Abstract
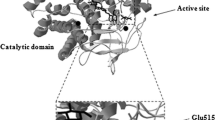
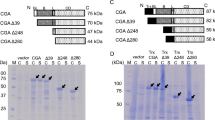
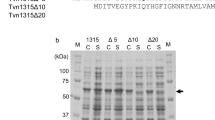
Five truncated constructs of Xcc_est GDSL esterase from Xanthomonas campestris were heterologously expressed and purified. The truncated constructs with a RGD motif had higher specific activities than those without the motif. The specific activity of wild-type Xcc_est was 32.5 ± 2.7 U/mg, while the RGD mutant was 12.5 ± 4.9 U/mg. Moreover, we expressed mature forms of the Xcc_est protein and the RGD mutant as inclusion bodies and, after refolding, there was no significant difference between the two constructs in specific activity. These results suggest that the RGD motif affects the esterase-domain folding in vivo during the translocation process.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W et al (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Arpigny JL, Jaeger KE (1999) Bacterial lipolytic enzymes: classification and properties. Biochem J 343:177–183
Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von HG et al (2004) Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol 340:783–795
Casimir CA, Guan CL, Yen CL et al (2004) GDSL family of serine esterases/lipases. Prog Lipid Res 43:534–552
Dekker N, Merck K, Tommassen J et al (1995) In vitro folding of Escherichia coli outer-membrane phospholipase A. Eur J Biochem 232:214–219
Fisher CL, Pei GK (1997) Modification of a PCR-based site-directed mutagenesis method. Biotechniques 23:570–574
Henderson IR, Navarro GF, Nataro JP (1998) The great escape: structure and function of the autotransporter proteins. Trends Microbiol 6:370–378
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lee HW, Byun SM (2003) The pore size of the autotransporter domain is critical for the active translocation of the passenger domain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 307:820–825
Ruoslahti E (1996) RGD and other recognition sequences for integrins. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 12:697–715
Talker-Huiber D, Jose J, Glieder A et al (2003) Esterase EstE from Xanthomonas vesicatoria (Xv_EstE) is an outer membrane protein capable of hydrolyzing long-chain polar esters. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 61:479–487
Wang JJ, Liu L, Cao YP et al (2009) GDSL esterase Xcc_est from Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris 8004 and its esterase domain: gene expression in Escherichia coli, refolding and characterization. Acta Microbiologica Sinica 49:191–197
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by 863 program (No. 2006AA02Z250), 973 program (No. 2004CB719606), the Ministry of Science and Technology, PR China and State key laboratory of microbial resources, CAS (SKLMR-080604)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jianjun Wang and Yanping Cao are contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Cao, Y. & Zheng, G. Mutation in the RGD motif decreases the esterase activity of Xcc_est . Biotechnol Lett 31, 1445–1449 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-0013-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-0013-6