Abstract
Objective
To investigate the xylose operon and properties of xylose isomerase and xylulokinase in Bacillus coagulans that can effectively ferment xylose to lactic acid.
Results
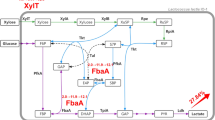
The xylose operon is widely present in B. coagulans. It is composed of four putative ORFs. Novel xylA and xylB from B. coagulans NL01 were cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. Sequence of xylose isomerase was more conserved than that of xylulokinase. Both the enzymes exhibited maximum activities at pH 7–8 but with a high temperature maximum of 80–85 °C, divalent metal ion was prerequisite for their activation. Xylose isomerase and xylulokinase were most effectively activated by Ni2+ and Co2+, respectively.
Conclusions
Genomic analysis of xylose operon has contributed to understanding xylose metabolism in B. coagulans and the novel xylose isomerase and xylulokinase might provide new alternatives for metabolic engineering of other strains to improve their fermentation performance on xylose.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad S, Scopes RK (2002) Isolation and properties of a constitutive d-xylulokinase from a novel thermophilic Saccharococcus caldoxylosilyticus DSM 12041 (ATCC 700356). Enzyme Microb Technol 30:627–632
Chaillou S, Bor YC, Batt CA, Postma PW, Pouwels PH (1998) Molecular cloning and functional expression in Lactobacillus plantarum 80 of xylT, encoding the d-xylose–H+ symporter of Lactobacillus brevis. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4720–4728
Del Campo JSM, Chun Y, Kim JE, Patiño R, Zhang YHP (2013) Discovery and characterization of a novel ATP/polyphosphate xylulokinase from a hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga maritima. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 40:661–669
Eiteman MA, Ramalingam S (2015) Microbial production of lactic acid. Biotechnol Lett 37:955–972
Erlandson KA, Park JH, Khal E, Kao HH, Basaran P, Brydges S, Batt CA (2000) Dissolution of xylose metabolism in Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3974–3980
Fan LJ, Zhang YC, Qu W, Wang JK, Shao WL (2011) Cloning and analysis of the xylAB operon and characterization of xylose isomerase from Thermoanaerobacter ethanolicus. Biotechnol Lett 33:593–598
Flanagan T, Waites MJ (1992) Purification and characterization of d-xylulokinase from the pentose-fermenting yeast Pichia stipitis NCYC 1541. Enzyme Microb Technol 14:975–979
Harhangi HR, Akhmanova AS, Emmens R (2003) Xylose metabolism in the anaerobic fungus Piromyces sp. strain E2 follows the bacterial pathway. Arch Microbiol 180:134–141
Jin YS, Jones S, Shi NQ, Jeffries TW (2002) Molecular cloning of XYL3 (d-xylulokinase) from Pichia stipitis and characterization of its physiological function. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1232–1239
Karhumaa K, Sanchez RG, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2007) Comparison of the xylose reductase–xylitol dehydrogenase and the xylose isomerase pathways for xylose fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Factories 6:5
Kersters-Hilderson H, Callens M, van Opstal O, Vangrysperre W, de Bruyne C (1987) Kinetic characterization of d-xylose isomerases by enzymatic assays using d-sorbitol dehydrogenase. Enzyme Microb Technol 9:145–148
Kovalevsky AY, Hanson L, Fisher SZ (2010) Metal ion roles and the movement of hydrogen during reaction catalyzed by d-xylose isomerase: a joint X-ray and neutron diffraction study. Structure 18:688–699
Lawlis VB, Dennis MS, Chen EY, Smith DH, Henner DJ (1984) Cloning and sequencing of the xylose isomerase and xylulose kinase genes of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 47:15–21
Liu SY, Wiegel J, Gherardini FC (1996) Purification and cloning of a thermostable xylose (glucose) isomerase with an acidic pH optimum from Thermoanaerobacterium strain JW/SL-YS 489. J Bacteriol 178:5938–5945
Lokman BC, van Santen P, Verdoes JC, Krüse J, Leer RJ, Posno M, Pouwels PH (1991) Organization and characterization of three genes involved in d-xylose catabolism in Lactobacillus pentosus. Mol Gen Genet 230:161–169
Nogué VS, Karhumaa K (2015) Xylose fermentation as a challenge for commercialization of lignocellulosic fuels and chemicals. Biotechnol Lett 37:761–772
Patel M, Ou MS, Harbrucker R, Aldrich HC, Buszko ML, Ingram LO, Shanmugam KT (2006) Isolation and characterization of acid-tolerant, thermophilic bacteria for effective fermentation of biomass-derived sugars to lactic acid. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:3228–3235
Rozanov AS, Zagrebelny SN, Beklemishev AB (2009) Cloning of Escherichia coli K12 xylose isomerase (glucose isomerase) gene and studying the enzymatic properties of its expression product. Appl Biochem Microbiol 45:31–37
Su F, Xu P (2014) Genomic analysis of thermophilic Bacillus coagulans strains: efficient producers for platform bio-chemicals. Sci Rep UK 4:3926
Tanaka K, Komiyama A, Sonomoto K, Ishizaki A, Hall S, Stanbury P (2002) Two different pathways for d-xylose metabolism and the effect of xylose concentration on the yield coefficient of l-lactate in mixed-acid fermentation by the lactic acid bacterium Lactococcus lactis IO-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:160–167
Van Dyk JS, Pletschke BI (2012) A review of lignocellulose bioconversion using enzymatic hydrolysis and synergistic cooperation between enzymes—factors affecting enzymes, conversion and synergy. Biotechnol Adv 30:1458–1480
Vangrysperre W, van Damme J, Vandekerckhove J, de Bruyne CK, Cornelis R, Kersters-Hilderson H (1990) Localization of the essential histidine and carboxylate group in d-xylose isomerases. Biochem J 265:699–705
Vankuyk PA, de Groot MJL, Ruijter GJG, de Vries RP, Visser J (2001) The Aspergillus niger d-xylulose kinase gene is co-expressed with genes encoding arabinan degrading enzymes, and is essential for growth on d-xylose and l-arabinose. Eur J Biochem 268:5414–5423
Vieille C, Hess JM, Kelly RM, Zeikus JG (1995) xylA cloning and sequencing and biochemical characterization of xylose isomerase from Thermotoga neapolitana. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:1867–1875
Wang L, Xue ZW, Zhao B, Yu B, Xu P, Ma YH (2013) Jerusalem artichoke powder: a useful material in producing high-optical-purity l-lactate using an efficient sugar-utilizing thermophilic Bacillus coagulans strain. Bioresour Technol 130:174–180
Zheng ZJ, Cai C, Jiang T, Zhao MY, Ouyang J (2014) Enhanced l-lactic acid production from biomass-derived xylose by a mutant Bacillus coagulans. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173:1896–1906
Zheng ZJ, Jiang T, Lin X, Zhou J, Ouyang J (2015) Draft genome sequence of Bacillus coagulans NL01, a wonderful l-lactic acid producer. Genome Announc 3:e00635-15
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China (BK20130970), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31300487, 51561145015), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD) for financial support.
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1—Bacterial strains, plasmids and primers used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhaojuan Zheng and Xi Lin have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Z., Lin, X., Jiang, T. et al. Genomic analysis of a xylose operon and characterization of novel xylose isomerase and xylulokinase from Bacillus coagulans NL01. Biotechnol Lett 38, 1331–1339 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2109-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2109-0