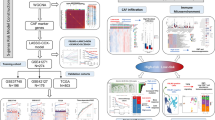
Abstract
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are an important component of the stroma. Studies showed that CAFs were pivotally in glioma progression which have long been considered a promising therapeutic target. Therefore, the identification of prognostic CAF markers might facilitate the development of novel diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. A total of 1333 glioma samples were obtained from the TCGA and CGGA datasets. The EPIC, MCP-counter, and xCell algorithms were used to evaluate the relative proportion of CAFs in glioma. CAF markers were identified by the single-cell RNA-seq datasets (GSE141383) from the Tumor Immune Single-Cell Hub database. Unsupervised consensus clustering was used to divide the glioma patients into different distinct subgroups. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression model was utilized to establish a CAF-related signature (CRS). Finally, the prognostic CAF markers were further validated in clinical specimens by RT‒qPCR. Combined single-cell RNA-seq analysis and differential expression analysis of samples with high and low proportions of CAFs revealed 23 prognostic CAF markers. By using unsupervised consensus clustering, glioma patients were divided into two distinct subtypes. Subsequently, based on 18 differentially expressed prognostic CAF markers between the two CAF subtypes, we developed and validated a new CRS model (including PCOLCE, TIMP1, and CLIC1). The nomogram and calibration curves indicated that the CRS was an accurate prognostic marker for glioma. In addition, patients in the high-CRS score group had higher immune infiltration and tumor mutation burden levels. Moreover, the CRS score had the potential to predict the response to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy and chemotherapy. Finally, the expression profiles of three CAF markers were verified by RT‒qPCR. In general, our study classified glioma patients into distinct subgroups based on CAF markers, which will facilitate the development of individualized therapy. We also provided insights into the role of the CRS in predicting the response to ICB and chemotherapy in glioma patients.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data of the current study are available from the following open public databases: TCGA (https://cancergenome.nih.gov), CGGA (http://www.cgga.org.cn/), and GTEx (https://gtexportal.org/home/datasets) as are described above. Other data will be obtained from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
References
Aldape K, Brindle KM, Chesler L, Chopra R, Gajjar A, Gilbert MR, Gottardo N, Gutmann DH, Hargrave D, Holland EC, Jones DTW, Joyce JA, Kearns P, Kieran MW, Mellinghoff IK, Merchant M, Pfister SM, Pollard SM, Ramaswamy V, Rich JN, Robinson GW, Rowitch DH, Sampson JH, Taylor MD, Workman P, Gilbertson RJ (2019) Challenges to curing primary brain tumours. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 16:509–520. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-019-0177-5
Aran D, Hu Z, Butte AJ (2017) xCell: digitally portraying the tissue cellular heterogeneity landscape. Genome Biol 18:220. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-017-1349-1
Becht E, Giraldo NA, Lacroix L, Buttard B, Elarouci N, Petitprez F, Selves J, Laurent-Puig P, Sautès-Fridman C, Fridman WH, de Reyniès A (2016) Estimating the population abundance of tissue-infiltrating immune and stromal cell populations using gene expression. Genome Biol 17:218. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-016-1070-5
Bouffet E, Larouche V, Campbell BB, Merico D, de Borja R, Aronson M, Durno C, Krueger J, Cabric V, Ramaswamy V, Zhukova N, Mason G, Farah R, Afzal S, Yalon M, Rechavi G, Magimairajan V, Walsh MF, Constantini S, Dvir R, Elhasid R, Reddy A, Osborn M, Sullivan M, Hansford J, Dodgshun A, Klauber-Demore N, Peterson L, Patel S, Lindhorst S, Atkinson J, Cohen Z, Laframboise R, Dirks P, Taylor M, Malkin D, Albrecht S, Dudley RW, Jabado N, Hawkins CE, Shlien A, Tabori U (2016) Immune checkpoint inhibition for hypermutant glioblastoma multiforme resulting from germline biallelic mismatch repair deficiency. J Clin Oncol 34:2206–2211. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2016.66.6552
Cao R, Ma B, Wang G, Xiong Y, Tian Y, Yuan L (2021) Characterization of hypoxia response patterns identified prognosis and immunotherapy response in bladder cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics 22:277–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omto.2021.06.011
Chen DS, Mellman I (2013) Oncology meets immunology: the cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity 39:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2013.07.012
Chen DS, Mellman I (2017) Elements of cancer immunity and the cancer-immune set point. Nature 541:321–330. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21349
Chen R, Cohen AL, Colman H (2016) Targeted therapeutics in patients with high-grade gliomas: past, present, and future. Curr Treat Options Oncol 17:42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11864-016-0418-0
Chen R, Smith-Cohn M, Cohen AL, Colman H (2017) Glioma subclassifications and their clinical significance. Neurotherapeutics 14:284–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-017-0519-x
Chen AX, Gartrell RD, Zhao J, Upadhyayula PS, Zhao W, Yuan J, Minns HE, Dovas A, Bruce JN, Lasorella A, Iavarone A, Canoll P, Sims PA, Rabadan R (2021a) Single-cell characterization of macrophages in glioblastoma reveals MARCO as a mesenchymal pro-tumor marker. Genome Med 13:88. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-021-00906-x
Chen Z, Zhuo S, He G, Tang J, Hao W, Gao WQ, Yang K, Xu H (2021b) Prognosis and immunotherapy significances of a cancer-associated fibroblasts-related gene signature in gliomas. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:721897. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.721897
Dagogo-Jack I, Shaw AT (2018) Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 15:81–94. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.166
Geeleher P, Cox N, Huang RS (2014) pRRophetic: an R package for prediction of clinical chemotherapeutic response from tumor gene expression levels. PLoS ONE 9:e107468. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107468
Goodman A, Patel SP, Kurzrock R (2017) PD-1-PD-L1 immune-checkpoint blockade in B-cell lymphomas. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14:203–220. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.168
Gulati P, Rühl J, Kannan A, Pircher M, Schuberth P, Nytko KJ, Pruschy M, Sulser S, Haefner M, Jensen S, Soltermann A, Jungraithmayr W, Eisenring M, Winder T, Samaras P, Tabor A, Stenger R, Stupp R, Weder W, Renner C, Münz C, Petrausch U (2018) Aberrant Lck signal via CD28 costimulation augments antigen-specific functionality and tumor control by redirected T cells with PD-1 blockade in humanized mice. Clin Cancer Res 24:3981–3993. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-17-1788
Hoshida Y, Brunet JP, Tamayo P, Golub TR, Mesirov JP (2007) Subclass mapping: identifying common subtypes in independent disease data sets. PLoS ONE 2:e1195. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001195
Jackson CM, Choi J, Lim M (2019) Mechanisms of immunotherapy resistance: lessons from glioblastoma. Nat Immunol 20:1100–1109. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-019-0433-y
Jia Q, Wu W, Wang Y, Alexander PB, Sun C, Gong Z, Cheng JN, Sun H, Guan Y, Xia X, Yang L, Yi X, Wan YY, Wang H, He J, Futreal PA, Li QJ, Zhu B (2018) Local mutational diversity drives intratumoral immune heterogeneity in non-small cell lung cancer. Nat Commun 9:5361. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07767-w
Jia Q, Wang J, He N, He J, Zhu B (2019) Titin mutation associated with responsiveness to checkpoint blockades in solid tumors. JCI Insight. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.127901
Johanns TM, Miller CA, Dorward IG, Tsien C, Chang E, Perry A, Uppaluri R, Ferguson C, Schmidt RE, Dahiya S, Ansstas G, Mardis ER, Dunn GP (2016) Immunogenomics of hypermutated glioblastoma: a patient with germline POLE deficiency treated with checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Cancer Discov 6:1230–1236. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-16-0575
Kalluri R (2016) The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 16:582–598. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2016.73
Kanehisa M (2019) Toward understanding the origin and evolution of cellular organisms. Protein Sci 28:1947–1951. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3715
Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28:27–30. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.27
Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Sato Y, Kawashima M, Ishiguro-Watanabe M (2023) KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 51:D587-d592. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac963
Lavin Y, Kobayashi S, Leader A, Amir ED, Elefant N, Bigenwald C, Remark R, Sweeney R, Becker CD, Levine JH, Meinhof K, Chow A, Kim-Shulze S, Wolf A, Medaglia C, Li H, Rytlewski JA, Emerson RO, Solovyov A, Greenbaum BD, Sanders C, Vignali M, Beasley MB, Flores R, Gnjatic S, Pe’er D, Rahman A, Amit I, Merad M (2017) Innate immune landscape in early lung adenocarcinoma by paired single-cell analyses. Cell 169:750-765.e717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.04.014
Li T, Fan J, Wang B, Traugh N, Chen Q, Liu JS, Li B, Liu XS (2017) TIMER: a web server for comprehensive analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Cancer Res 77:e108–e110. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-17-0307
Li M, Li G, Kiyokawa J, Tirmizi Z, Richardson LG, Ning J, Das S, Martuza RL, Stemmer-Rachamimov A, Rabkin SD, Wakimoto H (2020) Characterization and oncolytic virus targeting of FAP-expressing tumor-associated pericytes in glioblastoma. Acta Neuropathol Commun 8:221. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-020-01096-0
Louis DN, Perry A, Wesseling P, Brat DJ, Cree IA, Figarella-Branger D, Hawkins C, Ng HK, Pfister SM, Reifenberger G, Soffietti R, von Deimling A, Ellison DW (2021) The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Neuro Oncol 23:1231–1251. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noab106
Mayakonda A, Lin DC, Assenov Y, Plass C, Koeffler HP (2018) Maftools: efficient and comprehensive analysis of somatic variants in cancer. Genome Res 28:1747–1756. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.239244.118
McAndrews KM, Chen Y, Darpolor JK, Zheng X, Yang S, Carstens JL, Li B, Wang H, Miyake T, Correa de Sampaio P, Kirtley ML, Natale M, Wu CC, Sugimoto H, LeBleu VS, Kalluri R (2022) Identification of functional heterogeneity of carcinoma-associated fibroblasts with distinct IL-6 mediated therapy resistance in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Discov. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-20-1484
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Liao P, Vecchione-Koval T, Wolinsky Y, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan JS (2017) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2010–2014. Neuro Oncol 19:v1–v88. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nox158
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Truitt G, Boscia A, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan JS (2018) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2011–2015. Neuro Oncol 20:iv1–iv86. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noy131
Phillips HS, Kharbanda S, Chen R, Forrest WF, Soriano RH, Wu TD, Misra A, Nigro JM, Colman H, Soroceanu L, Williams PM, Modrusan Z, Feuerstein BG, Aldape K (2006) Molecular subclasses of high-grade glioma predict prognosis, delineate a pattern of disease progression, and resemble stages in neurogenesis. Cancer Cell 9:157–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2006.02.019
Racle J, Gfeller D (2020) EPIC: a tool to estimate the proportions of different cell types from bulk gene expression data. Methods Mol Biol 2120:233–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0327-7_17
Saha D, Martuza RL, Rabkin SD (2017) Macrophage polarization contributes to glioblastoma eradication by combination immunovirotherapy and immune checkpoint blockade. Cancer Cell 32:253-267.e255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2017.07.006
Sahai E, Astsaturov I, Cukierman E, DeNardo DG, Egeblad M, Evans RM, Fearon D, Greten FR, Hingorani SR, Hunter T, Hynes RO, Jain RK, Janowitz T, Jorgensen C, Kimmelman AC, Kolonin MG, Maki RG, Powers RS, Puré E, Ramirez DC, Scherz-Shouval R, Sherman MH, Stewart S, Tlsty TD, Tuveson DA, Watt FM, Weaver V, Weeraratna AT, Werb Z (2020) A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Cancer 20:174–186. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-019-0238-1
Semmel D, Ware C, Kim JY, Peters KB (2018) Evidence-based treatment for low-grade glioma. Semin Oncol Nurs 34:465–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soncn.2018.10.008
Shi Y, Kong Z, Liu P, Hou G, Wu J, Ma W, Cheng X, Wang Y (2021) Oncogenesis, microenvironment modulation and clinical potentiality of FAP in glioblastoma: lessons learned from other solid tumors. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051142
Sun D, Wang J, Han Y, Dong X, Ge J, Zheng R, Shi X, Wang B, Li Z, Ren P, Sun L, Yan Y, Zhang P, Zhang F, Li T, Wang C (2021) TISCH: a comprehensive web resource enabling interactive single-cell transcriptome visualization of tumor microenvironment. Nucleic Acids Res 49:D1420-d1430. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa1020
Topalian SL, Drake CG, Pardoll DM (2015) Immune checkpoint blockade: a common denominator approach to cancer therapy. Cancer Cell 27:450–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2015.03.001
Touat M, Li YY, Boynton AN, Spurr LF, Iorgulescu JB, Bohrson CL, Cortes-Ciriano I, Birzu C, Geduldig JE, Pelton K, Lim-Fat MJ, Pal S, Ferrer-Luna R, Ramkissoon SH, Dubois F, Bellamy C, Currimjee N, Bonardi J, Qian K, Ho P, Malinowski S, Taquet L, Jones RE, Shetty A, Chow KH, Sharaf R, Pavlick D, Albacker LA, Younan N, Baldini C, Verreault M, Giry M, Guillerm E, Ammari S, Beuvon F, Mokhtari K, Alentorn A, Dehais C, Houillier C, Laigle-Donadey F, Psimaras D, Lee EQ, Nayak L, McFaline-Figueroa JR, Carpentier A, Cornu P, Capelle L, Mathon B, Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Chakravarti A, Bi WL, Chiocca EA, Fehnel KP, Alexandrescu S, Chi SN, Haas-Kogan D, Batchelor TT, Frampton GM, Alexander BM, Huang RY, Ligon AH, Coulet F, Delattre JY, Hoang-Xuan K, Meredith DM, Santagata S, Duval A, Sanson M, Cherniack AD, Wen PY, Reardon DA, Marabelle A, Park PJ, Idbaih A, Beroukhim R, Bandopadhayay P, Bielle F, Ligon KL (2020) Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of hypermutation in gliomas. Nature 580:517–523. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2209-9
Trylcova J, Busek P, Smetana K Jr, Balaziova E, Dvorankova B, Mifkova A, Sedo A (2015) Effect of cancer-associated fibroblasts on the migration of glioma cells in vitro. Tumour Biol 36:5873–5879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3259-8
Van Meir EG, Hadjipanayis CG, Norden AD, Shu HK, Wen PY, Olson JJ (2010) Exciting new advances in neuro-oncology: the avenue to a cure for malignant glioma. CA Cancer J Clin 60:166–193. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.20069
Wang LJ, Lv P, Lou Y (2022) A novel TAF-related signature based on ECM remodeling genes predicts glioma prognosis. Front Oncol 12:862723. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.862723
Wilkerson MD, Hayes DN (2010) ConsensusClusterPlus: a class discovery tool with confidence assessments and item tracking. Bioinformatics 26:1572–1573. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq170
Xu L, Deng C, Pang B, Zhang X, Liu W, Liao G, Yuan H, Cheng P, Li F, Long Z, Yan M, Zhao T, Xiao Y, Li X (2018) TIP: a web server for resolving tumor immunophenotype profiling. Cancer Res 78:6575–6580. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-18-0689
Yang W, Soares J, Greninger P, Edelman EJ, Lightfoot H, Forbes S, Bindal N, Beare D, Smith JA, Thompson IR, Ramaswamy S, Futreal PA, Haber DA, Stratton MR, Benes C, McDermott U, Garnett MJ (2013) Genomics of drug sensitivity in cancer (GDSC): a resource for therapeutic biomarker discovery in cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D955-961. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1111
Yoshihara K, Shahmoradgoli M, Martínez E, Vegesna R, Kim H, Torres-Garcia W, Treviño V, Shen H, Laird PW, Levine DA, Carter SL, Getz G, Stemke-Hale K, Mills GB, Verhaak RG (2013) Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data. Nat Commun 4:2612. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3612
Zeng D, Ye Z, Shen R, Yu G, Wu J, Xiong Y, Zhou R, Qiu W, Huang N, Sun L, Li X, Bin J, Liao Y, Shi M, Liao W (2021) IOBR: multi-omics immuno-oncology biological research to decode tumor microenvironment and signatures. Front Immunol 12:687975. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.687975
Zhao J, Chen AX, Gartrell RD, Silverman AM, Aparicio L, Chu T, Bordbar D, Shan D, Samanamud J, Mahajan A, Filip I, Orenbuch R, Goetz M, Yamaguchi JT, Cloney M, Horbinski C, Lukas RV, Raizer J, Rae AI, Yuan J, Canoll P, Bruce JN, Saenger YM, Sims P, Iwamoto FM, Sonabend AM, Rabadan R (2019) Immune and genomic correlates of response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in glioblastoma. Nat Med 25:462–469. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0349-y
Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M, Khodabakhshi AH, Tanaseichuk O, Benner C, Chanda SK (2019) Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat Commun 10:1523. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09234-6
Acknowledgements
We all authors sincerely acknowledge the contributions from TCGA and CGGA databases for offering convenient access to datasets. In addition, we thank Dr. Siwen Wang for the help in statistics and encouragement.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61575058), the Talent Introduction Project of Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital (No. C-2021-QDJJ03-01), and the Project of Medicine and Health Science and Technology of Zhejiang Province (NO.2024KY015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XY, HZ, XG, ZL, and SH conceived and designed the study and drafted the manuscript. HZ, JD, and JZ provided analytical technical support. XY, ZL, and JZ participated in the production of charts and pictures. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University.
Informed Consent
The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, X., Gao, X., Dong, J. et al. Integration of Single-Cell and Bulk RNA-seq Data to Identify the Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subtypes and Risk Model in Glioma. Biochem Genet (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-024-10751-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-024-10751-3