Abstract
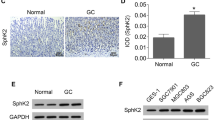
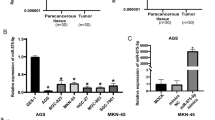
Gambogic acid (GA) has been observed to effectively impede the progression of numerous types of cancers. In this study, we investigated the effects of miR-1275 and Secreted Protein Acidic and Cysteine Rich (SPARC) on GA in gastric cancer (GC). miR-1275 and SPARC expression were determined in GC cell lines and tissues using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The correlation between miR-1275 and SPARC expression was ascertained using Pearson’s correlation coefficient. Cell proliferation was assessed using the cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. The Transwell assay was conducted to examine cell migration. A dual-luciferase reporter assay was used to verify the regulatory relationship between miR-1275 and SPARC. The levels of SPARC, Bcl-2, and Bax proteins were estimated using western blotting. To verify the effects of GA on the growth of GC cells in vivo, a tumorigenesis experiment was performed in nude mice. GA suppressed GC cell viability and migration, facilitated apoptosis, and inhibited tumor growth in vivo and in vitro. Low levels of miR-1275 been observed in GC cell lines and tissues. GA-treated GC cells manifested high miR-1275 levels. In functional experiments, miR-1275 enhanced the influence of GA on cell apoptosis, migration, and proliferation. Furthermore, GA treatment suppressed SPARC upregulation in GC cell lines and tissues. Pearson’s correlation coefficient revealed that miR-1275 expression negatively correlated with SPARC expression. Mechanistically, miR-1275 promoted growth inhibition in GA-treated GC cells by targeting SPARC. Our study indicates that miR-1275 enhances the suppressive effect of GA on GC progression by inhibiting SPARC expression. Through this study, we contribute to the knowledge of a new mechanism by which GA suppresses GC progression.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets that have been used and/or analyzed during the study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not available.
References
Ali Syeda Z, Langden SSS, Munkhzul C, Lee M, Song SJ (2020) Regulatory mechanism of microRNA expression in cancer. Int J Mol Sci 21(5):1723. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051723
Bradshaw AD, Sage EH (2001) SPARC, a matricellular protein that functions in cellular differentiation and tissue response to injury. J Clin Investig 107(9):1049–1054. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci12939
Charalampakis N, Economopoulou P, Kotsantis I, Tolia M, Schizas D, Liakakos T et al (2018) Medical management of gastric cancer: a 2017 update. Cancer Med 7(1):123–133. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1274
Correia de Sousa M, Gjorgjieva M, Dolicka D, Sobolewski C, Foti M (2019) Deciphering miRNAs’ Action through miRNA editing. Int J Mol Sci 20(24):6249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246249
Fawzy IO, Hamza MT, Hosny KA, Esmat G, El Tayebi HM, Abdelaziz AI (2015) miR-1275: A single microRNA that targets the three IGF2-mRNA-binding proteins hindering tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma. FEBS Lett 589(17):2257–2265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2015.06.038
Feng J, Tang L (2014) SPARC in tumor pathophysiology and as a potential therapeutic target. Curr Pharm Des 20(39):6182–6190. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612820666140619123255
Gao ZW, Liu C, Yang L, He T, Wu XN, Zhang HZ et al (2021) SPARC Overexpression promotes liver cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth. Front Mol Biosci 8:775743. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2021.775743
Gupta S, Panda PK, Luo W, Hashimoto RF, Ahuja R (2022) Network analysis reveals that the tumor suppressor lncRNA GAS5 acts as a double-edged sword in response to DNA damage in gastric cancer. Sci Rep 12(1):18312. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-21492-x
He X, Shu Y (2020) miR-452 promotes the development of gastric cancer via targeting EPB41L3. Pathol Res Pract 216(1):152725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2019.152725
Hu S, Zheng Q, Wu H, Wang C, Liu T, Zhou W (2017) miR-532 promoted gastric cancer migration and invasion by targeting NKD1. Life Sci 177:15–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.03.019
Liang L, Zhang Z, Qin X, Gao Y, Zhao P, Liu J et al (2018) Gambogic acid inhibits melanoma through regulation of miR-199a-3p/ZEB1 signalling. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 123(6):692–703. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.13090
Lin D, Lin X, He T, Xie G (2020) Gambogic acid inhibits the progression of gastric cancer via circRNA_ASAP2/miR-33a-5p/CDK7 axis. Cancer Manag Res 12:9221–9233. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.S269768
Liu MD, Wu H, Wang S, Pang P, Jin S, Sun CF et al (2018) miR-1275 promotes cell migration, invasion and proliferation in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck via up-regulating IGF-1R and CCR7. Gene 646:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2017.12.049
Liu Y, Chen Y, Lin L, Li H (2020) Gambogic acid as a candidate for cancer therapy: a review. Int J Nanomed 15:10385–10399. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.S277645
Mei JW, Yang ZY, Xiang HG, Bao R, Ye YY, Ren T et al (2019) MicroRNA-1275 inhibits cell migration and invasion in gastric cancer by regulating vimentin and E-cadherin via JAZF1. BMC Cancer 19(1):740. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-019-5929-1
Nagaraju GP, Dontula R, El-Rayes BF, Lakka SS (2014) Molecular mechanisms underlying the divergent roles of SPARC in human carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 35(5):967–973. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgu072
Nian Q, Li J, Han Z, Liang Q, Liu M, Yang C et al (2022) SPARC in hematologic malignancies and novel technique for hematological disease with its abnormal expression. Biomed Pharmacother 153:113519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113519
Pan Z, Xie R, Song W, Gao C (2021) MicroRNA-592 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion in colorectal cancer by directly targeting SPARC. Mol Med Rep 23(4):11900. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2021.11900
Qi W, Zhang Q (2021) Development and clinical validation of a 3-miRNA signature to predict prognosis of gastric cancer. PeerJ 9:e10462. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.10462
Rosset EM, Bradshaw AD (2016) SPARC/osteonectin in mineralized tissue. Matrix Biol 52–54:78–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2016.02.001
Sato T, Oshima T, Yamamoto N, Yamada T, Hasegawa S, Yukawa N et al (2013) Clinical significance of SPARC gene expression in patients with gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol 108(6):364–368. https://doi.org/10.1002/jso.23425
Shaalan YM, Handoussa H, Youness RA, Assal RA, El-Khatib AH, Linscheid MW et al (2018) Destabilizing the interplay between miR-1275 and IGF2BPs by Tamarix articulata and quercetin in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Prod Res 32(18):2217–2220. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2017.1366478
Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, van Grieken NC, Lordick F (2020) Gastric cancer. Lancet 396(10251):635–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31288-5
Sun KY, Peng T, Chen Z, Huang J, Zhou XH (2016) MicroRNA-1275 suppresses cell growth, and retards G1/S transition in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma by down-regulation of HOXB5. J Cell Commun Signal 10(4):305–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-016-0351-9
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA 71(3):209–49. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Tan Z (2019) Recent advances in the surgical treatment of advanced gastric cancer: a review. Med Sci Monit 25:3537–3541. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.916475
Tang Q, Lu M, Zhou H, Chen D, Liu L (2017) Gambogic acid inhibits the growth of ovarian cancer tumors by regulating p65 activity. Oncol Lett 13(1):384–388. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2016.5433
Wang Y, Sui Y, Tao Y (2019) Gambogic acid increases the sensitivity to paclitaxel in drug-resistant triple-negative breast cancer via the SHH signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep 20(5):4515–4522. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10697
Wang S, Long S, Deng Z, Wu W (2020) Positive role of chinese herbal medicine in cancer immune regulation. Am J Chin Med 48(7):1577–1592. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0192415x20500780
Xu J, Yang S, Gu X, Shen H, Wang L, Xu W et al (2019) SPARC correlates with unfavorable outcome and promotes tumor growth in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Mol Pathol 110:104276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.104276
Yin J, Chen G, Liu Y, Liu S, Wang P, Wan Y et al (2010) Downregulation of SPARC expression decreases gastric cancer cellular invasion and survival. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 29(1):59. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-9966-29-59
Zhang D, Chu Y, Qian H, Qian L, Shao J, Xu Q et al (2020) Antitumor activity of thermosensitive hydrogels packaging gambogic acid nanoparticles and tumor-penetrating peptide iRGD against gastric cancer. Int J Nanomed 15:735–747. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.S231448
Zhang Z, Liang L, Cao G (2021) Critical role of miR-26a-5p/Wnt5a signaling in gambogic acid-induced inhibition of gastric cancer. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 35(4):e22721. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22721
Zhou Z, Ma J (2019) Gambogic acid suppresses colon cancer cell activity in vitro. Exp Ther Med 18(4):2917–2923. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2019.7912
Zou T, Gao Y, Qie M (2021) MiR-29c-3p inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition to inhibit the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of cervical cancer cells by targeting SPARC. Ann Transl Med 9(2):125. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-7272
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
The author have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AC and PFX executed the experiments and analysis of data. XKZ and YH designed and devised the study. AC and JL obtained the data. PFX and JL processed and interpreted the data. This manuscript has been read and approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
This research has been approved by the Ethics Committee of Wuhan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine (approval number: 2022013, Wuhan, China). The processing of clinical samples is in strict compliance with the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki. All patients provided their written informed consent. The procedures executed in the animal study were approved by the animal ethics committee of Wuhan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine (approval number: WHTCM2021174). All animal experiments comply with the ARRIVE guidelines.
Consent to Participate
All patients signed a written informed consent.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, A., Xia, P., Zhou, X. et al. MiR-1275 Targeting SPARC Promotes Gambogic Acid-Induced Inhibition of Gastric Cancer. Biochem Genet 61, 2481–2495 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10381-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10381-1