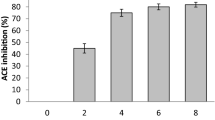
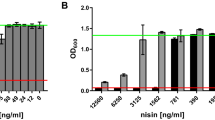
Abstract
Objective
To improve the process for the production of milk-derived antihypertensive peptides, including a 12-residue peptide (FFVAPFPECVGK) from αS1-casein.
Results
A synthetic gene encoding this peptide was cloned within the pediocin operon, replacing the nucleic acid sequence encoding the mature pediocin peptide (papA) and resulting in a translational fusion between the pediocin leader peptide and the 12-residue hypotensive (C-12) peptide. The recombinant operon was subsequently cloned immediately downstream of the nisA promoter to allow for inducible gene expression within Streptococcus thermophilus ST128, Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis ML3 and Lactobacillus casei C2. RT-PCR was used to confirm recombinant gene expression in complex medium; and SDS-PAGE analysis showed that the pediocin secretion machinery, encoded by papC and papD, allowed for secretion of the recombinant peptide from both L. lactis ML3 and L. casei C2 in a chemically defined medium.
Conclusion
The use of a nisin as a “food-grade” inducer molecule, and generally-regarded-as-safe LAB species suggests that this system could be used for the production of functional food ingredients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boelsma E, Kloek J (2009) Lactotripeptides and antihypertensive effects: a critical review. Br J Nutr 101:776–786
Bryan EM, Bae T, Kleerebezem M, Dunny GM (2000) Improved vectors for nisin-controlled expression in gram-positive bacteria. Plasmid 44:183–190
Burianek LL, Yousef AE (2000) Solvent extraction of bacteriocins from liquid cultures. Lett Appl Microbiol 31:193–197
Coderre PE, Somkuti GA (1999) Cloning and expression of the pediocin operon in Streptococcus thermophilus and other lactic fermentation bacteria. Curr Microbiol 39:295–301
FDA (2014) Nisin preparation: affirmation of GRAS status as a direct human food ingredient. 21 CFR 184.1538
Fitzgerald RJ, Meisel H (2000) Milk protein-derived peptide inhibitors of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme. Br J Nutr 84(Suppl 1):S33–S37
Foltz M, Meynen EE, Bianco V, van Platerink C, Koning TMMG, Kloek J (2007) Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from a lactotripeptide-enriched milk beverage are absorbed intact into the circulation. J Nutr 137:953–958
Fu RY, Chen J, Li Y (2005) Heterologous leaky production of transglutaminase in Lactococcus lactis significantly enhances the growth performance of the host. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8911–8919
Hazebrouck S, Pothelune L, Azevedo V, Corthier G, Wal JM, Langella P (2007) Efficient production and secretion of bovine beta-lactoglobulin by Lactobacillus casei. Microb Cell Fact 6:12
Kim JH, Mills DA (2006) Improvement of a nisin-inducible expression vector for use in lactic acid bacteria. Plasmid 58:275–283
Liu D, Sun H, Zhang L, Li S, Qin Z (2007) High-level expression of milk-derived antihypertensive peptide in Escherichia coli and its bioactivity. J Agric Food Chem 55:5109–5112
Lv GS, Huo GC, Fu XY (2003) Expression of milk-derived antihypertensive peptide in Escherichia coli. J Dairy Sci 86:1927–1931
Maruyama S, Nakagomi K, Tomizuka N, Suzuki H (1985) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitor derived from an enzymatic hydrolysate of casein. II Isolation and bradykinin-potentiating activity on the uterus and the ileum of rats. Agric Biol Chem 49:1405–1409
Meisel H (2004) Multifunctional peptides encrypted in milk proteins. Biofactors 21:55–61
Nakamura Y, Yamamoto N, Sakai K, Okubo A, Yamazaki S, Takano T (1995) Purification and characterization of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors from sour milk. J Dairy Sci 78:777–783
Renye JA, Somkuti GA (2008) Cloning of milk-derived bioactive peptides in Streptococcus thermophilus. Biotechnol Lett 30:723–730
Renye JA, Somkuti GA (2010) Nisin-induced expression of pediocin in dairy lactic acid bacteria. J Appl Microbiol 108:2142–2151
Savijoki K, Ingmer H, Varmanen P (2006) Proteolytic systems of lactic acid bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:394–406
Somkuti GA, Steinberg DH (1988) Genetic transformation of Streptococcus thermophilus by electroporation. Biochimie 70:579–585
Stougaard P, Molin S (1981) Vertical dye-buoyant density gradients for rapid analysis and preparation of plasmid DNA. Anal Biochem 118:191–193
Sturrock ED, Natesh R, van Rooyen JM, Acharya KR (2004) Structure of angiotensin I-converting enzyme. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:2677–2686
Zhang G, Mills DA, Block DE (2009) Development of chemically defined media supporting high-cell-density growth of lactococci, enterococci, and streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:1080–1087
Acknowledgments
We thank BA Buttaro (Temple University) and GM Dunny (University of Minnesota) for providing the vector pMSP3535, and DH Steinberg for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mention of trade names or commercial products in this publication is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Renye, J.A., Somkuti, G.A. Nisin-induced expression of a recombinant antihypertensive peptide in dairy lactic acid bacteria. Biotechnol Lett 37, 1447–1454 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1817-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1817-1