Abstract
Objectives
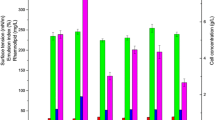
Sulfate-reducing bacteria and H2S exist widely in oil production systems, and in situ production of rhamnolipids is promising for microbial enhanced oil recovery (MEOR). However, information of the effect of S2− on rhamnolipids production is scarce.
Results
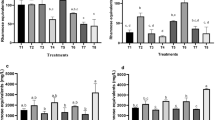
Two facultative anaerobic rhamnolipids-producing bacterial strains, Pseudomonas aeruginosa SG and WJ-1, were used. Above 10 mg S2−/l, both cell growth and rhamnolipids production were inhibited. A large inoculum (9 %, v/v) failed to completely relieve the inhibitory effect of 10 mg S2−/l. Below 30 mg S2−/l, both strains resumed rhamnolipid production through co-culturing with the denitrifying and sulphide-removing strain Pseudomonas stutzeri DQ1.
Conclusions
H2S has a direct but reversible inhibitory effect on rhamnolipids production. Control of H2S in oilfields is indispensable to MEOR, and the co-culture method is effective in restoring rhamnolipid production in presence of S2−.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bejarano OD, Thalasso F, Cuervo López FM, Texier AC (2013) Inhibitory effect of sulfide on the nitrifying respiratory process. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 88:1344–1349
Bødtker G, Thorstenson T, Lillebø BL, Thorbjørnsen BE, Ulvøen RH, Sunde E, Torsvik T (2008) The effect of long-term nitrate treatment on SRB activity, corrosion rate and bacterial community composition in offshore water injection systems. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35:1625–1636
Brown LR (2010) Microbial enhanced oil recovery (MEOR). Curr Opin Microbiol 13:316–320
Dastgheib SMM, Amoozegar MA, Elahi E, Asad S, Banat IM (2008) Bioemulsifier production by a halothermophilic Bacillus strain with potential applications in microbially enhanced oil recovery. Biotechnol Lett 30:263–270
Grigoryan A, Lambo A, Lin S, Cornisn SL, Jack TR, Voordouw G (2009) Souring remediation by field-wide nitrate injection in an Alberta oil field. J Can Petrol Technol 48:58–61
Gudiña EJ, Pereira JF, Costa R, Coutinho JA, Teixeira JA, Rodrigues LR (2013) Biosurfactant-producing and oil-degrading Bacillus subtilis strains enhance oil recovery in laboratory sand-pack columns. J Hazard Mater 261:106–113
Guidotti TL (1996) Hydrogen sulphide. Occup Med (Lond) 46:367–371
Hitzman DO, Sperl GT, Sandbeck KN (1996) Method for reducing the amount of and preventing the formation of hydrogen sulfide in an aqueous system. Biotechnol Adv 2:236
Hubert C, Voordouw G (2007) Oil field souring control by nitrate-reducing Sulfurospirillum spp. that outcompete sulfate-reducing bacteria for organic electron donors. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2644–2652
Marchant R, Banat IM (2012) Biosurfactants: a sustainable replacement for chemical surfactants? Biotechnol Lett 34:1597–1605
Morikawa M, Hirata Y, Imanaka T (2000) A study on the structure–function relationship of the lipopeptide biosurfactants. Biochim Biophys Acta 1488:211–218
Müller MM, Kügler JH, Henkel M, Gerlitzki M, Hörmann B, Pöhnlein M, Syldatk C, Hausmann R (2012) Rhamnolipids-next generation surfactants? J Biotechnol 162:366–380
Nemati M, Jenneman GE, Voordouw G (2011) Mechanistic Study of microbial control of hydrogen sulfide production in oil reservoirs. Biotechnol Bioeng 74:424–434
Raza ZA, Khan MS, Khalid ZM, Rehman A (2006) Production kinetics and tensioactive characteristics of biosurfactant from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant grown on waste frying oils. Biotechnol Lett 28:1623–1631
Wang F, Chapman PM (1999) Biological implications of sulfide in sediment—a review focusing on sediment toxicity. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:2526–2532
Xia WJ, Luo ZB, Dong HP, Yu L, Cui QF, Bi YQ (2012) Synthesis, Characterization, and Oil Recovery Application of Biosurfactants Produced by Indigenous Pseudomonas aeruginosa WJ-1 Using Waste Vegetable Oils. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166:1148–1166
Xu X, Chen C, Wang A, Guo W, Zhou X, Lee DJ, Ren N, Chang JS (2014) Simultaneous removal of sulfide, nitrate and acetate under denitrifying sulfide removal condition: modeling and experimental validation. J Hazard Mater 264:16–24
Youssef NH, Duncan KE, Nagle DP, Savage KN, Knapp RM, McInerney MJ (2004) Comparison of methods to detect biosurfactant production by diverse microorganisms. J Microbiol Methods 56:339–347
Youssef N, Simpson DR, Duncan KE, Mclnerney MJ, Folmsbee M, Fincher T, Knapp RM (2007) In situ biosurfactant production by Bacillus Strains injected into a limestone petroleum reservoir. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:1239–1247
Youssef N, Simpson DR, Mclnerney MJ, Duncan KE (2013) In-situ lipopeptide biosurfactant production by Bacillusstrains correlates with improved oil recovery in two oil wells approaching their economic limit of production. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 81:127–132
Zhao F, Shi R, Zhang J, Han S, Ma F, Zhang Y (2015) Characterization and evaluation of a denitrifying and sulfide removal bacterial strain isolated from Daqing Oilfield. Pet Sci Technol 33:694–701
Zhou Z, Xing C, An Y, Hu D, Qiao W, Wang L (2014) Inhibitory effects of sulfide on nitrifying biomass in the anaerobic–anoxic–aerobic wastewater treatment process. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 89:214–219
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31100098) and the Program of China Daqing Oilfield Company Limited. Thanks Professor Hanping Dong for providing bacterial strain P. aeruginosa WJ-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, F., Ma, F., Shi, R. et al. Production of rhamnolipids by Pseudomonas aeruginosa is inhibited by H2S but resumes in a co-culture with P. stutzeri: applications for microbial enhanced oil recovery. Biotechnol Lett 37, 1803–1808 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1859-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1859-4