Abstract
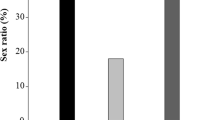
The parasitoid Apanteles taragamae Viereck (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) has been introduced into Benin by the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA-Benin station) from Taiwan in an attempt to control the cowpea pod borer, Maruca vitrata Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Crambidae), a serious pest of flowers and pods of cowpea Vigna unguiculata Walp. (Leguminosae: Fabaceae). Both the pest and its parasitoid are currently mass-reared using a cowpea and maize flour-based meridic diet. In this study, the suitability of germinating seeds from three cowpea varieties, Kpodji-guèguè, Tawa and TVX3236, as substrates, was tested for rearing A. taragamae under laboratory conditions. The seeds that were soaked for 48 h were the most suitable for M. vitrata larval rearing with up to 87 % survival. The highest parasitism rate of M. vitrata larvae by A. taragamae was observed on the local variety Tawa. Compared to meridic diet, the development cycle of the parasitoid was shorter on Tawa sprouts which also lead to the highest lifetime fecundity. The parasitoid sex ratio varied significantly between feeding substrates with a higher proportion of female wasps on the improved varieties TVX2336 and local variety Kpodji-guèguè. Rearing M. vitrata larvae on germinating cowpea grains is 4.38 times cheaper than on meridic diet. The data are discussed with emphasis on the effects of feeding substrates quality on life history parameters of insect pests and their parasitoids.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi B, Ahmed K, Khalique F, Ayub N, Liu H, Kazmi S, Aftab M (2007) Rearing the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera, on a tapioca-based artificial diet. J Insect Sci 7:35. doi:10.1673/031-007-3501
Brodeur J, Boivin G (2004) Functional ecology of immature parasitoids. Annu Rev Entomol 49:27–49
Carpenter JE, Greany PD (1998) Comparative development and performance of artificially reared versus host-reared Diapetimorpha introita (Cresson) (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) wasps. Biol Control 11:203–208
Carpenter JE, Ferkovich SM, Greany PD (2001) Fecundity and longevity of Diapetimorpha introita (Cresson) (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) reared on artificial diets: effects of a lipid extract from host pupae and culture media conditioned with an insect cell line. Fla Entomol 84:43–49
Chen LH, Wells CE, Fordham JR (1975) Germinated seeds for human consumption. J Food Sci 40:1290–1294
Colinet H, Salin C, Boivin G, Hance TH (2005) Host age and fitness-related traits in a koinobiont aphid parasitoid. Ecol Entomol 30:473–479
Dannon EA, Tamò M, Huis A, Dicke M (2010) Functional response and life history parameters of Apanteles taragamae, a larval parasitoid of Maruca vitrata. BioControl 55:363–378
Danthu P, Roussel J, Neffati M (2003) La graine et la germination d’Acacia raddiana. In: Grouzis M, Le Floc’h E (eds) Un arbre au désert Acacia raddiana. IRD, Paris, pp 265–283
Dicke M (1999) Direct and indirect effects of plants on the performance of beneficial organisms. In: Ruberson JR (ed) Handbook of pest management. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 105–153
Donaldson JS, Walter GH (1984) Sex ratios of Spalangia endius (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae), in relation to current theory. Ecol Entomol 9:395–402
Dzemo WD, Niba AS, Aswe J (2010) A comparative study of the bionomics of Clavigralla tomentosicollis Stal (Hemiptera: Coreidae) on three varieties of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp). Afr J Agric Res 5:567–572
Ekesi S (1999) Insecticide resistance in field populations of the legume pod-borer, Maruca vitrata Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae), on cowpea, Vigna unguiculata (L.), Walp in Nigeria. Int J Pest Manag 45:57–59
El-Jasser ASH (2011) Chemical and biological properties of local cowpea seed protein grown in Gizan Region. Int J Agric Res Rev 1:68–75
Enujiugha VN, Badejo AA, Iyiola SO, Oluwamukomi MO (2003) Effect of germination on the nutritional and functional properties of African oil bean (Pentaclethra macrophylla Benth) seed flour. Food Agric Environ 1:72–75
Fanti P, Vinson SB (2000) In vitro rearing of Muscidifurax zaraptor (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae) on artificial diets with and devoid of insect material. Biol Control 18:49–54
Greenberg SM, Sappington TW, Legaspi BC, Liu T-X, Sétamou M (2001) Feeding and life history of Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on different host plants. Ann Entomol Soc Am 94:566–575
Harvey JA, Bezember TM, Elzinga JA, Strand MR (2004) Development of the solitary endoparasitoid Microplitis demolitor: host quality does not increase with host age and size. Ecol Entomol 29:35–43
Henter HJ (2004) Constrained sex allocation in a parasitoid due to variation in male quality. J Evol Biol 17:886–896
Huang C, Peng W-K, Talekar NS (2003) Parasitoids and other natural enemies of Maruca vitrata feeding on Sesbania cannabina in Taiwan. BioControl 48:407–416
Jackai L, Raulston JR (1988) Rearing the legume pod borer, Maruca testulalis Geyer (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) on artificial diet. Trop Pest Manag 34:168–172
Kamara AY, Chikoye D, Omoigui LO, Dugje IY (2007) Influence of insecticide spraying regimes and cultivar on insect pests and yield of cowpea in the dry savannas of north-eastern Nigeria. J Food Agric Environ 5:154–158
Liao CT, Lin CS (2000) Occurrence of the legume pod borer, Maruca testulalis, Geyer (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) on cowpea (Vigna unguiculata Walp) and its insecticidal application trial. Plant Prot Bull 42:213–222
Nordlund DA, Wu ZX, Greenberg SM (1997) In vitro rearing of Trichogramma minutum Riley (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) for ten generations, with quality assessment comparisons of in vitro and in vivo reared adults. Biol Control 9:201–207
Ochieng RS, Bungu MDO (1983) Studies on the legume pod borer, Maruca testulalis (Geyer)-IV. A model for mass rearing: rearing on artificial diet. Insect Sci Appl 4:83–88
Okeyo-Owuor BJ, Agwaro PO, Simbi COJ (1983) Studies on the pod borer Maruca vitrata (Geyer)-V larval population. Insect Sci Appl 4:75–81
Olu M, Ogunmoyela OAB, Oluwajoba SO (2011) Essential amino acid composition of sprouted and unsprouted maize (Zea mays) & cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) grain as compared with FAO reference protein and egg protein. Int J Acad Res 3:121–123
Onyango FO, Ochieng’Odero JPR (1993) Laboratory rearing of the legume pod borer, Maruca testulalis Geyer (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) on semi-synthetic diet. Insect Sci Appl 14:719–722
Osman MA (2007) Effect of different processing methods, on nutrient composition, antinutrional factors, and in vitro protein digestibility of Lablab bean [Lablab purpuresus (L) sweet]. Pak J Nutr 6:299–303
Ramakrishna V, Rani PJ, Rao PR (2006) Anti-nutritional factors during germination in Indian bean (Dolichos lablab L.) seeds. World J Dairy Food Sci 1:6–11
Rasha MK, Gibriel AY, Nagwa MHR, Ferial MA-S, Esmat AA-A (2011) Influence of legume processing treatments individually or in combination on their trypsin inhibitor and total phenolic contents. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 5:1310–1322
Reihaneh AG, Mehdi GD (2011) Evaluation of changes in phytase, α-amylase and protease activities of some legume seeds during germination. Int Conf Biosci Biochem Bioinforma 5:353–356
Sarfraz M, Dosdall LM, Keddie BA (2007) Resistance of some cultivated Brassicaceae to infestations by Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). J Econ Entomol 100:215–224
Shah SA, Zeb A, Masood T, Noreen N, Abbas SJ, Samiullah M, Alim MdA, Muhammad A (2011) Effects of sprouting time on biochemical and nutritional qualities of mungbean varieties. Afr J Agri Res 6:5091–5098
Sharma HC (1998) Bionomics, host plant resistance, and management of the legume pod borer, Maruca vitrata a review. Crop Prot 17:373–386
Singh SR, Jackai LEN, Dos Santos JHR, Adalla CB (1990) Insect pest of cowpea. In: Singh SR (ed) Insect pests of food legumes. Wiley, Nigeria, pp 43–89
Syed TS, Abro GH (2003) Effect of brassica vegetable hosts on biology and life table parameters of Plutella xylostella under laboratory conditions. Pak J Biol Sci 6:1891–1896
Tamò M, Srinivasan R, Dannon E, Agboton C, Datinon B, Dabire C, Baoua I, Ba M, Haruna B, Pittendrigh BR (2012) Biological control: a major component for the long-term cowpea pest management strategy. In: Boukar O, Coulibaly O, Fatokun C, Lopez K, Tamò M (eds) Innovative research along the cowpea value chain. Proceedings of the 5th World Cowpea Research Conference, 27 September–1 October 2010 Saly, Senegal, pp 249–259
Unmole L (2009) Laboratory rearing of the legume pod borer, Maruca vitrata Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) on mung bean sprouts. Univ Maurit Res J 15:577–584
van Emden HF, Kifle AT (2002) Performance of the parasitoid Aphidius colemani when reared on Myzus persicae on a fully defined artificial diet. BioControl 47:607–616
Voster IHJ, van Jansen RW, van Zijl JJB, Venter SL (2007) The importance of traditional leafy vegetables in South Africa. Afr J Food Agric Nutr Dev 7:1–12
Wittmeyer JL, Coudron TA (2001) Life table parameters, reproduction rate, intrinsic rate of increase, and estimated cost of rearing Podisus maculiventris (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) on an artificial diet. J Econ Entomol 94:1334–1352
Acknowledgments
This study was supported the Dry Grains Pulses Collaborative Research Support Program (CRSP) by the Bureau for Economic Growth, Agriculture and Trade, U.S.A.I.D. under the terms of Grant No. EDH-A-00-07-00005, and GIZ/BMZ Project No. 09.7860.1-001.00. The authors are grateful to Dr. Georg Goergen for taxonomic assistance and Mr. Mathias Azokpota and Ms. Judith Glèlè for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Torsten Meiners.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wetro, E., Tounou, A.K., Agboton, C. et al. Bionomics of the parasitoid Apanteles taragamae as influenced by different diets fed to its host, Maruca vitrata . BioControl 59, 55–65 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-013-9547-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-013-9547-6