Abstract
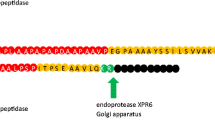
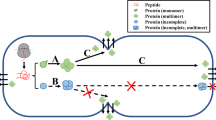
Fifty signal peptides of Pediococcus pentosaceus were characterized by in silico analysis and, based on the physicochemical analysis, (two potential signal peptides Spk1 and Spk3 were identified). The coding sequences of SP were amplified and fused to the gene coding for green fluorescent protein (GFP) and cloned into Lactococcus lactis pNZ8048 and pMG36e vectors, respectively. Western blot analysis indicated that the GFP proteins were secreted using both heterologous SPs. ELISA showed that the secretion efficiency of GFP using Spk1 (0.64 μg/ml) was similar to using Usp45 (0.62 μg/ml) and Spk3 (0.58 μg/ml).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baradaran A, Foo HL, Sieo CC, Raha AR (2012) Isolation, identification and characterization of lactic acid bacteria from Polygonum minus. Rom Biotechnol Lett 17(2):7245–7252
Bendtsen D (2004) Improved prediction of signal peptides: Signalp 3.0. J Mol Biol 340(4):783–795
Bolotin A, Wincker P, Mauger S, Jaillon O, Malarme K, Weissenbach J, Ehrlich SD, Sorokin A (2001) The complete genome sequence of the lactic acid bacterium Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis IL1403. Gen Res 11(5):731–753
Brockmeier U, Caspers M, Freudl R, Jockwer A, Noll T, Eggert T (2006) Systematic screening of all signal peptides from Bacillus subtilis: a powerful strategy in optimizing heterologous protein secretion in Gram-positive bacteria. J Mol Biol 362(3):393–402
Choo K, Ranganathan S (2008) Flanking signal and mature peptide residues influence signal peptide cleavage. BMC Bioinformatics 9:S15. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-9-S12-S15
Desvaux M, Hébraud M, Talon R, Henderson I (2009) Secretion and subcellular localizations of bacterial proteins: a semantic awareness issue. Trends Microbiol 17(4):139–145
Gomi M, Sonoyama M, Mitaku S (2004) High performance system for signal peptide prediction: SOSUIsignal. Chem-Bio Inform J 4(4):142–147
Hiller K, Grote A, Scheer M, Munch R, Jahn D (2004) PrediSi: prediction of signal peptides and their cleavage positions. Nucleic Acid Res 32(Web Server Issue):W375–W379
Le Loir Y, Nouaille S, Commissaire J, Bretigny L, Gruss A, Langella P (2001) Signal peptide and propeptide optimization for heterologous protein secretion in Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(9):4119–4127
Le Loir Y, Azevedo V, Oliveira SC, Freitas DA, Miyoshi A, Bermudez-Humaran LG, Nouaille S, Ribeiro LA, Leclercq S, Gabriel JE, Guimaraes VD, Oliveira MN, Charlier C, Gautier M, Langella P (2005) Protein secretion in Lactococcus lactis: an efficient way to increase the overall heterologous protein production. Microb Cell Fact 4(1):2
Lindholm A, Smeds A, Palva A (2004) Receptor binding domain of Escherichia coli F18 fimbrial adhesin FedF can be both efficiently secreted and surface displayed in a functional form in Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2061–2071
Morello E, Bermdez-Humarn L, Llull D, Solé V, Miraglio N, Langella P, Poquet I (2008) Lactococcus lactis, an efficient cell factory for recombinant protein production and secretion. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 14(1–3):48–58
Sriraman K, Jayaraman G (2006) Enhancement of recombinant streptokinase production in Lactococcus lactis by suppression of acid tolerance response. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72(6):1202–1209
Tremillon N, Issaly N, Mozo J, Duvignau T, Ginisty H, Devic E, Poquet E (2010) Production and purification of staphylococcal nuclease in Lactococcus lactis using a new expression-secretion system and a pH-regulated mini-reactor. Microb Cell Fact 9(1):37. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-9-37
Villatoro-Hernandez J, Loera-Arias M, Gamez-Escobedo A, Franco-Molina M et al (2008) Secretion of biologically active interferon-gamma inducible protein-10 (IP-10) by Lactococcus lactis. Microb Cell Fact 7:22–32
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation, Malaysia and Malaysian Genome Institute (MGI) for funding this study under the grant number 07-05-MGI-GMB011. We also thank Kees Leenhouts for the kind gift of plasmids pNZ8048 and pMG36e, and L. lactis hosts NZ9000 and MG1363.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baradaran, A., Sieo, C.C., Foo, H.L. et al. Cloning and in silico characterization of two signal peptides from Pediococcus pentosaceus and their function for the secretion of heterologous protein in Lactococcus lactis . Biotechnol Lett 35, 233–238 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-1059-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-1059-4