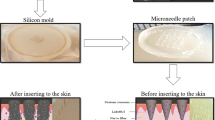
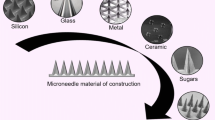
Abstract
There has been an increasing interest in applying biotechnology in formulating and characterising new and innovative drug delivery methods, e.g., drug-loaded biodegradable microneedles within the area of transdermal delivery technology. Recently, microneedles have been proposed for use in pain management, e.g., post-operative pain management through delivery of a local anaesthetic, namely, lidocaine. Lidocaine is a fairly common, marketed prescription-based, local anaesthetic pharmaceutical, applied for relieving localised pain and lidocaine-loaded microneedles have been explored. The purpose of this review is to evaluate the properties of biodegradable polymers that may allow the preparation of microneedle systems, methods of preparing them and pharmacokinetic conditions in considering the potential use of lidocaine for delivery through the skin.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen LV, Popovich NG, Ansel HC (2005) Ansel’s pharmaceutical dosage forms and drug delivery systems, 8th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, p 131
Ameri M, Fan FC, Maa YF (2010) Parathyroid hormone PTH(1–34) formulation that enables uniform coating on a novel transdermal microprojection delivery system. Pharm Res 27:303–313
Ami Y, Tachikawa H, Takano N, Miki N (2011) Formation of polymer microneedle arrays using soft lithography. J Micro Nanolithogr MEM 10:011503. doi:10.1117/1.3553393
Armani DK, Liu C (2000) Microfabrication technology for polycaprolactone, a biodegradable polymer. J Micromech Microeng 10:80–84
Arora A, Prausnitz MR, Mitragotri S (2008) Micro-scale devices for transdermal drug delivery. Int J Pharm 364:227–236
Banga AK (2009) Microneedle-mediated transdernal delivery: how to contribute to meaningful research to advance this growing field. Transdermal 1:8–13
Bariya SH, Gohel MC, Mehta TA, Sharma OP (2011) Microneedles: an emerging transdermal drug delivery system. J Pharm Pharmacol 64:11–29
Bodhale DW, Nisar A, Afzulpurkar N (2010) Structural and microfluidic analysis of hollow side-open polymeric microneedles for transdermal drug delivery application. Microfluid Nanofluid 8:373–392
Chen B, Wei J, Tay FEH, Wong YT, Iliescu C (2008) Silicon microneedles array with biodegradable tips for transdermal drug delivery. Microsyst Technol 14:1015–1019
Choi NS, Kim CH, Cho KY, Park JK (2002) Morphology and hydrolysis of PCL/PLLA blends compatibilized with P(LLA-co-ϵ CL) or P(LLA-b-ϵ CL). J Appl Polym Sci 86:1892–1898
Chu LY, Choi SO, Prausnitz MR (2010) Fabrication of dissolving polymer microneedles for controlled drug encapsulation and delivery: bubble and pedestal microneedle designs. J Pharm Sci 99:4228–4238
Costa JCS, Neves JS, de Souza MVN, Siqueira RA, Romeiro NC, Boechat N, e Silva PMR, Martins MA (2008) Synthesis and antispasmodic activity of lidocaine derivatives with reduced local anesthetic action. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:1162–1166
Dai W, Zhu J, Shangguan A, Lang M (2009) Synthesis, characterization and degradability of the comb-type poly(4-hydroxyl-ε-caprolactone-co-ε-caprolactone)-γ-poly(l-lactide). Eur Polym J 45:1659–1667
Danhier F, Ansorena E, Silva JM, Coco R, Le Breton A, Préat V (2012) PLGA-based nanoparticles: an overview of biomedical applications. J Control Release 161:505–522
Dash TK, Konkimalla BVB (2012) Polymeric modification and its implication in drug delivery: poly-ε-caprolactone (PCL) as a model polymer. Mol Pharm 9:2365–2379
Daugimont L, Baron N, Vandermeulen G, Pavselj N, Miklavcic D, Jullien M-C, Cabodevila G, Mir LM, Préat V (2010) Hollow microneedle arrays for intradermal drug delivery and DNA electroporation. J Membr Biol 236:117–125
Del Campo A, Greiner C (2007) SU-8: a photoresist for high-aspect-ratio and 3D submicron lithography. J Micromech Microeng 17(6):R81–R95
Desai MJ, Radhika S, Wang D (2008) Treatment of pain in Dercum’s disease with Lidoderm® (Lidociane 5% Patch): a case report. Pain Med 9:1224–1226
Djabri A, Guy RH, Delgado-Charro MB (2012) Transdermal iontophoresis of ranitidine: an opportunity in paediatric drug therapy. Int J Pharm 435:27–32
Donnelly RF, Singh TRR, Tunney MM, Morrow DIJ, McCarron PA, O’Mahony C, Woolfson AD (2009) Microneedle arrays allow lower microbial penetration than hypodermic needles in vitro. Pharm Res 26:2513–2522
Donnelly RF, Singh TRR, Woolfson AD (2010) Microneedle-based drug delivery systems: microfabrication, drug delivery and safety. Drug Deliv 17:187–207
Donnelly RF, Majithiya R, Singh TRR, Morrow DIJ, Garland MJ, Demir YK, Migalska K, Ryan E, Gillen D, Scott CJ, Woolfson AD (2011) Design, optimization and characterisation of polymeric microneedle arrays prepared by a novel laser-based micromoulding technique. Pharm Res 28:41–57
Fiala S, Brown MB, Jones SA (2011) Dynamic in situ eutectic formation for topical drug delivery. J Pharm Pharmacol 63:1428–1436
Fredenberg S, Wahlgren M, Reslow M, Axelsson A (2011) The mechanisms of drug release in poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-based drug delivery systems—a review. Int J Pharm 415:34–52
Fujita H (1997) A decade of MEMS and its future. IEEE 10th Annual International Workshop on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems: 1–8. doi:10.1109/MEMSYS.1997.581729
Gabor F, Ertl B, Wirth M, Mallinger R (1999) Ketoprofen-poly(dl-lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres: influence of manufacturing parameters and type of polymer on the release characteristics. J Microencapsul 16:1–12
Garland MJ, Migalska K, Mahmood TM, Singh TR, Woolfson AD, Donnelly RF (2011) Microneedle arrays as medical devices for enhanced transdermal drug delivery. Expert Rev Med Devices 8(4):459–482
Garland MJ, Migalska K, Tuan-Mahmood TM, Singh TRR, Majithija R, Caffarel-Salvador E, McCarthy HO, Woolfson AD, Donnelly AF (2012) Influence of skin model on in vitro performance of drug-loaded soluble microneedle arrays. Int J Pharm 434:80–89
Garlotta D (2001) A literature review of poly(lactic acid). J Polym Environ 9:63–83
Gerstel MS, Place VA (1976) Drug delivery device. Alza Corporation. US Patent 3,964,482
Ginde R, Gupta R (1987) In vitro chemical degradation of poly(glycolic acid) pellets and fibers. J Appl Polym Sci 33:2411–2429
Gittard SD, Chen B, Xu H, Ovsianikov A, Chichkov BN, Monteiro-Riviere NA, Narayan NJ (2012) The effects of geometry on skin penetration and failure of polymer microneedles. J Adhesion Sci Technol. doi:10.1080/01694243.2012.705101
Gupta J, Gill HS, Andrews SN, Prausnitz MR (2011) Kinetics of skin resealing after insertion of microneedles in human subjects. J Control Release 154:148–155
Han M, Kim DK, Kang SH, Yoon HR, Kim BY, Lee SS, Kim KD, Lee HG (2009) Improvement in antigen-delivery using fabrication of a grooves-embedded microneedle array. Sens Actuators B Chem 137:274–280
Han TY, Park KY, Ahn JY, Kim SW, Jung HJ, Kim BJ (2012) Facial skin barrier function recovery after microneedle transdermal delivery treatment. Dermatol Surg 38:1816–1822
Henry S, McAllister DV, Allen MG, Prausnitz MR (1998) Microfabricated microneedles: a novel approach to transdermal drug delivery. J Pharm Sci 87:922–925
Hruby JM (2001) LIGA technologies and applications. M R S Bull [online]. 337–340. www.mrs.org/publications/bulletin
Jeong WL, Park JH, Prausnitz MR (2008) Dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Biomaterials 29:2113–2124
Kaewprapan K, Inprakhon P, Marie E, Durand A (2012) Enzymatically degradable nanoparticles of dextran esters as potential drug delivery systems. Carbohydr Polym 88:875–881
Kalluri H, Banga AK (2011) Formation and closure of microchannels in skin following microporation. Pharm Res 28:82–94
Kalpan G, Shalini VS, Jonnalagadda S, Kumar N (2007) Fast degradable poly(l-lactide-co-e-caprolactone) microspheres for tissue engineering: synthesis, characterization, and degradation behavior. J Polym Sci A1(45):2755–2764
Katz NP, Gammaitoni AR, Davis MW, Dworkin RH (2002) Lidocaine patch 5% reduces pain intensity and interference with quality of life in patients with postherpetic neuralgia: an effectiveness trial. Pain Med 3:324–332
Ke CJ, Lin YJ, Hu YC, Chiang WL, Chen KJ, Yang WC, Liu HL, Fu CC, Sung HW (2012) Multidrug release based on microneedle arrays filled with pH-responsive PLGA microsphere. Biomaterials 33:5156–5165
Khanna P, Luongo K, Strom JA, Bhansali S (2010) Sharpening of hollow silicon microneedlesto reduce skin penetration force. J Micromech Microeng 20:1–8
Kim BJ, Kim HJ, Jung SM, Sung JK, Lee HH (2009) Fabrication of microneedle using laser written PDMS mold for molecular transport into plant skin. Biochip J 3:281–286
Kim MY, Jung B, Park JH (2012a) Hydrogel swelling as a trigger to release biodegradable polymer microneedles in skin. Biomaterials 33:668–678
Kim YC, Park JH, Prausnitz MR (2012b) Microneedles for drug and vaccine delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64:1547–1568
Kissin I (2012) How does the lidocaine patch (5%) relieve pain? Pain 153(6):1332–1333
Klose D, Siepmann F, Willart JF, Descamps M, Siepmann J (2010) Drug release from PLGA-based microparticles: effects of the “microparticle:bulk fluid” ratio. Int J Pharm 383:123–131
Kolli CS, Banga AK (2008) Characterization of solid maltose microneedles and their use for transdermal delivery. Pharm Res 25:104–112
Kundu J, Mohapatra R, Kundu SC (2011) Silk fibroin/sodium carboxymethylcellulose blended ilms for biotechnological applications. J Biomat Sci Polym E 22:519–539
Kwon SY (2004) In vitro evaluation of transdermal drug delivery by a micro-needle patch. Controlled Release Society 31st Annual Meeting Transactions. TheraJect Inc. no. 115
Lai PL, Hsu CC, Liu TH, Hong DW, Chen LH, Chen WJ, Chu IM (2012) Mixed micelles from methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)–polylactide and methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)–poly(sebacic anhydride) copolymers as drug carriers. React Funct Polym 72:846–855
Lee SW, Lee SS (2008) Shrinkage ratio of PDMS and its alignment method for the wafer level process. Microsyst Technol 14:205–208
Lee SJ, Lee IW, Lee YM, Lee HB, Khang G (2004) Macroporous biodegradable natural/synthetic hybrid scaffolds as small intestine submucosa impregnated poly(dl-lactide-co-glycolide) for tissue-engineered bone. J Biomater Sci Polym E 15:1003–1017
Lee JW, Park JH, Prausnitz MR (2008) Dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Biomaterials 29:2113–2124
Lee JW, Choi SO, Felner EI, Prausnitz MR (2011a) Dissolving microneedle patch for transdermal delivery of human growth hormone. Small 7(4):531–539
Lee K, Lee CY, Jung H (2011b) Dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug administration prepared by stepwise controlled drawing of maltose. Biomaterials 32:3134–3140
Lhernould MS, Delchambre A (2011) Innovative design of hollow polymeric microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Microsyst Technol 17:1675–1682. doi:10.1007/s00542-011-1355-2
Lippmann JM, Pisano AP (2006) In-plane, hollow microneedles via polymer investment molding. Proceedings: IEEE Micro Electro Mechanical Systems Workshop: 262–265
Lippmann JM, Geiger EJ, Pisano AP (2007) Polymer investment molding: method for fabricating hollow, microscale parts. Sens Actuators A Phys 134(1):2–10
Loo SCJ, Tan ZYS, Chow YS, Lin SLI (2010) Drug release from irradiated PLGA and PLLA multi-layered films. J Pharm Sci 99:3060–3071
Lorenz H, Despont M, Fahrni N, La Bianca N, Renand P, Vettiger P (1997) SU-8: a low-cost negative resist for MEMS. J Micromech Microeng 7:121–124
Luckachan GE, Pillai CKS (2011) Biodegradable polymers—a review on recent trends and emerging perspective. J Polym Environ 19:637–676
Marasso SL, Canavese G, Cocuzza M (2011) Cost efficient master fabrication process on copper substrates. Microelectron Eng 88:2322–2324
Martin CJ, Allender CJ, Brain KR, Morrissey A, Birchall JC (2012) Low temperature fabrication of biodegradable sugar glass microneedles for transdermal drug delivery applications. J Control Release 158:93–101
Matteucci M, Fanetti M, Casella M, Gramaica F, Gaviolo L, Tormen M, Grenci G, De Angelis F, Di Fabrizio E (2009) Poly vinyl alcohol re-usable masters for microneedle replication. Microelectron Eng 86:752–756
Mattioli S, Kenny JM, Armentano I (2012) Plasma surface modification of porous PLLA films: analysis of surface properties and in vitro hydrolytic degradation. J Appl Polym Sci 125(S2):E239–E247
Mazarro R, Cabezas LI, De Lucas A, Garcia I, Rodríguez JF (2009) Study of different catalysts and initiators in bulk copolymerization of dl-lactide and glycolide. J Macromol Sci A 46:1049–1059
Mehta R, Kumar V, Bhunia H, Upadhyay SN (2005) Synthesis of poly(lactic acid): a review. J Macromol Sci Pol R 45:325–349
Microchem Corp. Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS). www.microchem.com
Miyano T, Tobinaga Y, Kanno T, Matsuzaki Y, Takeda H, Wakui M, Hanada K (2005) Sugar micro needles as transdermic drug delivery system. Biomed Microdev 7:185–188
Monheit GD, Campbell RM, Neugent H, Nelson CP, Prather CL, Bachtell N, Eng D, Holmdahl L (2009) Reduced pain with use of proprietary hyaluronic acid with lidocaine for correction of nasolabial folds: a patient-blinded, prospective, randomised controlled trial. Dermatol Surg 36:94–101
Mundargi RC, Babu VR, Rangaswamy V, Patel P, Aminabhavi TM (2008) Nano/micro technologies for delivering macromolecular therapeutics using poly(dl-lactide-co-glycolide) and its derivatives. J Control Release 125:193–209
Natarajan S, Chang-Yen DA, Gale BK (2008) Large-area, high-aspect-ratio SU-8 molds for the fabrication of PDMS microfluidic devices. J Micromech Microeng 18:1–11
Olatunji O, Das DB (2010) Painless drug delivery using microneedles. Current technologies to increase the transdermal delivery of drugs (Editor: Joan Escober Chavez). Bentham Science Publishers (available online at http://www.benthamdirect.org/pages/b_getarticlebybook.php). ISBN:978-1-60805-191-5
Olatunji O, Das DB (2011) Drug delivery using microneedles. Comprehensive biotechnology. In: Zhanfeng Cui, 2nd edn. Elsevier, UK
Orive G, Hernandez RM, Gascon AR, Dominguez-Gil A, Pedraz JL (2003) Drug delivery in biotechnology: present and future. Curr Opin Biotech 14:659–664
Ouyang CP, Ma G, Zhao SX, Wang L, Wu LP, Wang Y, Song CX, Zhang ZP (2011) Preparation and characterization of the molecular weight controllable poly(lactide-co-glycolide). Polym Bull 67:793–803
Park JH, Davis S, Yoon YK, Prausnitz MR, Allen MG (2003) Micromachined biodegradable microstructures. In The 16th Annual International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, IEEE, Piscataway, NJ: 371–374
Park JH, Allen MG, Prausnitz MR (2006) Polymer microneedles for controlled release drug delivery. Pharm Res 23:1008–1019
Park JH, Choi SO, Kamath R, Yoon YK, Allen MG, Prausnitz MR (2007a) Polymer particle-based micromolding to fabricate novel microstructure. Biomed Microdev 9:223–234
Park JH, Yoon YK, Choi SO, Prausnitz MR, Allen MG (2007b) Tapered conical polymer microneedles fabricated using an integrated lens technique for transdermal drug delivery. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 54:903–913
Petrisor G, Ion RM, Brachais CH, Couvercelle JP, Chambin O (2012) Designing medical devices based on silicon polymeric material with controlled release of local anaesthetics. J Macromol Sci A 49:439–444
Proprietary Lidoderm. Endo pharmaceuticals, Inc., Chadds Ford, CA. http://www.lidoderm.com/
Proprietary Prevelle Silk. www.mentorcorp.com
Proprietary Xylocaine. http://www.astrazeneca.co.uk/medicines/products-az/Product/xylocaine
Qvortrup K, Taveras KM, Trastrup O, Nielsen TE (2011) Chemical synthesis on SU-8. Chem Commun 47:1309–1311
Rajabi O, Salari R, Tayyari SF (2011) Study of structure and properties of lidocaine: hydroxpropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex. J Pharm Res 4:1562–1563
Raphael AP, Prow TW, Crichton ML, Chen X, Fernando GJP, Kendall MAF (2010) Targeted, needle-free vaccinations in skin using multilayered, densely-packed, dissolving microprojection arrays. Small 6(16):1785–1793
Ro AJ, Falotico R, Davé V (2012) Morphological and degradation studies of sirolimus-containing poly(lactide-co-glycolide) discs. J Biomed Mater Res B 100B(3):767–777
Roy TBV, Blanch HW, Wilke CR (1982) Lactic acid production by Lactobacillus delbreuckill in a hollow fiber fermentor. Biotechnol Lett 4:483–488
Ryu WH, Vyakarnam M, Greco RS, Prinz FB, Fasching RJ (2007) Fabrication of multi-layered biodegradable drug delivery device based on micro-structuring of PLGA polymers. Biomed Microdevices 9:845–853
Safavieh R, Pla Roca M, Qasaimeh MA, Mirzaei M, Juncher D (2010) Straight SU-8 pins. J Micromech Microeng 20:1–9
Saliterman SS (2006) Fundamentals of bioMEMS and medical microdevices. Wiley Interscience: 531
Schreiber S, Ronfani L, Chiaffoni GP, Matarazzo L, Minute M, Panontin E, Poropat F, Germani C, Barbi E (2013) Does EMLA cream application interfere with the success of venepuncture or venous cannulation? A prospective multicentre observational study. Eur J Pediatr 172:265–268
Shaikh VR, Dagade DH, Hundivale DG, Patil KJ (2011) Volumetric studies of aqueous solutions of local anesthetical drug compounds [hydrochlorides of procaine (PC HCl), lidocaine (LC HCl) and tetracaine (TC HCl)] at 298.15 K. J Mol Liq 164:239–242
Shakeel M, Pathan Dilnawaz N, Ziyaurrrahman AR, Akber B, Bushra S (2011) Microneedle as a novel drug delivery system: a review. Int Res J Pharm 2:72–77
Subedi RK, Oh SY, Chun MK, Choi HK (2010) Recent advances in transdermal drug delivery. Arch Pharm Res 33:339–351
Sullivan SP, Murthy N, Prausnitz MR (2008) Minimally invasive protein delivery with rapidly dissolving polymer microneedles. Adv Mater 20:933–938
Texmac Inc (USA). www.texmac.com
Thaysen AC, Morris AR (1947) The use of hydrofluoric acid in making glass microneedles. J Gen Microbiol 221:641
Trautmann A, Heuck F, Mueller C, Ruther P, Paul O (2005) Replication of microneedle arrays using vacuum casting and hot embossing. Transducers 2:1420–1423
Tzeng YS, Chen SG (2012) Tumescent technique in digits: a subcutaneous single-injection digital block. Am J Emerg Med 30:592–596
Ullah I, Baloch MK, Durrani GF (2012) Solubility of lidocaine in ionic, nonionic and zwitterionic surfactants. J Solut Chem 41:215–222
Viero Y, He Q, Mazenq L, Ranchon H, Fourniols JY, Bancaud A (2012) Efficient prototyping of large-scale pdms and silicon nanofluidic devices using PDMS-based phase-shift lithography. Microfluid Nanofluid 12(1–4):465–473
Wahit MU, Akos NI, Laftah WA (2012) Influence of natural fibers on the mechanical properties and biodegradation of poly(lactic acid) and poly(ε-caprolactone) composites: a review. Polym Compos 33:1045–1053
Walraven JA (2003) Introduction to applications and industries for microelectromechanical systems (MEMS). International Test Conference Proceedings IEEE: 674-680
Wang MW, Jeng JH (2009) Optimal molding parameter design of pla micro lancet needles using the taguchi method. Polym Plast Technol 48:730–735
Wang XL, Yang KK, Wang YZ (2003) Properties of starch blends with biodegradable polymers. Polym Rev 43:358–409
Woodruff MA, Hutmaker DW (2010) The return of a forgotten polymer—polycaprolactone in the 21st century. Prog Polym Sci 35:1217–1256
Yang S, Feng Y, Zhang L, Chen N, Yuan W, Jin T (2012) A scalable fabrication process of polymer microneedles. Int J Nanomed 7:1415–1422
Ye X, Liu H, Ding Y, Li H, Lu B (2009) Research on the cast molding process for high quality PDMS molds. Microelectron Eng 86:310–313
You X, Chang JH, Ju BK, Pak JJ (2011) Rapidly dissolving fibroin microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Mat Sci Eng C 31(8):1632–1636
Youn SW, Okuyama C, Takahasi M, Maeda R (2008) A study on fabrication of silicon mold for polymer hot-embossing using focused ion beam milling. J Mater Process Tech 201:548–553
Zhang J, Tan KL, Gong HQ (2001) Characterization of the polymerization of SU-8 photoresist and its applications in micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS). Polym Test 20:693–701
Zhang Y, Brown K, Siebenaler K, Determan A, Dohmeier D, Hansen K (2012) Development of lidocaine-coated microneedle product for rapid, safe, and prolonged local analgesic action. Pharm Res 29:170–177
Zhao J, Mayes RH, Chen G, Chan PS, Xiong ZJ (2003) Polymer micromould design and micromoulding process. Plast, Rubber Compos 32:240–247
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nayak, A., Das, D.B. Potential of biodegradable microneedles as a transdermal delivery vehicle for lidocaine. Biotechnol Lett 35, 1351–1363 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1217-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1217-3