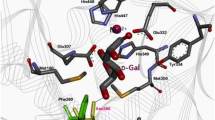
Abstract
A three-dimensional structural model of Escherichia coli fructosamine 6-kinase (FN6K), an enzyme that phosphorylates fructosamines at C6 and catalyzes the production of the fructosamine 6-phosphate stable intermediate, was generated using the crystal structure of 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate kinase isolated from Thermus thermophilus as template. The putative active site region was then investigated by site-directed mutagenesis to reveal several amino acid residues that likely play important roles in the enzyme reaction. Met220 was identified as a residue that plays a role in substrate recognition when compared to Bacillus subtilis derived FN6K, which shows different substrate specificity from the E. coli FN6K. Among the various Met220-substituted mutant enzymes, Met220Leu, which corresponded to the B. subtilis residue, resulted in an increased activity of fructosyl-valine and decreased activity of fructosyl-lysine, thus increasing the specificity for fructosyl-valine by 40-fold.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baek CH, Farrand SK, Lee KE, Park DK, Lee JK, Kim KS (2003) Convergent evolution of Amadori opine catabolic systems in plasmids of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol 185:513–524
Bowie JU, Lüthy R, Eisenberg D (1991) A method to identify protein sequences that fold into a known three-dimensional structure. Science 253:164–170
Chilton WS, Stomp AM, Beringue V, Bouzar H, Vaudequin-Dransart V, Petit A, Dessaux Y (1995) The chrysopine family of Amadoritype crown gall opines. Phytochemistry 40:619–628
Delpierre G, Rider MH, Collard F, Stroobant V, Vanstapel F, Santos H, Van Schaftingen E (2000) Identification, cloning, and heterologous expression of a mammalian fructosamine-3-kinase. Diabetes 49:1627–1634
Keil P, Mortensen HB, Christophersen C (1985) Fructosylvaline. A simple model of the N-terminal residue of human haemoglobin A1c. Acta Chem Scand B 39:191–193
Kim KS, Baek CH, Lee JK, Yang JM, Farrand SK (2001) Intracellular accumulation of mannopine, an opine produced by crown gall tumors, transiently inhibits growth of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 14:793–803
Lüthy R, Bowie JU, Eisenberg D (1992) Assessment of protein models with three-dimensional profiles. Nature 356:83–85
Ogawa K, Stöllner D, Scheller F, Warsinke A, Ishimura F, Tsugawa W, Ferri S, Sode K (2002) Development of a flow-injection analysis (FIA) enzyme sensor for fructosyl amine monitoring. Anal Bioanal Chem 373:211–214
Sakaguchi A, Tsugawa W, Ferri S, Sode K (2003) Development of highly sensitive fructosyl-valine enzyme sensor employing recombinant fructosyl amine oxidase. Electrochemistry 71:442–445
Sakaguchi A, Ferri S, Sode K (2005) SocA is a novel periplasmic binding protein for fructosyl amino acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 336:1074–1080
Sali A, Blundell TL (1993) Comparative protein modeling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J Mol Biol 234:779–815
Sode K, Takahashi Y, Ohta S, Tsugawa W, Yamazaki T (2001) A new concept for the construction of an artificial dehydrogenase for fructosyl amine compounds and its application for an amperometric fructosyl amine sensor. Anal Chim Acta 435:151–156
Sode K, Ohta S, Yanai Y, Yamazaki T (2003) Construction of a molecular imprinting catalyst using target analogue template and its application for an amperometric fructosylamine sensor. Biosens Bioelectron 18:1485–1490
Szwergold BS, Howell S, Beisswenger PJ (2001) Human fructosamine-3-kinase––Purification, sequencing, substrate specificity, and evidence of activity in vivo. Diabetes 50:2139–2147
Tsugawa W, Ishimura F, Ogawa K, Sode K (2000) Development of an enzyme sensor utilizing a novel fructosyl amine oxidase from a marine yeast. Electrochemistry 68:869–871
Tsugawa W, Ogawa K, Ishimura F, Sode K (2001) Fructosyl amine sensing based on Prussian blue modified enzyme electrode. Electrochemistry 69:973–975
Van Schaftingen E, Delpierre G, Collard F, Fortpied J, Gemayel R, Wiame E, Veiga-da-Cunha M (2007) Fructosamine 3-kinase and other enzymes involved in protein deglycation. Adv Enzyme Regul 47:261–269
Vaudequin-Dransart V, Petit A, Poncet C, Ponsonnet C, Nesme X, Jones JB, Bouzar H, Chilton WS, Dessaux Y (1995) Novel Ti plasmids in Agrobacterium strains isolated from fig tree and chrysanthemum tumors and their opine-like molecules. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 8:311–321
Wiame E, Delpierre G, Collard F, Van Schaftingen E (2002) Identification of a pathway for the utilization of the Amadori product fructose lysine in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 277:42523–42529
Wiame E, Duquenne A, Delpierre G, Van Schaftingen E (2004) Identification of enzymes acting on alpha-glycated amino acids in Bacillus subtilis. FEBS Lett 577:469–472
Yamazaki T, Ohta S, Yanai Y, Sode K (2003) Molecular imprinting catalyst based artificial enzyme sensor for fructosylamines. Anal Lett 36:75–89
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kojima, K., Mikami-Sakaguchi, A., Kameya, M. et al. Substrate specificity engineering of Escherichia coli derived fructosamine 6-kinase. Biotechnol Lett 35, 253–258 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-1062-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-1062-9