Abstract
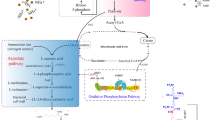
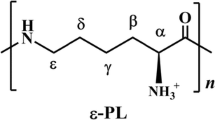
Poly(ε-l-lysine) (ε-PL) is a naturally occurring poly(amino acid) characterized by a unique structure linking ε-amino and carboxyl groups of l-lysine. Due to its various functions and its biodegradability and non-toxicity, the ε-PL polymer has attracted increasing attention in recent years. ε-PL is frequently found in various strains of Streptomyces sp. This review gives an up-to-date overview regarding the biosynthesis of ε-PL focussing mainly on results obtained from ten newly isolated producer strains, using the two-stage culture method of cell growth and ε-PL production cultures. The production of nearly monodispersed ε-PL is covered together with the development of ε-PL specific hydrolases and the release of synthesized ε-PL into the culture broth. From these results, coupled with the termination of polymerization through nucleophilic chain transfer, the biosynthetic mechanism of the polymer is discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashby RD, Solaiman DKY, Foglia TA (2002) Poly(ethylene glycol)-mediated molar mass control of short-chain- and medium-chain-length poly(hydroxyalkanoates) from Pseudomonas oleovorans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:154–159
Ashby RD, Solaiman DKY, Foglia TA (2005) Synthesis of short-/medium-chain-length poly(hydroxyalkanoate) blends by mixed culture fermentation of glycerol. Biomacromolecules 6:2106–2112
Ashiuchi M, Misono H (2003) Poly-γ-glutamic acid. In: Fahnestock SR, Steinbüchel A (eds) Biopolymers, vol 7. Wiley, Weinheim Germany, pp 123–173
Finking R, Marahiel MA (2004) Biosynthesis of nonribosomal peptides. Annu Rev Microbiol 58:453–488
Hamano Y, Nicchu I, Hoshino Y et al (2005) Development of gene delivery systems for the ε-poly-l-lysine producer, Streptomyces albulus. J Biosci Bioeng 99:636–641
Hamano Y, Yoshida T, Kito M et al (2006) Biological function of the pld gene product that degrades ε-poly-l-lysine in Streptomyces albulus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:173–181
Hamano Y, Nicchu I, Shimizu T et al (2007) ε-Poly-l-lysine producer, Streptomyces albulus, has feedback-inhibition resistant aspartokinase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol (in press). DOI 10.1007/s00253-007-1052-3
Hiraki J (2000) ε-Polylysine: its development and utilization. Fine Chem 29:18–25
Hiraki J, Ichikawa T, Ninomiya S et al (2003) Use of ADME studies to confirm the safety of ε-polylysine as a preservative in food. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 37:328–340
Hirayama C, Sakata M, Nakamura M et al (1999) Preparation of poly(ε-l-lysine) adsorbents and application to selective removal of lipopolysaccharides. J Chromatogr B 721:187–195
Hirohara H, Takehara M, Saimura M et al (2006) Biosynthesis of poly(ε-l-lysine)s in two newly isolated strains of Streptomyces sp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:321–331
Hirohara H, Saimura M, Takehara M et al (2007) Substantially monodispersed poly(ε-l-lysine)s frequently occurred in newly isolated strains of Streptomyces sp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol (in press). DOI 10.1007/s00253-007-1082-x
Kawai T, Kubota T, Hiraki J et al (2003) Biosynthesis of ε-poly-l-lysine in a cell-free system of Streptomyces albulus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 311:635–640
Kito M, Onji Y, Yoshida T et al (2002a) Occurrence of ε-poly-l-lysine-degrading enzyme in ε-poly-l-lysine-tolerant Sphingobacterium multivorum OJ10: purification and characterization. FEMS Microbiol Lett 207:147–151
Kito M, Takimoto R, Yoshida T et al (2002b) Purification and characterization of an ε-poly-l-lysine-degrading enzyme from an ε-poly-l-lysine producing strain of Streptomyces albulus. Arch Microbiol 178:325–330
Kito M, Takimoto R, Onji Y et al (2003) Purification and characterization of an ε-poly-l-lysine-degrading enzyme from the ε-poly-l-lysine-tolerant Chryseobacterium sp. OJ7. J Biosci Bioeng 96:92–94
Kleerebezem M, Quadri LE (2001) Peptide pheromone-dependent regulation of antimicrobial peptide production in gram-positive bacteria: a case of multicellular behavior. Peptides 22:1579–1596
Madden LA, Anderson AJ, Shah DT et al (1999) Chain termination in polyhydroxyalkanoate synthesis: involvement of exogenous hydroxy-compounds as chain transfer agents. Int J Biol Macromol 25:43–53
March JC, Bentley WE (2004) Quorum sensing and bacterial cross-talk in biotechnology. Curr Opin Biotechnol 15:495–502
Nishikawa M, Ogawa K (2002) Distribution of microbes producing antimicrobial ε-poly-l-lysine polymers in soil microflora determined by a novel method. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3575–3581
Nishikawa M, Ogawa K (2006) Inhibition of epsilon-poly-l-lysine biosynthesis in Streptomycetaceae bacteria by short-chain polyols. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:2306–2312
Núñez LE, Méndez C, Braña AF et al (2003) The biosynthetic gene cluster for the β-lactam carbapenem thienamycin in Streptomyces cattleya. Chem Biol 10:301–311
Obst M, Steinbüchel A (2004) Microbial degradation of poly(amino acid)s. Biomacromolecules 5:1166–1176
Oppermann-Sanio FB, Steinbüchel A (2002) Occurrence, functions and biosynthesis of polyamides in microorganisms and biotechnological production. Naturwissenschaften 89:11–22
Shih IL, Shen MH, Van YT (2006) Microbial synthesis of poly(ε-lysine) and its various applications. Bioresour Technol 97:1148–1159
Shima S, Sakai H (1977) Polylysine produced by Streptomyces. Agric Biol Chem 41:1807–1809
Shima S, Sakai H (1981) Poly-l-lysine produced by Streptomyces. III. Chemical studies. Agric Biol Chem 45:2503–2508
Shima S, Oshima S, Sakai H (1983) Biosynthesis of ε-poly-l-lysine by washed mycelium of Streptomyces albulus No-346. Nippon Nôgeikagaku Kaishi 57:221–226
Shima S, Matsuoka H, Iwamoto T et al (1984) Antimicrobial action of ε-poly-l-lysine. J Antibiot 37:1449–1455
Tsujita T, Takaichi H, Takaku T et al (2006) Antiobesity action of ε-polylysine, a potent inhibitor of pancreatic lipase. J Lipid Res 47:1852–1858
Walsh CT (2004) Polyketide and nonribosomal peptide antibiotics: modularity and versatility. Science 303:1805–1810
Yoshida T, Nagasawa T (2003) ε-Poly-l-lysine: microbial production, biodegradation and application potential. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 62:21–26
Yoshida T, Hiraki J, Nagasawa T (2003) ε-Poly-l-lysine. In: Fahnestock SR, Steinbüchel A (eds) Biopolymers, vol 7. Wiley, Weinheim Germany, pp 107–121
Acknowledgments
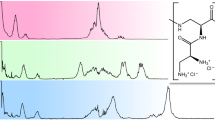
We thank J. Hiraki and Y. Onji of Chisso (Tokyo, Japan) for kindly providing purified ε-PL samples. The authors also thank K. Makino and T. Kodaki of the Institute of Advanced Energy, Kyoto University, for allowing the use of the 600 MHz NMR spectrometer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saimura, M., Takehara, M., Mizukami, S. et al. Biosynthesis of nearly monodispersed poly(ε-l-lysine) in Streptomyces species. Biotechnol Lett 30, 377–385 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9563-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9563-7