATP, and nucleotide sulfate in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. Annu Rev Biochem 67:49–69
Liu L, Hirschberg CB (2013) Developmental diseases caused by impaired nucleotide sugar transporters. Glycoconj J 30:5–10
Liu L, Xu YX, Hirschberg CB (2010) The role of nucleotide sugar transporters in development of eukaryotes. Semin Cell Dev Biol 21:600–608
Lu X, Hou X, Shi S, Körner C, Stanley P (2010) Slc35c2 promotes Notch1 fucosylation and is required for optimal signaling in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem 285:36245–36254
Lübke T, Marquardt T, Etzioni A, Hartmann E, von Figura K, Körner C (2001) Complementation cloning identifies CDG-IIc, a new type of congenital disorders of glycosylation, as a GDP-fucose transporter deficiency. Nat Genet 28:73–76
Lühn K, Wild MK, Eckhardt M, Gerardy-Schahn R, Vestweber D (2001) The gene defective in leukocyte adhesion deficiency II encodes a putative GDP-fucose transporter. Nat Genet 28:69–72
Lühn K, Laskowska A, Pielage J, Klambt C, Ipe U, Vestweber D, Wild MK (2004) Identification and molecular cloning of a functional GDP-fucose transporter in Drosophila melanogaster. Exp Cell Res 301:242–250
Ma B, Simala-Grant JL, Taylor DE (2006) Fucosylation in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Glycobiology 16:158R–184R
Maggioni A, von Itzstein M, Gerardy-Schahn R, Tiralongo J (2007) Targeting the expression of functional murine CMP-sialic acid transporter to the E. coli inner membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 362:779–784
Moriwaki K, Noda K, Nakagawa T, Asahi M, Yoshihara H, Taniguchi N, Hayashi N, Miyoshi E (2007) A high expression of GDP-fucose transporter in hepatocellular carcinoma is a key factor for increases in fucosylation. Glycobiology 17:1311–1320
Münster AK, Eckhardt M, Potvin B, Mülenhoff M, Stanley P, Gerardy-Schahn R (1998) Mammalian cytidine 5′-monophosphate N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase: a nuclear protein with evolutionarily conserved structural motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:9140–9145
Pastuszak I, Ketchum C, Hermanson G, Sjoberg EJ, Drake R, Elbein AD (1998) GDP-l-fucose pyrophosphorylase. purification, cDNA cloning, and properties of the enzyme. J Biol Chem 273:30165–30174
Pines O, Inouye M (1999) Expression and secretion of proteins in E. coli. Mol Biotechnol 12:25–34
Rosen BP, Tsuchiya T (1979) Preparation of everted membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli for the measurement of calcium transport. Methods Enzymol 56:233–241
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatias T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, NY
Tiralongo J, Maggioni A (2011) The targeted expression of nucleotide sugar transporters to the E. coli inner membrane. Methods Mol Biol 705:237–249
Tiralongo J, Ashikov A, Routier F, Eckhardt M, Bakker H, Gerardy-Schahn R, von Itzstein M (2006) Functional expression of the CMP-sialic acid transporter in Escherichia coli and its identification as a simple mobile carrier. Glycobiology 16:73–81
Tonetti M, Sturla L, Bisso A, Zanardi D, Benatti U, De Flora A (1998) The metabolism of 6-deoxyhexoses in bacterial and animal cells. Biochimie 80:923–931
Vallon T, Ghanegaonkar S, Vielhauer O, Müller A, Albermann C, Sprenger G, Reuss M, Lemuth K (2008) Quantitative analysis of isoprenoid diphosphate intermediates in recombinant and wild-type Escherichia coli strains. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81:175–182
Volff JN, Eichenseer C, Viell P, Piendl W, Altenbuchner J (1996) Nucleotide sequence and role in DNA amplification of the direct repeats composing the amplifiable element AUD1 of Streptomyces lividans 66. Mol Microbiol 21:1037–1047
Xu YX, Liu L, Caffaro CE, Hirschberg CB (2010) Inhibition of Golgi apparatus glycosylation causes endoplasmic reticulum stress and decreased protein synthesis. J Biol Chem 285:24600–24608
Yanisch-Perron C, Vieira J, Messing J (1985) Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33:103–119
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Stephan Nußberger (Universtät Stuttgart) for his support with the electron microscope and to Josef Altenbuchner (Universtät Stuttgart) for providing us with plasmid pJOE2702. The authors acknowledge the financial support by a grant from the German Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BioChance Plus 0315170) to Jennewein Biotechnologie GmbH, Rheinbreitbach, Germany. We also thank Jennewein Biotechnologie GmbH for the supply of strains and plasmids.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Parts of the presented results have been filed as a patent application.
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1—Strains and plasmids used in this study.
Supplementary Fig. 1—DNA and sequence of the codon optimized fucT1 gene.
Supplementary Fig. 2—Kinetic data of the GDP-l-fucose transport by FucT1.
Additional information
Karin Förster-Fromme and Sarah Schneider have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Förster-Fromme, K., Schneider, S., Sprenger, G.A. et al. Functional expression of a human GDP-l-fucose transporter in Escherichia coli . Biotechnol Lett 39, 219–226 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2233-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2233-x